Reports
Health
Wellness
Around 6.2 million Americans of 65 years and above are ravaged by Alzheimer's. Alzheimer's is characterized by amyloid plaques in the brain. A new study found that people taking certain drugs for type 2 diabetes had less amyloid protein in the brain. Further, people taking these drugs also displayed a slower cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s is one of the ten leading causes of death in the US. Medically, Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurological disorder, i.e., the nerve cells in the brain start to die, and the brain shrinks.
The area of the brain to get affected earliest is the hippocampus, which is responsible for memory. However, the onset of disease can occur much earlier than the appearance of the first symptoms.
Gradually, neuronal cell death progresses to other areas of the brain. This leads to severe memory impairment and loss of ability to carry out everyday tasks.
To date, there is no cure or treatment for Alzheimer’s. Further progression of the disease ultimately results in death due to severe loss of brain function involving dehydration, malnutrition, or infection.
Xcode Life’s Gene Health Report analyzes 50+ genetic markers for Alzheimer’s disease to give possible predisposition and recommendations. Check your Alzheimer’s Disease risk here.
Biological markers or biomarkers are characteristics that can be objectively measured as an indicator of a pathological or normal physical process.
For Alzheimer’s, scientists usually look for two proteins as the disease’s biomarkers.
Amyloid plaques are stacked forms of the beta-amyloid protein fragment. Beta-amyloid is a protein fragment cut from the amyloid protein precursor (APP). Usually, these protein fragments are cleansed from the brain by microglia.
Image Source: Brain Blogger
The image here depicts amyloid plaques formed around nerve cells in the brain.
In Alzheimer's patients, the beta-amyloid does not get eliminated and starts forming clusters in the brain. In their early cluster stage, the beta-amyloid starts destroying synapses or nerve junctions - leading to memory loss in the individual. Upon forming plaques, the beta-amyloid protein contributes towards brain/nerve cell death.
Tau proteins are part of the neuron’s (nerve cell) internal support and transport system.
Image Source: Utah Public Radio
In Alzheimer’s, the tau proteins change their shape and structure to form tangles in the neuronal fibers. These tangles disrupt normal tau protein functioning and become toxic for the cells, thus leading to cell death.
The most prevalent genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s is the ApoE (apolipoprotein E) gene. The 4 type of this gene is known to confer the highest risk factor and is present among 50% of Alzheimer’s patients.
The ApoE gene present on chromosome 19 makes a protein that helps transport cholesterol and other fat molecules through the bloodstream.
While there are two other types of the ApoE gene ( 2 & 3), only the 4 variant is associated with increased risk for Alzheimer’s. Having one or both copies of ApoE 4 in the body increases Alzheimer’s risk. The prevalence of individuals carrying one copy is about 25%, while only 2-3% carry both copies.
Know your ApoE gene Status with Xcode Life’s Gene Health Report.
Alzheimer’s is one of the diseases where age, especially old age, plays a significant role. Although Alzheimer’s development is not part of the normal aging process, old age increases the risk.
MCI is characterized by a decline in memory and associated thinking abilities, disrupting an individual's normal societal or work-environment functioning. Usually, an MCI diagnosis with primary memory deficit leads to Alzheimer's associated dementia.
Certain factors which pose a risk for cardiac problems also increase Alzheimer’s risk. Some of them are
Additionally, people with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of Alzheimer's disease. This may be due to higher blood sugar levels which have been linked to amyloid plaque buildup.
DPP-4 inhibitors or gliptins are oral diabetes drugs used to block the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4. DPP-4i acts on incretins (a group of hormones that stimulate the release of insulin). In addition, it reduces glucagon (a hormone that increases blood sugar levels), thereby decreasing blood sugar levels.
A previous study exploring the effect of DPP-4i use on dementia among type 2 diabetes patients revealed an increased impact on dementia, albeit not in Alzheimer’s patients.
Studies revealed an increased risk of inflammatory bowel and hypoglycemia when combined with another class of diabetic drug, sulphonylureas (like glipizide and glimepiride), in type 2 diabetic patients.
Know your body’s predisposition to the metabolism of DPP-4i and sulphonylurea drugs with Xcode Life’s pharmacogenomics report, Personalized Medicine.
Scientists at the American Academy of Neurology explored the effect of DPP-4i use in Alzheimer’s patients who may/may not suffer from type 2 diabetes (T2D).
The study involved 282 people with either pre-clinical, early, or probable diagnosis of Alzheimer's. Individuals were of an average age of 76 and were followed for a six-year period. These people comprised of:
Researchers measured the amyloid content in the individuals’ brains using a brain scan.
Study participants were made to take a common thinking and memory test called Mini-Mental State Exam (MSME) every 12 months for 2.5 years to track cognitive decline. The test consisted of questions like counting backward from 100 by sevens or copying a picture on paper. The score ranged from zero to thirty.
Between the three subgroups, Alzheimer’s individuals having T2D and on DPP-4i drugs:
Further adjustment of factors that could affect MSME scores, the same Alzheimer’s individuals with T2D and using DPP-4i drugs scored even lower decline by 0.77 points per year.
Diabetes is a chronic disorder wherein the body no longer responds to insulin. The disease could reduce the efficiency of the body’s immune system. As such, diabetes is a common comorbidity of COVID-19, with up to 20% of patients requiring intensive medical care. With lockdowns and social restrictions in place across the globe, here are some ways in which you can protect yourself from the novel coronavirus.
The current COVID-19 pandemic has affected all our lives in one way or another. The cases report a range of symptoms from mild or asymptomatic cases to severe forms of pneumonia that could lead to the patient’s death.
With newer evidence released on a daily and monthly basis, researchers worldwide are trying to deduce the infection pattern, characteristic symptoms, potential treatment patterns, and drugs.
COVID-19 is an infection of a new coronavirus called the SARS-CoV-2 that emerged in the Wuhan region in China. This disease was so widely spread, that the World Health Organisation declared a global pandemic in March 2020.
The SARS-CoV-2 is a type of coronavirus, which falls under the same family as SARS and MERS. Some experiments have hypothesized that the virus has some affinity to angiotensin-converting enzyme receptor 2 (ACE2), which acts as the gateway to the human body.
As many scientists rush to find the cure for the disease, a pressing question remains- why is there such a disparity between patients of COVID-19? How are there some individuals showing absolutely no symptoms, and on the other hand, why are some patients exhibiting severe pneumonia-like symptoms?
The known factors, like age and previous medical history, makes an individual more susceptible to showing severe symptoms.
However, there are cases of perfectly healthy young people showing severe symptoms as well. Some underlying genetic factors can be responsible for this.
As mentioned above, one hypothesized path that the virus takes to the body is through latching onto the ACE2 receptor.
Scientists have found variants of the gene that codes for ACE2, which could influence how the protein functions or impact the structure. This, in turn, affects how the virus could infect a person.
Another factor that could influence how the virus infects an individual could be the person’s blood group.
The ABO gene determines the blood type of a person and could shine a light on how susceptible a person is to the virus.
Both these genes are from preliminary studies, and this needs more validation and a larger group of volunteers to conclude any observation.
Diabetes is a condition in which there is an impairment in the body’s ability to produce or respond to insulin.
This results in abnormal levels of carbohydrates and elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
People with diabetes are at an increased risk, as they have an impaired immune response to infection.
This applies to both cytokine profiles and activation of T-cells and macrophages.
The impact of having an impaired response to insulin affects the body’s response to viral infection and potential secondary infection in the lungs.
A study compared hospitalization rates of COVID-19 patients and the underlying medical conditions.
Of all the volunteers in the study, 7% were hospitalized and admitted in the ICU, and 77% were not hospitalized. While analyzing the patients with diabetes, up to 20% were hospitalized, and only 45% were not hospitalized.
This data shows that patients with diabetes require extra medical attention if diagnosed with COVID-19.
Patients with type 2 diabetes are also at risk of being obese. This is an additional risk factor for severe infection.
In the case of the 2009 H1N1 epidemic, about twofold more patients diagnosed with the disease, with a history of obesity, ended in ICU, and took longer to recover.
Finally, the most common co-morbidities to COVID-19 are hypertension and diabetes.
These diseases are both treated with ACE2 inhibitors.
This means that a patient with an ACE inhibitor would have an increased expression of ACE2.
Since the novel coronavirus targets ACE2, it could facilitate COVID-19 infection, and place these patients at a high risk of disease and fatality.
Genetics plays a role in type 2 diabetes; however, factors like lifestyle choices play a larger role in the manifestation of this disease.
A choice for healthy living can heavily lower the chances of developing type 2 diabetes.
This includes staying healthy by maintaining a healthy weight and choosing healthy foods.
It is possible to test for your genetic predisposition towards diabetes using your 23andMe DNA raw data.
If you have are a diabetic/ have a predisposition to diabetes, it is important to be prepared. Some measures that you can take are:
There are three main pillars of diabetes maintenance, monitoring, exercise, and diet. Measures that you can take with respect to exercise and monitoring are explained above, and the following details a diet plan that you can follow.
COVID-19 is caused by a novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. The symptoms and the path of infection are still being studied, with new data being released on a daily basis. Individuals with comorbidities, especially like diabetes and hypertension, must strictly follow social distancing practices. If they do step out, measures of wearing a face mask, carrying a sanitizer, and washing hands thoroughly with soap can help prevent infection.
Could genetics play a role in the severity of COVID-19?
COVID-19 Infection in People with Diabetes
Upload your DNA raw data to Xcode Life to know your genetic predisposition to diabetes.
|
Liquid calories or high sugar drinks are often consumed less rationally than food that is chewed. Most people do not “count” the calories they drink. However, a great deal of damage could be coming from liquid calories.
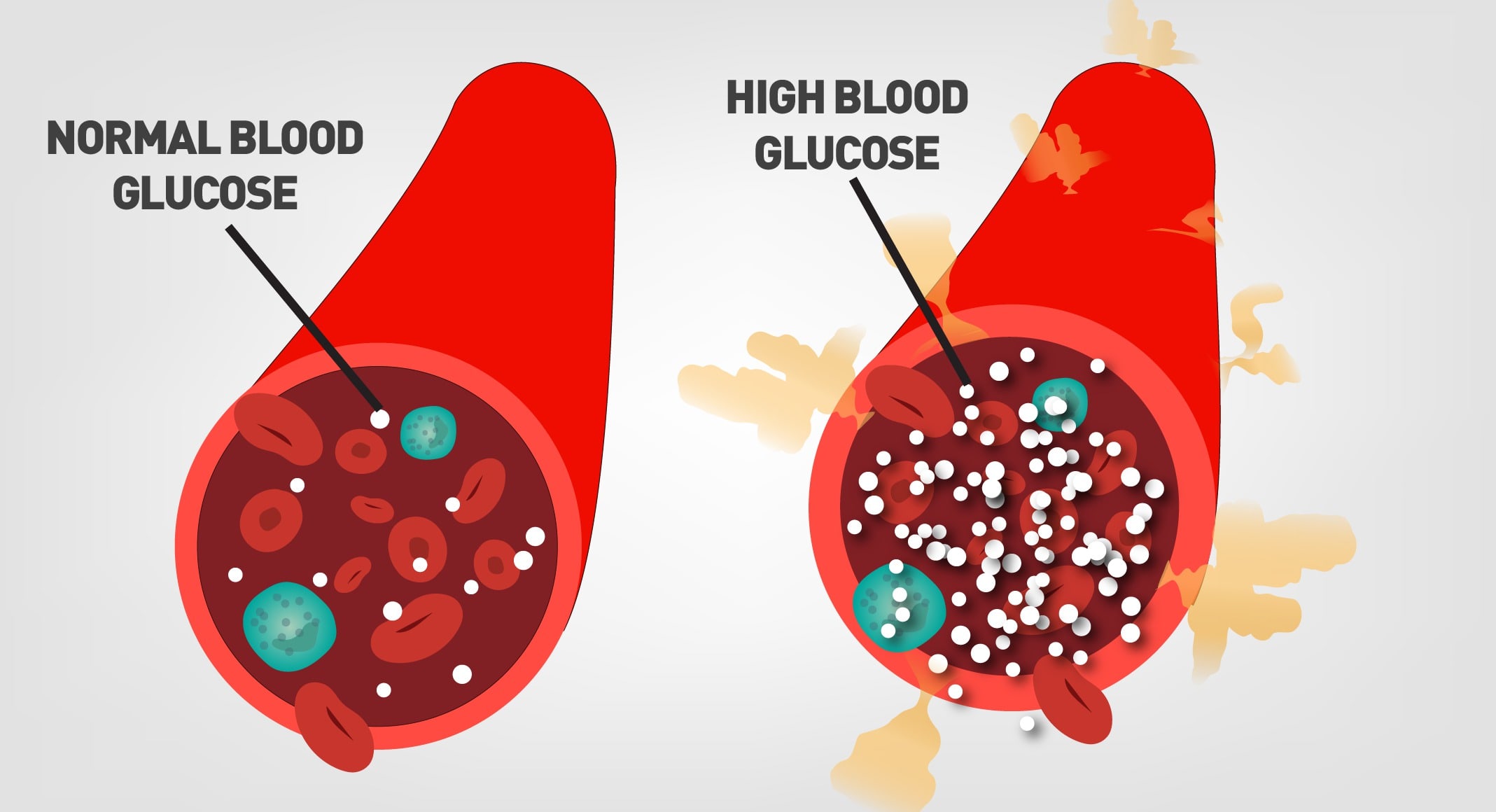
Sugar in drinks gets into the blood faster than sugar in solid foods, thus increasing blood sugar levels rapidly. Repeated increases in blood sugar levels lead to insulin resistance, which eventually leads to obesity, diabetes and other health conditions. People habitually consume colas, bottled fruit beverages with added sugar, teas and coffees with sugar, and all sorts of sugar sweetened beverages(ssb).
These drinks are consumed casually at home as a replacement for water, at entertainment centers, after sports, and at social events. Many people quench their thirst with these drinks instead of water, ignoring the calorie labels(a.k.a warning labels) on them. The fine print shows an alarmingly high level of sugar that research studies have found to be associated with a risk for obesity and thereby an increased risk for diabetes. These drinks confer risk of diabetes.
While the risk for diabetes associated with drinking sweetened beverages has always been known, a new study shows the extent of risk. Researchers from Karolinska University in Sweden showed that consuming 2 glasses of sugary drinks every day could double diabetes risk.
In the study, two or more of 200 milliliters servings(~ one and a half cans) of the sugary drinks when consumed every day was found to increase the risk for diabetes by two-fold. People who preferred drinks that were sweetened with artificial sweeteners were equally at risk for diabetes.
Diabetes risk was the same whether one consumed drinks sweetened with sugar or artificial sweetener
Josefin Edwall Löfvenborg who is a nutritionist at Sweden’s Karolinska Institute spoke about the relevance of the study “Not all studies have been able to look at sugary and artificially beverages separately. (but) it's getting more and more established that soft drinks increase the risk of type II diabetes."
‘Effect of Larger Quantities’
"We wanted to see the effect of larger intakes than two," stated Löfvenborg highlighting the second part of the study that determined diabetes risk among people who drank more than 1 liter of sugary drink every day. The risk was found to increase 10 fold in this group, reiterating the effect of consuming high sugar drink on diabetes risk.
Cups quickly add up to a liter in a day: a few cups of coffee or tea a day, some canned beverages, a can of soda or cola, cappuccino, lassi, etc. all can add up to contribute towards the risk of diabetes.
[idea]
Is soda the new cigarette?
High sugar drinks like sugary soft drinks are being additionally taxed in places like California and Berkley in the U.S. In Kerala, India, fat tax of 14.5% is levied on junk food at International food chains which include burgers and high sugar drinks consumed in these chains. Such high tax is levied to lower consumptions as high sugar drinks are implicated in the rising obesity epidemic and diabetes numbers in the world. In California and Berkley, soda consumption has dropped by one fifth after the tax on soda was executed. Cigarettes are taxed similarly to lower consumptions, this boils down to soda being on the same plane as cigarettes. [/idea]
Not everyone reacts equally to dietary risk factors, certain genes have been shown to modify (predispose or protect) disease risk. In a recent study, it was found that people with certain gene variants were at a higher risk for diabetes even when they consumed the same dietary components as others. This would mean that people who consume high sugar drinks may have a higher risk for diabetes but the level of risk may be modulated by the genes they carry.
Family history is an important genetic risk factor for diabetes. The risk for diabetes is increased if both parents are diabetic, as compared with either parent or neither parent being diabetic. Predisposition to diabetes can be determined through a simple and economical saliva-based genetic test.
Xcode’s Health Genetics test is a companion to the Master Health Checkup (MHC). This genetic test covers predisposition to diabetes, obesity, hypertension and heart disease in one, low-cost test. When taken together with blood test data from MHC, it provides a complete picture of the various risk factors. Nutritional, dietary and lifestyle counseling is provided to lower the risk towards the normal range.
You can write to us at hello+support@xcode.in to find out more.
SNP or Single Nucleotide Polymorphism can simply be termed as copying error made by cells during the process of making new cells wherein a ‘wrong’ nucleotide is present in the DNA sequence in the place of a ‘correct’ nucleotide. For e.g., let’s assume that the normal sequence of a particular section of DNA in humans is AATGCT. A SNP is when the sequence becomes AATGCA, where the last letter (nucleotide) instead of ‘T’ is replaced with ‘A’. These copying errors are like typographical errors which lead to variations in the DNA. These typos in DNA might affect protein function and structure, when present within genes that form these proteins. These variations in the DNA are the root cause for majority of health conditions, differences in response to drugs or diseases etc.
SNPs can be associated with lifestyle related conditions like diabetes, obesity and stroke. These SNPs also contribute to difference in food metabolism e.g. lactose intolerance.
With over 30 million people diagnosed to be diabetic, India is well on its way to becoming the diabetes capital of the world!
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body cannot regulate the production or usage of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that converts sugar, starches, and other food into energy. This energy is either used immediately or stored as fat or glycogen. In a diabetic, the body does not produce enough insulin to move the sugar into cells, and the sugar gets accumulated in the blood.
Type 2 diabetes occurs later in life and hence is referred to as adult-onset diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, the muscle and fat cells in the body become resistant to insulin which causes the pancreas to make more insulin. As long as the pancreas continues to produce insulin to overcome this resistance, blood glucose levels remain normal. However, after several years the resistance of the cells continues to increase and the pancreas begins to produce lesser insulin. This result in hyperglycemia (abnormally high levels of sugar in the blood) and the symptoms of type 2 diabetes start manifesting. Type 2 diabetes is most often seen in obese or overweight people and the elderly.
Type 2 diabetes is asymptomatic in the majority of the cases over a long period of time. If symptoms do occur, they include fatigue, increased hunger (polyphagia), frequent urination (polyuria) and increased thirst (polydipsia), blurred vision, erectile dysfunction, and poor wound healing.
Genes have a role in glucose metabolism, and genetic variations within these genes affect their function, thereby increasing the risk for type 2 diabetes.
Our traits are basically divided into genetic and environmental. Genetic factors are the ones a person is born with, and a large chunk of these factors are inherited from the previous generations. Environmental factors include chemical, physical, nutritional, infectious and behavioural factors. Many prevailing diseases such as diabetes and cancer are caused by the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Both the factors will play a part in influencing the diseases. Some may be more influenced by the genetic factors while others will be largely affected by the environmental factors. But, most of the diseases are always associated with the genetic makeup and many inherited diseases can be influenced by environmental conditions.
If you have a genetic predisposition to antisocial behaviour, you may not demonstrate the trait until you experience abuse or neglect in your childhood. If you have had a stress-free and normal childhood, you will never express this specific genetic trait. The expression of a specific trait towards which you are genetically predisposed can be prevented by protective environmental factors. If you have a predisposition to alcohol abuse and live in an alcohol-prohibited environment, it may not express itself. Thus, protective genetic factors have a comparatively less significant effect if environmental exposure is strong.
Response to environmental exposure depends on the genotype, which is a term that defines your genetic make-up for a specific trait/disease. If you have had stress in your early life, it may cause depression in later years. This is only when certain genotypes are present. A person’s genotype can also determine their response to specific medications and their side-effects through various biochemical mechanisms. There is an entire branch of science that studies this called Pharmacogenomics.
If we can identify our genes and characterize their interactions with the environment, we can have intervention strategies to target them. Therefore, when studying the genetic make-up of individuals to determine their natural predisposition towards certain traits and diseases, it is very important to take into consideration the environmental factors like diet, lifestyle, work environment etc, to be able to characterize their inclination towards these traits and their risk for developing specific diseases.
A 2006 research study in New England Journal of Medicine had two interesting observations. One, a variation of the TCF7L2 gene is linked to prediabetes (blood sugar is high but below diabetes range) which indicates a higher likelihood of developing diabetes. Other data showed that changes in food habits and physical activity could reduce or stop disease development, even in people with disease-risk increasing genetic variants.
Every human cell contains a nucleus with chromosomes, that carry the ‘building block’ of life (or DNA) arranged in specific groups (or genes), which are responsible for all our biological characteristics. Often person-to-person genetic differences result from gene mutations (or changes) that may either directly cause disease (e.g. sickle cell anemia) or combine with dietary and environmental factors to increase the probability of disease occurrence (e.g. diabetes, obesity, heart disease and stroke).
[idea]
[hr height="30" style="default" line="default" themecolor="1"]
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body cannot regulate the production or usage of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that converts sugar, starches, and other food into energy. This energy is either used immediately or stored as fat or glycogen. In a diabetic, the body does not produce enough insulin to move the sugar into cells, and the sugar gets accumulated in the blood.
[/idea]
[info_box title="There are three main types of diabetes:" image="" animate=""]
Type 2 diabetes occurs later in life and hence is referred to as adult-onset diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, the muscle and fat cells in the body become resistant to insulin which causes the pancreas to make more insulin. As long as the pancreas continue to produce insulin to overcome this resistance, blood glucose levels remain normal. However, after several years the resistance of the cells continues to increase and the pancreas begin to produce lesser insulin. This result in hyperglycemia (abnormally high levels of sugar in the blood) and the symptoms of type 2 diabetes start manifesting. Type 2 diabetes is most often seen in obese or overweight people and the elderly.
[one_second]
[hr height="30" style="default" line="default" themecolor="1"]
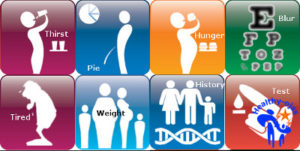
Type 2 diabetes is asymptomatic in majority of the cases over a long period of time.. If symptoms do occur, they include fatigue, increased hunger (polyphagia), frequent urination (polyurea) and increased thirst (polydipsia), blurred vision, erectile dysfunction and poor wound healing..
[/one_second]
[one_second]
[/one_second]
[hr height="30" style="default" line="default" themecolor="1"]
The cornerstone of any diabetic therapy is healthy lifestyle. Although the immediate goal of diabetes treatment is to lower high blood glucose levels, it requires lifelong treatment and monitoring to prevent diabetes-related complications.
Every diabetic individual and his family members must be aware of some basic diabetes management skills such as, blood glucose monitoring, diabetic diet, medications, how to recognize and treat high and low blood sugar etc.
[hr height="30" style="default" line="default" themecolor="1"]
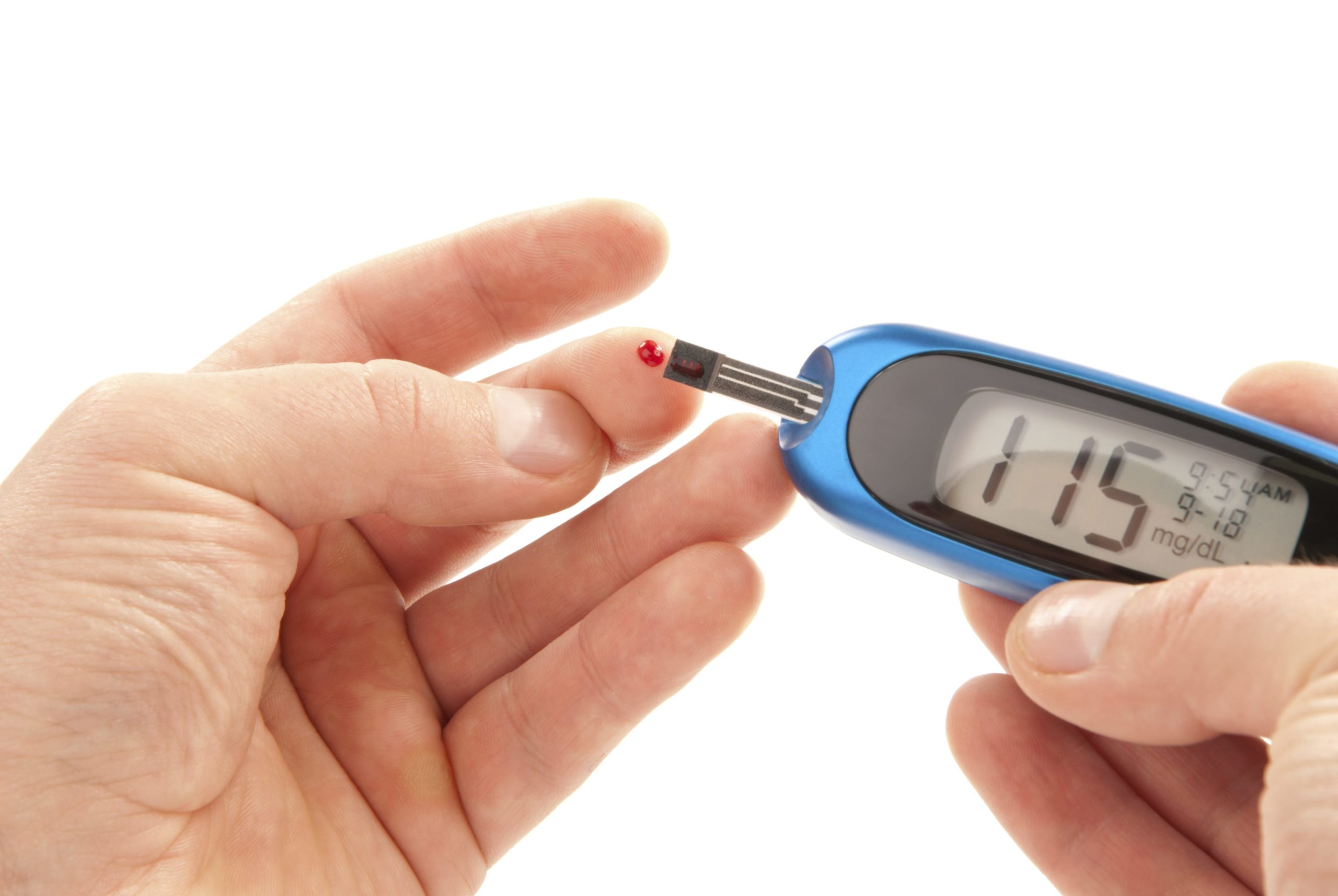 Self testing (using a glucometer) gives an exact blood sugar reading. The results are used to keep an optimal blood sugar levels by adjusting food, activity and medications.
Self testing (using a glucometer) gives an exact blood sugar reading. The results are used to keep an optimal blood sugar levels by adjusting food, activity and medications.
Diabetics should follow a strict diabetes diet to avoid blood sugar from becoming extremely high or low. The timings of the meals are also important as it prevents blood sugar levels fluctuating. Most diabetic diets are designed to be well-balanced meals which help in managing the body weight.
Regular physical activity can control blood sugar and helps shed extra fat to achieve a healthy weight. Exercise improves the blood flow and decreases the insulin resistance.
If diet and exercise fail to optimize the blood sugar levels medicines are prescribed. Some of medicines are alpha-glucosidase inhibitors,biguanides, exenatide, mitiglinide, pramlintide, sitagliptin, saxagliptin,meglitinides,sulfonylureas and thiazolidinediones.
If the combined therapy of medicines, exercise and diet still fails to optimize the blood sugar levels, insulin injections are prescribed.
[hr height="30" style="default" line="default" themecolor="1"]
Although genes play the major role in type 2 diabetes, a healthy lifestyle (wholesome diet, exercise, adequate rest) goes a long way in preventing type 2 diabetes symptoms and associated complications. If you have any of the risk factors, early detection tests may be performed. Medications to delay or prevent the onset of diabetes have shown to be successful.
