Reports
Health
Wellness
Cystic Fibrosis is a progressive genetic disease that is inherited in a recessive manner.
Cystic fibrosis is characterized by persistent and frequent lung infections, and limits the ability to breathe over time.
The disease is caused by mutations in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator or CFTR gene.
About 75% of new dignosis of cystic fibrosis happens in children below the age of 2 - Source: Healthline
This gene encodes a protein that is inserted into the cell membranes of the inner lining surface of organs and forms a channel that regulates the movement of salt and water in and out of cells.
Such disease-causing mutations affect the body's ability to efficiently secrete sweat, tears, digestive juices and mucus.
Important: The Cystic Fibrosis report is only applicable to 23andMe v5 chip raw data holders
When the CFTR gene functions normally, it aids in the transport of chloride to the cell surface and helps attract water to the surface as well.
This maintains the fluidity of the mucus in most organs.
A mutation in the CFTR leads to improper gene function because of which there is no chloride and water at the cell surface.
The mucus becomes thick and sticky in most organs.
In the lungs, this type of mucus traps bacteria and other microbes eventually leading to lung infections.
Cystic fibrosis, is an autosomal recessive genetic disease.
This means the disease will only manifest in individuals who receive two mutated copies of the CFTR gene (one from each parent) will get the disease.
More than 500 known mutations of the CFTR gene have been documented to cause cystic fibrosis, although most of them are rare.
How To Analyze Your APOE Gene With Your DNA Raw Data?
Though cystic fibrosis can be diagnosed using genetic testing, there are other ways to detect this disease.
These include newborn screening, a sweat test, and clinical evaluation.
Since cystic fibrosis runs in families, couples thinking of having children can take a genetic test and evaluate their results by consulting a physician or genetic counselor.
If the genetic test reveals that you are a carrier of the disease variants, it might be useful to share your result with your family members to help them understand their risk of developing the disease.
Consulting a genetic counselor is always helpful in such cases.
Though there are about 500 mutations known for the genes, the genetic tests done for cystic fibrosis help detect only the most common ones.
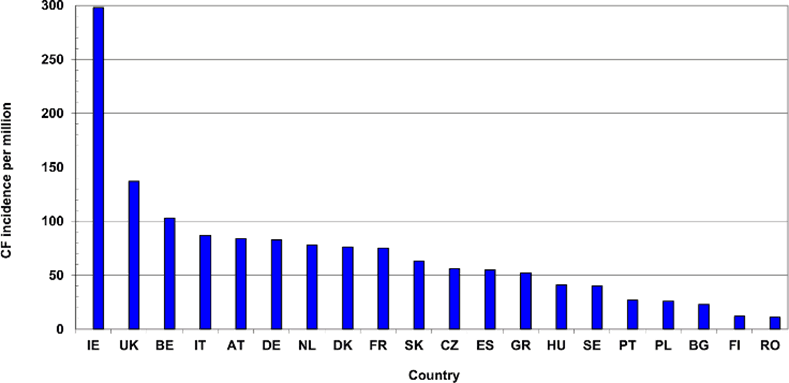
Source: Research Gate
There are more than 70,000 people living with cystic fibrosis in the world today.
In African-Americans and Hispanic-Americans, the carrier rates are 1 in 65 and 1 in 46, respectively.
However, CFTR mutations are much rarer in Asians — with an incidence of 1 in 90.
It is also interesting to note that 1 out of 29 Caucasians, including Ashkenazi Jews, carry one copy of a CFTR mutation.
Since cystic fibrosis is inherited in a recessive manner, an individual must have two copies of the recessive gene, one inherited from each parent.
This means that both parents must have at least one copy of the defective variant.
Individuals with just one copy of the gene are called carriers and do not themselves suffer from the disease.
The effects of having a combination of two different mutations also vary.
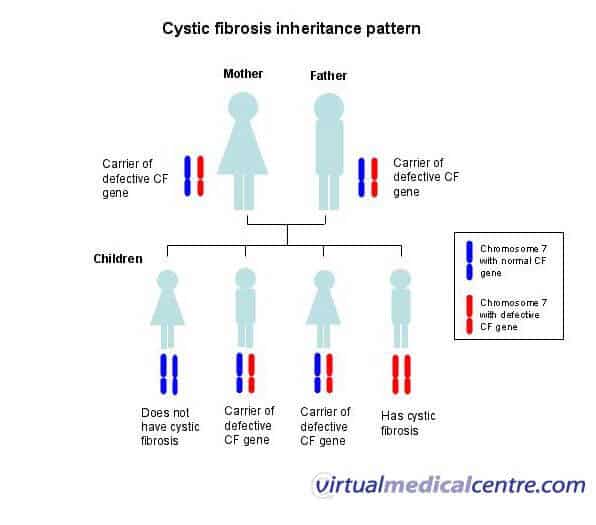
Source: Virtual Medical Centre
Sometimes, a person who has two mutated copies of CFTR might suffer from severe lung and pancreatic disease.
In other cases, lung function may be almost normal but there might be some pancreatic effects.
In some rare cases, there might be only reproductive system effects with little or no noticeable symptoms at all.
Hand-Picked article for you: Have Your 23andMe Raw Data? Use It To Get 500+ Health-Realted Genetic Traits!
One of the reproductive system effects of CFTR mutation is a congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD).
Men who have been diagnosed with a low sperm count might be suffering from one CFTR mutation that they should be aware of, as this could be the reason for their infertility if they carry a second, unreported mutation on the other copy of the CFTR gene.
If you are concerned about this, you must consult a health professional.
One relatively common CFTR mutation is the deltaF508 mutation.
Individuals with two copies of this mutation have more severe symptoms than those with one copy of this mutation and a copy of another CFTR mutation or two non-deltaF508 mutations.
In many cases, when cystic fibrosis is suspected in newborns, they are screened by assessing the level of a certain enzyme in dried spots of blood.
Other tests are done on babies who test positive for this test in order to rule out or confirm the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis.
In the United States, all newborns are screened for cystic fibrosis as a general rule.
It is important to know which mutation or mutations cause cystic fibrosis in a person as this helps explore the available treatment options.
Today, the treatment of cystic fibrosis focuses primarily on unfixing the mucus, treating infections and supplying adequate nutrition.
In individuals with the G551D mutation, the drug ivacaftor is available for directly treating the dysfunctional CFTR protein.
Currently, the possibility of using ivacaftor for treating CF patients with a handful of other CFTR mutations is being studied. However, it is quite unlikely it would be an effective treatment for the deltaF508 mutation.
23andme celiac disease genetic testing involves assessment of genetic markers associated with gluten sensitivity and celiac disease from your 23andme raw data. The DNA raw data is available to you when you buy the 23andme genetic test for Ancestry.
In recent years, the number of people found to have celiac disease has grown many folds due to increased awareness and ease of diagnosis.
So, why do you need to do genetic testing for coeliac disease? About 1 in 100 people in the U.S have celiac disease. However, 2.5 million people with celiac disease do not know that they have it, i.e they are undiagnosed.
Here are a few important facts about celiac disease genetic testing that everyone must know.
References:
Assigning haplogroups during raw data analysis primarily depends on the number of Y chromosome and mtDNA gene markers present in your raw data. In some raw data files, such as in female samples, the Y chromosome data will not be present. In certain other cases, the company may not include Y and Mitochondrial DNA markers in their raw data or too few data points are present. In such cases, a haplogroup cannot be assigned.
For example, the autosomal raw data from Family Tree DNA’s Family Finder test does not contain markers from the Y chromosome and mtDNA. In this case, our tool will be unable to associate a haplogroup to the sample.
If you are getting a parent haplogroup such as H, N etc. this is likely because only the mutation corresponding to the parent haplogroup was found but not the ones corresponding to their subclades. This is also likely due to insufficient SNPs in your raw data file.
Below is a table showing the number of Y chromosome and mtDNA markers present in the raw data from different companies.
[table “54” not found /]For some of you, especially those with AncestryDNA raw data, it is not uncommon to find a paternal haplogroup in your report.
In case you find this information in your report please feel free to ignore it.
To answer the question of why a paternal haplogroup is being assigned in the first place, it is necessary to describe a little about the way Ancestry DNA labels their chromosome. The Y chromosome is labeled as chromosome 24. If you open your raw data text file and search for chromosome 24, it should be completely devoid of any “calls” or values like A, T, G or C. If you find any such entries in the columns labeled Allele 1 and Allele 2 in your AncestryDNA raw data, that would be picked up by the algorithms of third party tools or websites and assign a relevant haplogroup to it.
Now for biological males, all the gene markers in the Y chromosome will have an entry, and correctly so since males have a Y chromosome. Hence the assigned haplogroup from this data is valid. However for biological females this will be assigned from whatever calls that are found in their raw data. Hence this information is not valid.
Do you suffer from sniffles or a runny nose? Does drinking red wine make your face flush? Do you get sudden and unexplained headaches? These are some histamine intolerance symptoms which often feel like they appeared without any apparent trigger.
Histamine is a biogenic amine which is derived when the amino acid histidine is decarboxylated. This bioamine is stored in the mast cells and in the basophils and is produced by the body during allergic reactions. It is also known to be a neurotransmitter as well as a vasodilator. Though the condition is termed histamine intolerance, the body can ‘tolerate’ a certain amount of histamine. It’s only when there is histamine overload that people with reduced activity of the DAO enzyme start exhibiting histamine intolerance symptoms.
The body metabolizes histamine via the following two known degradation pathways
Apart from the histamine produced by the body, ingested histamine is also degraded by one of the two pathways.
Histamine intolerance symptoms include nasal congestion, irregular menstrual cycles, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, hives or headaches.
Histamine Intolerance test: A blood test to determine the level of DAO enzyme activity is not very definitive as the level of DAO enzyme in the blood is not reflective of its activity levels in the body. In a study conducted on 384 children with chronic abdominal pain, the level of serum DAO enzyme tested did not correlate with the levels of serum or urine histamine. When the children were put on a low histamine diet, 50% showed reduction in symptoms. According to ‘German guideline for the management of adverse reactions to ingested histamine’ (2017), measuring DAO enzyme activity in the serum was inconclusive in the detection of histamine intolerance.
Genetic testing for determining DAO enzyme activity can be used for informative purpose but there are other factors which could contribute to the development of histamine intolerance.
When there is a reduction in the activity of the DAO enzyme, it is shown to be associated with an increased risk of histamine intolerance. DAO enzyme is synthesized from the AOC1 gene. 23andme raw data includes the following polymorphisms
Use your 23andme raw data or your Ancestry DNA raw data to check for AOC1- rs10156191
[table “47” not found /]Use your 23andme raw data or your Ancestry DNA raw data to check for- AOC1- rs1049742
[table “48” not found /]Use your 23andme raw data or your Ancestry DNA raw data to check for-AOC1- rs1049793
[table “49” not found /]Use your 23andme raw data or your Ancestry DNA raw data to check for-AOC1- rs2052129
[table “50” not found /]Use your 23andme raw data or your Ancestry DNA raw data to check for-AOC1- rs2268999
[table “51” not found /]MTHFR and histamine intolerance
The methylation cycle is also associated with the breakdown of histamine and other monoamine neurotransmitters. Finding out about the MTHFR mutations carried will help in identifying the extent of histamine clearance via the methylation pathway. To do this, 23andme raw data or Ancestry DNA raw data may be uploaded onto sites like Genetic genie which list out the various MTHFR mutations. However, although Genetic genie provides a list of SNPs, Xcode Life, provides recommendations and likely enzyme activity levels based on the 2 prominent MTHFR SNPs- C677T, A1298C.
The most effective treatment for histamine intolerance is to opt for a low histamine diet. Many research studies have found that elimination diet, or a low histamine diet, can help in identifying if an individual has histamine intolerance.
High histamine foods
Here is a list of high histamine foods
Intoxication due to histamine may occur due to consumption of spoiled tuna or mackerel, which are high histamine foods, and should, therefore, be avoided.
Low histamine foods
The bane of opting for low histamine foods is that it could increase the risk for malnutrition. Care should be taken to include sufficient nutrition to ensure good health.
A low histamine diet is primarily to identify the presence of histamine intolerance and it should be carried out by eliminating certain high histamine foods and then slowly adding them, checking for the return of symptoms. It should ideally be carried out under the supervision of a medical practitioner. The extent of histamine intolerance varies from one individual to another.
An ideal way of designing your own low histamine diet is to opt for one or two vegetarian meals. Meat should be consumed when it is prepared the same day, though the skin of poultry has high histamine levels, irrespective of when it is prepared. Portion control could also play an important role, a bit of lime present in a dish like hummus may not harm while a glass of lime juice could.
DAO supplement
One of the major factors for histamine intolerance is the reduced DAO enzyme activity. There are many DAO supplements that are available to boost the activity of this enzyme, thereby reducing the extent of histamine intolerance.
A word of caution on DAO supplement production, many of these have porcine sources and contain rice and corn, and so should be avoided by individuals with any allergies to these. Alternatively, pea shoots are high in DAO and can be consumed by vegetarians or people looking for alternate DAO supplement.
Histamine intolerance can affect your quality of life and finding out about the level of DAO enzyme activity based on genetic variations may help in altering the diet to reduce symptoms. Xcode Life reports include information on SNPs associated with histamine intolerance and can be purchased here.
References:
One of the important questions plaguing most women during their middle age is whether they should opt for menopausal hormone therapy to alleviate menopausal symptoms.
Many women in this delicate phase count fretfully the number of sleepless nights, the night sweats and hot flashes that interrupt their otherwise normal life.
The U.S Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed a 2015 National Health Interview survey (NHIS) and found that over 56% of perimenopausal women failed to get sufficient sleep.
The dwindling levels of estrogen has been associated with the classic symptoms of menopause, which led people to believe that menopausal hormone therapy could lower the intensity of symptoms.
This made estrogen supplementation very popular during the late 1960s with the belief that it could make women ‘young forever’.
FDA approval for estrogen therapy for osteoporosis helped gain confidence of more women, with observational studies conducted in 1990s showing reductions in coronary heart disease and Alzheimer’s.
The first study that raised an alarm about the use of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk was the Women’s Health Initiative study. This study found that for every 10,000 person-years of use of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) use, there were 8 more invasive breast cancers.
Estrogen is a female hormone which is mostly produced in the ovaries. During breast development, the DNA present in the cells is constantly copied before the development of new breast cells.
This delicate process could increase the risk of development of genetic abnormalities.
Estrogen plays an important role in breast tissue development and supplementation with this hormone during menopause, therefore, has been shown to be associated with an increased risk for breast cancer.
The results of the Women’s Health initiative study led to a considerable drop in the use of hormone therapy in the U.S.
The assumption was that women would use it for a short period of time with the risk of breast cancer being uniform.
However, a large study conducted by the Breast Cancer Association Consortium on perimenopausal women showed that specific genetic variants modified the effect of hormone therapy use on the risk of breast cancer.
The study included a large sample size and three loci present on the chromosomes 13, 14 and 16 were found to alter breast cancer risk on menopausal hormone therapy use.
Women who had more than 5 or 6 high risk variants were found to have an 86% increased risk for breast cancer on MHT use while there was no association with breast cancer risk on MHT use among women with fewer than 2 risk variants.
The results of the study should stress the importance of identifying genetic variants and weighing the relief of symptoms against the unhealthy legacy of taking these medications.
You can now find out if you carry the variants associated with Menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk from Xcode’s Breast Cancer report by uploading your 23andMe or any other Ancestry DNA raw data.
You can read more about the Xcode Breast Cancer report here.
When 23andMe receives your saliva sample, it extracts cells (mostly cheek cells) from your saliva, then breaks down the cell and nucleus to get your DNA. Your DNA is then purified and multiplied several folds to make it easily detectable.
23andMe uses a “genotyping chip” to detect your DNA data. What part of your DNA is detected depends on which chip was used. 23andme has used different chips over the years. Think of it in terms of smart phones. Each year, new versions of chips are released with more and more functionality than the previous version. Similarly, the DNA chips are constantly upgraded and the latest “chip” is typically better than the previous version in terms of how much information it detects from your DNA.
In 2017, 23andMe migrated from the Illumina OmniExpress chip that was used across multiple ancestry DNA companies. The current 23andme v5 chip, the Global Screening Array (GSA) is a next-generation genotyping array for population-scale genetics, variant screening, pharmacogenomics studies, and precision medicine research. This version of the chip has around 650,000 SNPs suitable for both ancestry and health testing.
Keep in mind that 23andme includes a list of their own unique features to the standard GSA chip.
According to Illumina, the GSA covers a multi-ethnic, genome wide markers with curated clinical research variants and markers that serve as quality control for precision medicine research. The content has been selected for high imputation accuracy specifically to the minor allele frequencies above 1%. All the 26 1000 Genomes Project populations have been considered. The balance between the health and ancestry markers is evident in that, variants with established associations with diseases, pharmacogenomic relevance have been included. The content is curated based on ClinVar, National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), PharmGKB, Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAc Database). In-built quality control markers enable sample identification for applications in large scale genomics and screening, which is very useful for companies with a huge customer demand like 23andMe.
The Illumina Omniexpress chip, is the current chip version for other popular companies like Ancestry DNA and Family Tree DNA. However given the demand for third party re-analysis from companies like Xcode Life, and GSA’s compatibility with these tools, all other ancestry companies are likely to migrate to this version. While the OmniExpress chip was satisfactory for the European populations, it could not be applied to the other populations. The GSA is more inclusive of other world populations.
Because there are so few overlapping markers between the GSA and the OmniExpress this change will also present problems for companies and third-party websites that accept autosomal DNA transfers. A choice will need to be made as to whether to do comparisons using only the overlapping markers or whether to experiment with imputation. Xcode’s platform caters to all major genotyping platforms across the ancestry DNA testing companies.
Those of you who purchased the 23andMe kit after August 2017, will have reports based on Illumina’s latest v5 chip. Given that this chip is the most conducive with health-related traits, let’s take a look at a list of all traits that you can do from the raw data file:
| CHIP | NAME | NO. OF SNPs | Applications |
| 23andMe | Major categories | ||
| v1 | HumanHap550+ | 576,000 |
|
| v2 | HumanHap550+ | 597,000 | |
| v3 | HumanOmniExpress+ | 992,000 | |
| v4 | HTS iSelect HD | 611,000 | |
| v5* | Global Screening Array (GSA) | ~650,000 | |
| Ancestry DNA | |||
| v1 | OmniExpress Genotyping BeadChip | 701,400 | |
| v2* | OmniExpress Plus Genotyping BeadChip | 669,000 | |
| Family Tree DNA | |||
| - | OmniExpress microarray chip | 696,800** | |
| Living DNA | |||
| - | Global Screening Array (GSA) | ~650,000 | |
| MyHeritage | |||
| - | OmniExpress microarray chip | 696,800** | |
*current chip
**Only for autosomal and the X chromosome
A haplogroup is a global extension of your family. Depending on the sequence of genetic markers that they carry in their cells people can be grouped into specific ancestry DNA haplogroups. A group of individuals belonging to the same haplogroup can trace their roots back to a common ancestor. This usually also points to a specific geographical point since each haplogroup has a definite migratory pattern. If you want to know more about the science behind these ancestry DNA haplogroups, you can refer here
Besides their common geography and migratory pattern haplogroups are characterized by a de novo mutation. These mutations are carried and undergo vertical transmission through subsequent generations. When sufficient number of people carry this single base change in their DNA sequence they will together form a haplogroup. Needless to say that it takes thousands for sufficient individuals to carry the mutation (now called polymorphism) and form a haplogroup.
Haplogroups are not permanent. They have in the past phased-out and formed new ones. Though some of them have successfully sustained themselves to the present day. Nearly 50% of all Europeans have the haplogroup H. This means that they have all descended from a single person who had lived thousands of years back.
The head of the maternal or paternal haplogroup within whom the set of gene variation first occurred.
New haplogroups are formed when a gene mutation occurs in someone from a particular ancestral clan. However, it is not before many generations that enough people carry the mutation for it to spread, become prevalent to be considered as a haplogroup. Any haplogroups that start forming today will not be recognized as new ones for centuries, or even millennia. The haplogroups that form today will eventually be able to be traced back to the earliest known person to carry the mutation, just as today’s known haplogroups can be traced back to the earliest known person to carry it in the distant past.
Everyone inherits the DNA within a cell organelle called the mitochondria from the mother only. Hence maternal haplogroups are defined using variants in an individual’s mitochondrial DNA. Another interesting fact about the mitochondrial DNA is that it does not undergo the process of recombination with other types of DNA (like your nuclear DNA). This means it is inherited as it is with limited changes directly from you mother. Therefore individuals with the same maternal line will share the same maternal haplogroup. Each maternal haplogroup traces back to a single mutation at a specific location and time.
Y chromosome is found exclusively in males (with the exception of individuals with Klinefelter’s syndrome). The Y chromosome undergoes genetic recombination with the X chromosome at a specific region called the pseudoautosomal region. In other words, this region of the Y chromosome behaves like an autosome in spite of being a sex chromosome. However this a very small fraction. Around 95% of the Y chromosome remains unchanged across generations. This is used to trace your paternal ancestry. Though females do not have a Y chromosome, they would share the same paternal haplogroup with another male member of the direct line (e.g father, brother).
There are many of you out there who uploaded your raw data to Promethease expecting to learn some insights on your health. As the name implies, the simplified Promethease report is a simplified version of your Promethease report.
The simplified Promethease report sources content from your Promethease report and organizes it in a topical, concise, easily readable and printable table format. [/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]In the Simplified Promethease report, all health category-related information is organized into a printable table.
The Simplified Promethease report has information from your Promethease report organized in the following topics.
Over the years, we have had several requests from our customers asking if we can re-interpret the Promethease report for them. The Promethease report is full of technical information that is difficult to interpret by non technical folks. We have taken this feedback and addressed this issue. The simplified Promethease report is topically organized, concise - giving you the most relevant information, and presented in a printable format.
You can receive your Simplified Promethease report by uploading your Promethease report to Xcode.Life website. Please select “Simplified Promethease” as the product option.
We have temporarily discontinued this report.
