Reports
Health
Wellness
An individual’s height is many a time associated with health aspects. A good number of studies were carried out to understand if there could be any link between height and alleged health risks. A recent study by a group of researchers from Colorado’s Rocky Mountain medical center confirmed and added more density to those claims. Their study reported that a taller person could have a higher risk of diseases such as peripheral neuropathy or atrial fibrillation.
Height has been associated with health aspects in many past studies.
There is research that talks about how a tall person is happier than a shorter person while a short person lives a longer life than a tall one.
Other analyses have been carried out to understand the risk of diseases if you’re taller than average height.
They included a person’s height as well as other environmental factors affecting it into account.
All such experiments and data are observed to create a more personalized assessment of one’s health.
Researchers suggest that these data can help provide medical advice that is customized to the individual’s genetic makeup and tailor-make treatments. That said, more research needs to be carried out to convert this data into clinical care, says the team.
The phenome-wide study was carried out majorly on the non-Hispanic American population.
The phenome of an individual contains the visible traits - traits that are expressed. In this case, it is the measured height of the participants.
They collected data from the MVP- Million Veteran Program biobank.
The study aimed to understand if a person’s height alone was associated with health risks, not including the environmental factors.
The height of an individual is influenced by two factors – the genes they inherit and the environment they grow in.
They recorded two sets of data, one with genetically-predicted height and the other with contributing environmental factors such as nutrition and economic conditions.
The study tried to find associations to diseases such as coronary heart disease, fat levels, and a few cancers.
Answers to this and more in the Gene Health Report!
The study analyzed over 3000 clinical traits and checked for their correlation to height.
They reported that height does have links to increased or protective disease association.
A tall adult is more susceptible to suffering from peripheral neuropathy or infections of the skin and has lower chances of getting cardiovascular diseases.
In women, they found a strong correlation between asthma and a few peripheral nerve conditions and height.
However, researchers of this study suggested that more such studies were needed to translate this information into medical use.
Your height may be out of your control.
But, changing other aspects of your health isn’t.
The health risks associated with height can be influenced by lifestyle habits which you can change in your favor.
Although tall people are at higher risk for certain diseases, knowing this information can help you detect and avoid them early.
You can make better food choices, sleep differently, and reduce alcohol intake or smoking.
Advanced diagnosis of any disease can surely help to prevent them easily.
It has long been known that people with more friends are happier than those with fewer friends.
This observation is based on the theory that having close relationships makes people feel good and that being happy leads to increased productivity and success.
However, a recent study has shown that this theory may not be entirely correct.
In fact, it might actually be better to have few close friends than many casual acquaintances.
One basic principle of evolutionary biology is that the human brain has developed to function in ancestral environments and not the present one, like all the other organs.
The Savanna principle suggests that human brains may not necessarily be equipped to deal with elements absent in the ancestral environment.
This principle can be better explained with an example.
Research has revealed that rural residents living in industrialized countries tend to be happier than urban residents.
City life seems scarier, more alienating, and depressing for our brains. Town life, however, isn't perceived as threatening or stressful. Why?
It has got to do with the population density.
The brought to light data suggests that ancestors possibly lived in groupings of 150 people.
So the natural size of the neocortex region of the brain responsible for cognition and interaction is equipped for cohabitating 150 people.
It is possible that as population density rises, the brain feels uncomfortable and uneasy.
This could lead to a hampered sense of well-being.
For example, statistics say that job satisfaction decreases as organizational size increases.
The savanna theory of happiness may thus propose that the rising group sizes and population density can negatively impact subjective well-being. In addition, this negative effect may interact with general intelligence and have a stronger effect on the less intelligent ones than the more intelligent ones.
A new research study published in the British Journal of Psychology suggests that the hunter-gatherer lifestyle of our ancestors is the archetypal building block of what makes us happy now.
The study sampled around 15,000 individuals aged 18 to 28.
The people in densely populated areas were noted to have less satisfaction with the quality of their life.
The subsequent finding indicates that the greater the likelihood of close friendships with a particular person, the more satisfying an individual's quality of life is.
There is a caveat to this finding!
For those who are more intelligent and have higher IQs, the sociodemographic correlations between the numbers of friends and life satisfaction were way less pronounced.
In the low-IQ group, this correlation was twice as large.
Thus, we can draw that the higher the IQ, the lesser satisfaction you have with life if you have more friends.
Why is this the case?
Intelligent people are more driven and focused on long-term goals.
They aim farther ahead and are compelled and driven to use their intelligence for something more monumental than themselves.
Take, for instance, someone you went to school with or a friend who started their business.
While chasing their objectives, they prioritized staying focused enough to get results.
They eliminated social interactions as they concentrated on reaching higher and larger goals.
Intelligent people tend to view socializing as a hindrance and obstacle to ultimate success.
A long-term dreamer will prefer to stay at home and pursue their goals and aspirations than watch a football match or party all night with their friends.
However, this doesn't mean they don't respect or value their friends.
But when engaged in intense efforts to rise above, they regard socializing as a diversion and prefer to stay at home and work on their objectives.
Based on evolution, the human brain was formed to meet the ancestral needs for survival.
There were not many people, and the primary mode of continuance was hunting and gathering.
It was vital to have more contacts with extended family members to pass on information and help one another in these circumstances.
Socializing was also considered imperative for reproduction to ensure our survival.
The new demands of contemporary life have drastically affected our relationship patterns with one another.
The intelligent ones are better capable of handling the troubles arising due to new circumstances and complex interrelationships.
Likewise, they are better able to adapt to evolutionary and advanced changes.
Being smart helps surf through modern circumstances at ease and splice ancestral inclinations with present-day settings.
The ability to eliminate the primal need to have social interaction when pursuing your ambitions and dreams can help minimize the influence of urban areas on your well-being.
Intelligent people cherish relationships similar to others, but they put more stock in how they spend their time.
They don't devalue friendships and relationships; they seek pleasure from other pursuits.
The savannah theory of well-being offers a novel defeat to age-old questions about what makes people happy and why.
So, if you have a few close friends and would rather stay at home to Netflix and chill, don't sweat it. You're probably just exceptionally smart!
A droopy eyelid is characterized by the sagging of the upper eyelid - it droops downwards.
It is also called ptosis, a fancy word for “drooping.”
The edge of the upper eyelid is either lower than it should be or has excess baggy skin.
Sometimes, both these factors contribute to a droopy eyelid.
A multitude of factors contributes to a droopy eyelid.
According to a study, sagging eyelids can run in families, and at least one gene seems to play a role in causing eyelids to sag.
The same study also mentions that inherited factors account for 61 percent of the risk of sagging eyelids.
The H2AFY2 gene contains instructions for the production of core histone macro-H2A.2.
This protein regulates gene expression or how much product a gene produces.
The H2AFY2 gene is expressed in the skin and has been implicated in the systemic lupus erythematosus (an autoimmune skin condition) pathway.
Several studies have already established the role of histones in aging and cell senescence (cell death), which could explain the role of the H2AFY2 gene in eyelid sagging.
Four Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (gene changes) or SNPs in the H2AFY2 gene are significantly associated with eyelid sagging severity.
These SNPs are located in intronic parts of the H2AFY2 gene and very close to another gene called AIFM2 that induces apoptosis or programmed cell death.
| SNP | Variant Allele | Implication |
| rs16927253 | T | Dominant protective effect towards eyelid sagging |
| rs2271699 | G | Dominant protective effect towards eyelid sagging |
| rs2394654 | C | Dominant protective effect towards eyelid sagging |
| rs3750770 | T | Dominant protective effect towards eyelid sagging |
Doctors mostly do not start treatment for children with congenital ptosis right away.
They check their eyes periodically.
If there’s an indication of amblyopia, the doctors treat it with drops, patches, or glasses.
For adults, the most common treatment option for droopy eyes is surgery.
The surgery involves removing the extra skin and tucking the muscle that lifts the lid.
Another option would be reattaching and strengthening that muscle.
While these procedures are safe in most cases, there could also be some possible complications.
There are chances of surgery not being successful.
Sometimes, the procedure could also overcorrect the problem by leaving the eyelid either too high or too low, requiring further surgery.
Another management option is the ptosis crutch, also called the eye crutch.
It lifts your eyelids so you can see better.
Hydration: Dehydration contributes to saggy eyelids. Therefore, it is important to consume 8-10 glasses of water every day.
Cold compress for the eyes: Placing cucumbers or tea bags can help with the appearance of ptosis by alleviating swollen or puffy eyelids. But they don’t treat ptosis itself.
Diet: Certain foods like grapes and carrots help eye health.
Supplements: Lutein and B12 supplements may help reduce ptosis. However, there’s no concrete scientific evidence proving the same.
Please note that it is important to consult your medical practitioner before starting any supplements.
Eye serum: Eye serums are packed with nutrients, including vitamin C. They help rejuvenate and tighten the eyelids.
Eye exercises: While these exercises may not get rid of ptosis completely, they can help reduce the amount of eyelid droop briefly.
Eyelid massage: Gentle eye massages can help increase circulation and nerve responses.
Eye stimulation: Direct stimulation, either by concentrated eye movement or devices like electric toothbrushes, may help reduce ptosis.
Image: Stimulation of a droopy eyelid with an electric toothbrush
Eyelid resistance training: Blinking while raising your eyebrows and holding them in that position can create resistance for your eyes. This may help strengthen your eyelids.
Gazing: Staring at a particular object with your affected eye/s as long as possible can help reduce ptosis.
Congenital ptosis is not preventable.
Acquired ptosis in some cases (like age, eye trauma, muscle and nerve damage) may not be preventable as well.
Some factors you can change are refraining from alcohol and smoking and maintaining a healthy BMI.
Using spectacles instead of contact lenses and not rubbing your eyes often can also help avoid ptosis.
Exercise-induced muscle damage is the muscle soreness or fatigue associated with exercise. It especially occurs when performing a novel or unaccustomed exercise. Tart cherry juice is a popular post-workout drink. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of the cherries offer a protective effect against muscle damage and help reduce inflammation. A meta-analysis published in the international journal of sports nutrition and exercise metabolism has reported that tart cherry juice boosts muscle strength recovery and reduces post-workout soreness.
The sparkling crimson cherry juice is not only a bracing drink but also provides certain health benefits.
Tart cherry juice is made from hybrid cherries called Montmorency cherries.
Montmorency cherries usually ripe early, and they are highly used for making pies, preserves, and juices due to their sour taste.
Image: Montmorency Cherries
Apart from having a rich taste, they are also high in antioxidants, fiber, potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, and folic acid.
Tart cherries are rich in an anti-inflammatory compound called anthocyanin, which provides relief against inflammation associated with arthritis.
Consuming tart cherry juice increases the production of melatonin, a sleep hormone, in our bodies. Thus, tart cherry juice is very effective for managing sleep-related issues.
Antioxidants in tart cherries help reduce oxidative damage and improve cognitive abilities, especially in older people.
The most popular benefit of tart cherry juice is exercise recovery.
The high levels of flavonoids and anthocyanins present in tart cherry juice lessen the oxidative damage caused by exercise.
It is also found to lessen pain following exercise and decrease inflammation biomarkers.
Also Read: The Genetics of Exercise Recovery
The researchers from St. Mary's University and Northumbria University, England, documented the exercise recovery benefits of tart cherry juice.
The study results were published in the International Journal of Sports Nutrition and Exercise.
The meta-analysis of 14 studies included 223 male and 71 female participants whose average age was 26 years.
The participants were supplemented with American-grown Montmorency tart cherry juice, supplements, concentrate, and powder in all of the studies.
The participants' blood biomarkers - C - reactive protein, creatinine kinase, interleukin 6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha level- were measured.
| C - reactive protein (CRP) | This test is done to check for inflammation in your body. CRP levels increase with inflammation. |
| Creatinine kinase (CK) | CK plays a role in energy production. Measuring CK levels can help identify tissue or muscle damage. |
| Interleukin 6 (IL6) | IL6 regulates inflammatory and immune responses. IL6 test helps evaluate a person for conditions associated with inflammation. |
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) | TNF-α regulates various signaling pathways that lead to cell death in the event of infection or cancer. This test is done to checkfor any infections in the body. |
Study Findings
The study finally concluded that tart cherry juice could aid the recovery of muscle function and reduce muscle soreness post a strenuous workout session.
However, the mechanism behind this effect of tart cherry juice is yet to be determined.
https://www.sleepfoundation.org/nutrition/tart-cherry-juice
Get Deep Fitness Insights From Your 23andMe, AncestryDNA Raw Data
Colon cancer is among the third most common cancer affecting people. Almost 149,500 Americans are estimated to get diagnosed with colon cancer in 2021. A study by Umea University reveals that injudicious antibiotics use can be linked to an increased risk for colon cancer. In addition, the effect of antibiotics on the gut microbiome has been reported to be the cause of increased risk.
Antibiotics, when prescribed and taken in recommended amounts, help us fight infections. Studies have shown longstanding relations between antibiotics and gut microbiomes.
Over
The gut microbiome represents a colony of mutually beneficial microorganisms residing in the human gut. Antibiotics interact with these microorganisms and cause changes in composition and function.
Further, overuse of antibiotics leads to opportunistic infections by antibiotic-resistant microbes, which wreak havoc in the body. The gut microbes’ genetic expression, protein activity & general metabolism change, and replacement or restoration may take years. Often, the original state is hardly regained.
*Note: Opportunistic Infections are caused by pathogens that take advantage of a body situation not normally present.
Genetic expression is the process by which information stored in a gene is used to produce proteins to finally cause a physiological effect.
Colon cancer can be very elusive. The symptoms might not register right away, or it may look like the symptoms are caused by some other infection, irritable bowel syndrome, or inflammatory bowel.
Colon cancer initially manifests as polyps in the colon. These polyps are non-cancerous to begin with; they later develop into cancer. Survival entirely depends on the cancer stage, with the 5-year survival rate being 90.1 % for stage I colon cancer.
Certain types of bacteria in the gut microbiome produce sulfur which is known to be detrimental to DNA. DNA damage causes mutations that might be carcinogenic (having the potential to cause cancer).
Dietary patterns like a diet high in animal fat and protein are a classic risk factor for colon cancer. Additionally, the aforementioned dietary pattern is consistent with an increased diversity of sulfur-producing bacteria in the gut microbiome.
Bacteria like Streptococcus bovis are known inducers of cytokine production, which interfere with cell death in cancerous cells. Further, they enhance the production of new cancer cells and new blood vessels to supply the cancer cells.
Image: S.bovis associated with colon cancer
Source: https://casereports.bmj.com/content/2017/bcr-2017-219488.full
Notably, Helicobacter pylori is a known microbe contributing to colon cancer development. H.pylori contains an oncoprotein (cancer-causing protein) - cagA - which triggers a human oncoprotein in the stomach cells. This promotes the growth of cancer.
Image: H.pylori associated with colon cancer
Source: https://www.askdrray.com/colon-cancer-associated-with-h-pylori/
The study done at Umea University and led by Sai San Moon Lu explored the effects of antibiotic use on colon cancer risk.
Colon cancer data of 40,000 Swedish patients from 2010-2016 against a control group of 200,000 cancer-free individuals were analyzed. In addition, antibiotic use data was taken from the Swedish Prescribed Drug Register for 2005-2016.
Compared to men and women who took less or no antibiotics, individuals who took antibiotics ran a 17% greater risk of developing colon cancer in the first part (ascending colon).
*Note: The colon has three parts: ascending, transverse, and descending.
Moreover, women showed an inverse association, i.e., women with antibiotics use experienced a somewhat lesser risk for rectal cancer.
To study the mechanism of how antibiotics contributed to the development of colorectal cancer, the researchers performed an additional experiment.
They followed the effects of the use of a non-antibiotic antiseptic drug generally used for urinary infections.
The usage of this drug was not linked to gut microbiome disruption and colon cancer risk.
The current study’s findings suggest that antibiotics increase the risk of colon cancer by affecting the gut microbiome.
All in all, antibiotics become necessary in certain therapeutic situations. However, in cases of minor illness, individuals should take care to use antibiotics only upon the physician’s advice.
As of 2016, approximately 26.8 million people worldwide suffer from opioid use disorder (OUD), with more than 47,000 deaths from opioid overdose in the USA. A study presented at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2021 reported that there had been a steep rise in cardiac arrest trends resulting from opioid use compared to other causes.
OUD is a chronic and recurring condition that develops due to long-term use and dependence on opioids. Though in early stages, opioids interact and activate reward neural pathways, continued use increases the activation of anti-reward neural pathways. This leads to detrimental effects like emotional stress and recurrence.
A neural pathway is a series of connected neurons that send signals from one part of the brain to another.
Image: Neural Network
OUD is prevalent in the USA, with 3.4% of women and 3.9% of men suffering from it. Commonly used opioid medications include codeine and oxycodone.
An opioid overdose occurs due to opioid misuse. Legally prescribed opioids, usually used as painkillers, can quickly become a source of addiction if used chronically. Most chronic opioid users start with medically prescribed opioids and move to heroin.
Image Source: Opiant
The image depicts the demography of Opioid-related overdose deaths between 1999-2017
In recent years, a shift from heroin to fentanyl has been seen. Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is 50 times more potent than heroin. About 2 mg of fentanyl can kill most people.
In the event of overdose, naloxone can mediate the effects - slowed or total cessation of breathing.
Xcode Life’s Personalized Medicine report gives your body’s predisposition to drug interactions covering opioids, acetaminophen, and others. Check it out here.
Although opioids offer relief from acute pain, the side effects are immense - especially for people with existing heart problems.
A study has reported that the risk of death from heart diseases increased by 65% in patients who consumed opioids compared to those who took non-opioid painkillers.
The long-term effects of opioid use on heart health include:
Infectious endocarditis or heart infection occurs due to heroin (injected opioid) misuse — vegetations consisting of bacteria, platelets, and protein form in the heart blocking blood vessels. Since 2010, opioid use has increased the incidence of IE hospitalizations by 12-fold.
Bradycardia may not present as a severe side-effect, but it makes exercising difficult. Opioids affect the sinus node (part of the heart responsible for regulating electrical signals) by slowing it down. Consequently, the heart slows down.
Opioids obstruct electrical signals generated in the atria (a chamber of the heart), thus resulting in rapid, irregular heartbeats. This increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Opioids cause blood vessels to dilate or widen, leading to low blood pressure. Persistent low blood pressure can deprive the heart and brain of oxygen, thus hampering their functionality.
Explore your risk status for conditions like atrial fibrillation, stroke, and other 50+ health conditions with Xcode Life’s Gene Health Report.
According to recent data, opioid use interferes with key medications used for CVDs (cardiovascular diseases) and stroke.
For example, benzodiazepines are a class of drugs like Valium, which treats anxiety, seizures, and insomnia.
Opioid medications interact adversely with benzodiazepines and can lower heart function.
Apart from these heart problems, increased opioid use through injection is associated with increased rates of MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus).
In 2008, there was a considerable spike in hospitalization rates for strokes resulting from cerebral emboli linked to IE.
The study, co-authored by Ms. Senada Malik, examined trends in cardiac arrests resulting from opioid use for the duration of 2012-2018.
For the study, the US Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD) was analyzed for individuals suffering from cardiac arrests due to opioid use compared to those who did not use opioids.
The researchers observed an increasing trend in cardiac arrests due to opioid use for the said study period.
According to Ms. Malik, by 2018, the number of opioid-linked cardiac arrests was at par with cardiac arrests resulting from all other reasons considered together.
According to the NRD database, out of 1,410,475 hospitalizations for cardiac arrests, 3.1% were opioid-linked. These patients also had a tendency to have higher occurrences of alcohol abuse, smoking, and depression.
Opioid drug abuse is a severe public health burden. It not only has detrimental personal effects but also societal repercussions.
Abuse of opioid drugs leads to poor lifestyle choices, damages employment prospects, and plunges the person into poverty and depression. Some people even resort to criminal activities.
The American Heart Association (AHA) recently outlined a few recommendations to manage opioid use in existing heart and neurological problems.
All bodily happenings - those we know of and even those we do not know about - are processed by the brain (cognitive function). We feel and experience our body both outwardly (our physical appearance or the sensation of touch) and inwardly (the intensity of hunger or our heartbeat during physical activity). The brain is continuously at work, processing and answering external and internal stimuli (even which we do not consciously know about).
A study by Anglia Ruskin University examined the processing of signals from the internal organs by the brain. Adults with weak connectivity and brain processing capacity experience a lack of self-perception leading to body shaming and weight preoccupation.
Interoceptive awareness (IA) is knowing or being conscious of the body’s internal state and activities. The interoceptive system of the brain controls it.
The interoceptive system represents one of the least studied and comprehended parts of the body’s nervous system. In addition to overseeing IA, the interoceptive system controls our automatic or reflex movements (breathing, flinching, etc.).
Image Source: he’s extraordinary
Interoceptive awareness includes knowing about hunger, thirst, itching, emotions, and other bodily urges.
The part of the brain involved in IA is the insula. The insula is located deep inside the cortical region of the brain - hidden behind many folds.
Sensory impulses from all over the body send signals. These signals are received and processed by the insula to create IA. Some studies link IA functionality to the hippocampus.
IA affects self-awareness, recognition & regulation of emotions, ability to solve problems, and perspective.
The study by Anglia Ruskin University focused on examining the processing of internal body cues by the brain and its association to body image.
The study assessed 36 healthy adults in 4 different spheres:
The last two measurements were done to track interoceptive processing.
It was observed that some of the internal signals given out by the gut and heart are processed unconsciously. The brain processes such signals to continuously keep itself updated on the body’s internal state.
Weak brain responses to signals from both gut and heart were associated with increased body shame and weight preoccupation.
The researchers hypothesize that when the brain’s connectivity to the internal body state is weak, the brain overcompensates by putting more attention to the external body state.
This leads to the individual’s obsession with appearance as a measure for self-evaluation.
Further, differences in these internal connections between the brain and organs can help understand why and how people get afflicted with eating disorders.
The study’s findings are significant as the gut and heart signal measurements can be useful as biomarkers to identify and predict negative body image associated with eating disorders.
In addition, training individuals in interoceptive awareness can help amplify the unconscious signals and work towards a positive self-outlook.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is one of the most common genetic heart conditions to affect American people. Globally, HCM affects around 1 in 500 people. Although most people can get through life without any visible symptoms or only experience mild symptoms, some cases of HCM can prove life-threatening. The chances of sudden death without any visible sign are very high in HCM cases. A recent study by the University College London found a new gene that can cause HCM.
HCM is a heritable heart disorder characterized by the thickening of the septum separating the heart’s ventricles. The thickened muscle leads to an obstruction in proper blood flow. This makes an abnormal heart sound during the heartbeat.
*Note: Septum is the muscular wall that separates the heart’s right and left ventricles. Ventricles are two major chambers inside the heart that help pump blood.
Image Source: American Heart Association
The image depicts a healthy heart and HCM heart structural differences.
HCM may cause shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitation, dizziness, and fainting. Although the symptoms may not present with much life threat, HCM can cause other health complications such as:
Inheritance of HCM follows an autosomal dominant pattern, i.e., having an error or errors on one copy of the gene in each cell can cause the disease.
Affected individuals, therefore, have a parent with the illness which gets passed to them.
If you have a parent with HCM, there’s a 50% chance of the disorder being passed to you.
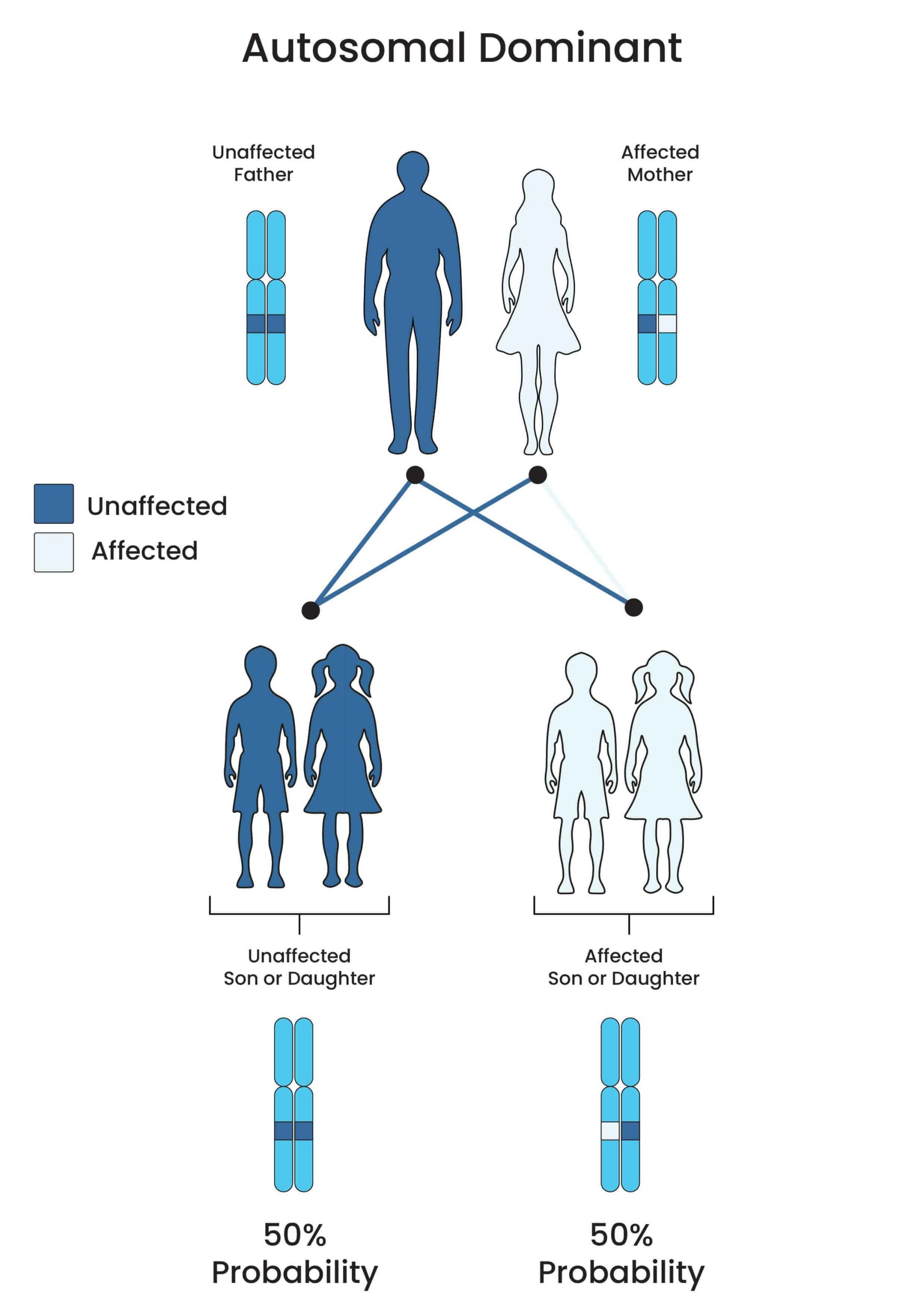
Image: Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
HCM is a polygenic disorder, i.e., it can be caused by mutations in two or more genes.
All the genes involved with this disorder appear to be related to the heart’s contraction via structures known as sarcomeres.
However, the exact mechanism of how the gene mutations lead to cardiac muscle hypertrophy is still unclear.
Know more about your genetic risk for HCM with Xcode Life’s ACMG Report!
The ALPK3 gene contains information for the production of the alpha-protein kinase 3. This protein regulates the growth of heart cells (cardiomyocytes) and is usually found in heart muscles or skeletal muscles.
In 2018, certain changes in the ALPK3 gene were found in a pediatric cardiomyopathy patient from Tunisia. The patient, a 3-year old boy, had hypertrophic & dilated cardiomyopathy and muscular and skeletal deformities.
The study conducted by University College London aimed to find the frequency of pathogenic variants of the ALPK3 gene in HCM patients.
*Pathogenic variant is a genetic change that has been proven to increase the risk of developing a particular disorder.
Researchers analyzed samples from 2817 HCM patients from healthcare centers in the UK, Spain, Latvia, Russia, Denmark, Brazil, and Argentina for the study.
DNA was extracted from the samples with subsequent whole-exome sequencing and analysis of ALPK3 gene changes.
The researchers further compared the frequency of the ALPK3 gene changes in the subjects against the general population.
They also conducted familial screening for the ALPK3 gene changes to pinpoint whether the presence of the changes meant disease manifestation.
The newly discovered pathogenic variants called truncating ALPK3 changes (after their nature of mutation) will be added to the list of genetic testing/screening for HCM.
The study’s findings will answer the questions of many HCM patients who got diagnosed but did not know the exact cause.
New findings of disease causal factors open new pathways of diagnosis and therapeutic targets, which might help many afflicted people.
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows your body to use glucose for energy. Insulin sensitivity refers to how well the cells in your body respond to insulin and uptake glucose from the blood. Recent research has reported that standing is associated with better insulin sensitivity; hence increasing the standing time on a daily basis might help prevent chronic diseases.
If your body is sensitive to insulin, it means that it can transport glucose from your blood into the cells to be used as an energy source.
A high insulin sensitivity results in a faster and more effective movement of glucose into cells.
Low insulin sensitivity is also called insulin resistance. The cells of the body do not respond to insulin, and as a result, do not absorb the glucose. This leads to high glucose levels in the body, eventually resulting in type 2 diabetes.
Image: Insulin sensitive vs Insulin resistant
A group of researchers from the University of Turku investigated the associations between insulin resistance and sedentary behavior in inactive working-age adults.
The participants had an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
This study was published in the Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport and reported that standing is associated with better insulin sensitivity.
The researchers observed the following:
The researchers further aim to study if reducing daily sitting time by an hour can impact energy metabolism and fat accumulation in the liver and the whole body.
.
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-09-association-insulin-sensitivity.html
