Reports
Health
Wellness
Our affinity for alcohol is not new; in fact, we developed it ten million years ago, even before we evolved into humans! The natural source of alcohol is fruits, with usually less than 1% of ethanol in ripe fruits and up to 8% in overripe fruits. The presence of alcohol was beneficial both for our primate ancestors as well as the plants that bore the fruits. The strong smell of alcohol traveled far and wide, attracting primates. This helped primates reach food sources while they helped the plants by dispersing the seeds. Alcohol was considered highly beneficial when fruits were its major source. In the present time, where alcoholic drinks are available in large quantities and are consumed in higher concentrations, they tend to do more harm than good.
The consumption of alcohol in some individuals causes blotches of erythema on their face and neck region, and sometimes on the entire body. Such an event is called an alcohol flush reaction.
Most of the time, it happens as a result of improper digestion of alcohol.
Accumulation of acetaldehyde in the body after alcohol consumption leads to this reaction.
When you consume alcohol, it gets metabolized to its byproduct acetaldehyde.
In typical cases, acetaldehyde gets metabolized further.
An enzyme called aldehyde dehydrogenase, coded by the gene ALDH2, is responsible for this metabolism.
However, some individuals have a defective gene that prevents the further metabolism of acetaldehyde.
This causes its accumulation in the body resulting in an alcohol flush reaction.
There are two types of enzymes responsible for the breakdown of alcohol: alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase. Acetate is synthesized with the help of aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH), mostly by ALDH2, a mitochondrial enzyme, but also by ALDH1, the cytosolic enzyme.
There are five different types of ADH enzymes based on structural similarity and kinetic properties.
Class I enzymes: The class I enzymes are coded by the ADH1A, ADH1B, and ADH1C genes, which are associated with about 70% of the total ethanol oxidizing capacity.
II: The class II enzymes are coded by the ADH4 gene, which is associated with about 30% ethanol oxidizing capacity.
III: The class III enzymes are coded by the ADH5 gene and is the only class of enzyme that is detected in the brain.
IV: The class IV enzymes are coded by the ADH7 gene and are found mainly in the upper digestive tract, where it oxidizes ethanol at high concentrations.
V: The class V enzymes coded ADH6 gene are found in a variety of substrates, including retinol but are less efficient in ethanol metabolism.
People of Asian descent, especially the East Asian descent, are more susceptible to have an alcohol flush reaction.
In fact, this red face phenomenon is also called the "Asian flush or "Asian glow."
According to some studies, over 70% of East Asians have genetic polymorphisms in either ADH or ALDH2, leading to intense flushing with ethanol consumption.
Other than the primary flushing red face, the other symptoms include:
While the flushing by itself may not to be dangerous, the reaction may have other health-related implications.
A 2013 study reported that people who experience an alcohol flush reaction on drinking might have a higher chance of developing hypertension, or high blood pressure.
Another study done on East Asian men in 2017 found an association between high risk of cancer, especially esophageal cancer, and flushing reaction.
This can be due to the high levels of acetaldehyde, which can trigger the growth of cancer cells.
When you report with suspected alcohol flush reaction, your doctor may first perform a physical examination. Other confirmatory tests also help with the diagnosis.
Skin test
It detects your allergy, if any, to a substance in alcoholic beverages such as grains like maize, rye, and wheat.
A little amount of the substance is injected into your skin, and the reaction is studied. If the skin appears red and raised, you are noted positive for the test.
Blood test
A blood test is done to detect the presence of antibodies like IgE that are found in the blood when there is an allergic reaction to a substance in alcohol.
Enzyme test
Measuring the amount of alcohol metabolizing enzymes, alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, can predict the intensity of reaction that one may experience.
Genetic test
The gene responsible for acetaldehyde metabolism in the body is ALDH2 that produces the enzyme ALDH2 or Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2.
Individuals who suffer from an alcohol flush reaction may have a faulty or deficient ALDH2 gene, and this can be identified using genetic testing.
There is no definitive treatment for the root cause of this reaction, ALDH2 deficiency.
However, there are options when it comes to managing the symptoms.
The only foolproof way to prevent this reaction is to avoid or limit your alcohol intake.
A lot of people tend to use OTC antihistamines to manage the reaction, but this is strongly not advisable.
The first and foremost step is to recognize your risk for this condition by studying your ALDH2 gene variants.
Check your 23andMe raw data or your Ancestry DNA raw data to find out the variant you carry
[table “77” not found /]According to the variant you carry, you might need to limit or discontinue alcohol consumption.
Alcohol irritates the gastric lining.
When you drink alcohol, even a small quantity of it, it causes your stomach to produce acid.
Consumption of excess alcohol leads to increased production of stomach acid, which can lead to gastritis.
In many cases, due to excess alcohol, it triggers pain in the stomach, causes diarrhea, vomiting, and even bleeding.
Alcohol affects almost all parts of our body.
Consumption of excess alcohol affects the part of the brain that controls hearing.
In fact, alcohol consumption affects ears and hearing in more than one way.
When we drink alcohol, it also gets absorbed in the fluid of our ears and causes a burning sensation.
Alcohol causes hot flashes in women, especially those going through menopause.
Having even a few sips of alcohol can make you feel warmer.
This is because alcohol makes the blood vessels underneath your skin dilate and increases the blood flow in them, which can induce the 'warm feeling.'
But in reality, alcohol reduces your core temperature.
Reducing alcohol consumption can immensely improve your health. Here is a list of a few things you can do to help you reduce drinking:
Upload the file to Xcode Life to get insights into 700+health-related traits!
Updated 05 May 2020
Nutrition can be defined as the process of providing or supplying the food required for health and growth.
It is also the branch of science and human medicine which deals with the practice of consuming and utilizing foods.
Moreover, a nutritious diet helps to strengthen the body's immunity.
The three main types of heterotrophic nutrition are:
There are seven essential macronutrients and micronutrients that our body requires every day, that include:
Handpicked article for you: 15 Amazing Facts on How Genes Affect Your Diet & Nutrition
Nutrition is vital for an individual's health and can make you maintain a healthy weight and reduce your risks of chronic health conditions.
It is estimated that about one-third of adults in the U.S are obese and approximately 17% of children and adolescents are obese.
Even for individuals of healthy weight, a poor diet can lead to health risks such as hypertension, heart diseases, diabetes, osteoporosis, cancer, etc.
Healthy eating will help you to get the required body nutrients.
Good nutrition: the key to good mental and physical health is consuming a balanced diet; eating the right food at the right time.
You have to eat a combination of foods from different food groups to meet your constitutional requirements every day.
A healthy diet consists of foods from each group taken in a recommended amount, with foods low in sugars and fat and low in sodium.
The basic principles of nutrition are:
The nutritional requirement for an average human being includes the following:
The benefits of good nutrition include the following:
Poor nutrition can affect an individual's natural health and wellbeing.
It can impair an individual's ability to lead an active and enjoyable life.
Precisely, improper nutrition can lead to stress, make you tired and reduce your capacity for chores and over time, it can lead to increased risk of diseases and health conditions like:
Handpicked article for you: Worrier Or Warrior? Analyze Your DNA Raw Data For COMT – The Warrior Gene
Needless to say, the brain is an essential body organ, and its primary function is to instruct other organs to perform each of their tasks.
Hence it is essential to keep the brain working in its optimal condition by consuming a healthy diet.
Certain foods can affect your brain and impact your memory, mood and increase your risk for certain conditions.
This can be easily prevented by avoiding those negative-impacting foods from your diet.
Recommended article: Why most things you know about nutrition and weight loss are plain wrong!
The signs that your body is getting adequate nutrition include:
A healthy diet includes the following:
Children (2-8 yrs old) 1400-2000 calories per day; Adolescent girls & women- 2200 calories per day; Adolescent boys & men- about 3000 calories per day
Here is a list of vitamins that your body require:
There are nine water-soluble vitamins and four fat-soluble vitamins, that includes:
It is mportant for cellular growth & development.
Sources: Dairy products, Fish, egg yolk, etc.
Essential for maintaining a healthy metabolism.
Sources: Cereals, grains, seeds, nuts, legumes, pork, etc.
It is an essential element for energy metabolism, adrenal function, proper vision, and healthy skin.
Sources: Dairy products, cereals, grains, lean meat, poultry, etc.
It is mportant for healthy growth and energy metabolism.
Sources: Seafood, milk, eggs, legumes, poultry, etc.
It Serves various bodily functions, fat metabolism and normalizes blood sugar.
Sources: Broccoli, avocado, eggs, milk, poultry, legumes, lentils, etc
It aids in the production of happy hormones- serotonin, dopamine, and melatonin.
Sources: Nuts, meat, Banana, poultry, Avocado, legumes, whole grains, etc.
It is essential for a healthy metabolism.
Sources: Whole grains, nuts, yeast, soybeans, egg yolks, etc.
It is required for the synthesis of DNA, RNA, RBCs and is very important for pregnant women since it helps prevent birth defects.
Sources: Liver, yeast, green leafy vegetables, avocados, legumes, asparagus, etc.
It is essential for the production of myelin for nerve fibers, DNA, RNA, and RBCs.
Sources: All animal products.
It helps to strengthen your blood vessel walls, promotes wound healing, iron absorption, prevents atherosclerosis, aids immunity and acts as an antioxidant.
Sources: Citrus fruits, melons, berries, peppers, broccoli, potatoes, etc.
The sunshine vitamin helps calcium absorption, maintains and builds healthy teeth and bones.
Sources: Milk, Butter, egg yolks, fatty fish, etc.
It guards fatty acids maintain RBCs and muscles and is an important antioxidant.
Sources: Eggs, margarine, mayonnaise, nuts, seeds, cereals, etc.
It helps in blood clotting.
Sources: Spinach, broccoli, green leafy vegetables, Cabbage, Cauliflower, cereals, fish, liver, beef, eggs, etc.
Per FSC (Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code), the ideal diet for an average adult includes:
Note: This is just a guide, but an individual’s intake may vary depending on their lifestyle and energy needs.
A food that has the right amount of proteins, essential fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals is called complete food.
Restricting yourself to one meal per day may have long-term adverse effects.
Some of the signs of nutritional deficiencies have been listed below:
Processed foods are harmful as they contribute majorly to obesity and health conditions globally.
Here are some reasons to justify this:
Vitamin supplements are not required for everyone, as long as you can obtain all the essential nutrients from a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
Some people opt to take vitamin supplements, but long-term administration could be harmful.
The Department of Health recommends specific supplements for a particular group of individuals who might be at risk of deficiency, as described below:
DRV is a system of nutritional requirements system followed by the United Kingdom Department of Health and the European Union’s Food Safety Authority.
The DRV system is of three types:
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends not more than 10% of an adult’s calories, i.e., less than 5% of added sugars, that too from natural sugars from honey, syrups and fruit juices.
According to this, the daily sugar limit is up to 6 tsp (for women) and up to 9 tsp (for men).
The National surveillance system is an approach that helps detect malnutrition and identifies populations who might be at risk of malnourishment.
Their report emphasizes the information, description, and methods used for monitoring nutrition in 16 different developing countries throughout the world.
The National Nutrition Monitoring & Related Research Act (1990) was enacted to establish a comprehensive, coordinated program and related research to help improve health assessment and nutrition of the U.S population.
Per the act,
A program is required to achieve coordination of federal nutrition monitoring efforts within a decade and assist state and local governments in participating in a nutrition monitoring network.
An inter-agency board is necessary for developing & implementing the program.
An advisory council required to offer scientific and technical advice and evaluate program effectiveness.
The Dr. Rhonda Patrick diet covers the following core diet strategies:
Apart from these diet strategies, she makes sure that she also includes all the essential vitamins and minerals required for optimal health.
Xcode Life’s Nutrition Report provides information on openness, extraversion ness, intelligence, entrepreneurship potential, and more than 25 such traits.
Lactose intolerance, aka lactase deficiency, the most common digestive problem, is a person’s ability to digest a natural sugar ‘lactose.’ Lactose sugar is broken down by an enzyme, lactase, that is produced in the small intestine. When there is a deficiency in this enzyme, the undigested lactose moves into the large intestine, and the bacteria present there interacts with the unprocessed lactose sugar and causes bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
WATCH: The Genetics Behind Lactose Intolerance
There are four types of lactose intolerance with a different cause for each class.
The most common form that makes one’s body to prevent secreting lactase enzyme by about age 5 (as early as two years old in the case of African-Americans).
Since lactase levels decrease, dairy products get challenging to break down.
Individuals with primary lactose intolerance secrete decidedly fewer amounts of lactase enzyme, and that makes it hard for them to digest dairy products by the time they turn adults.
This type is genetic and is common among Africans, Asians, Hispanics, Mediterranean and southern Europeans and less common among north or western Europeans.
It occurs due to any illness or injuries or post surgeries.
Any such conditions might affect your small intestine and lead to a reduction in lactase secretion.
Celiac disease and Crohn’s disease are the two most common intestinal diseases linked to low lactase secretion.
It occurs in premature babies. It usually lasts only for a short duration after birth and goes away on its own.
A rare type that happens when there is no lactase or a minimal amount of the enzyme produced by the small intestine right from birth.
It is a genetic disorder, and both parents have to pass the condition to their children.
Typical lactose tolerance symptoms include the following, and are exhibited about 30 minutes to two hours after having any milk-based food item:
However, if you experience symptoms such as hives or wheezing immediately after having milk, it is probably a milk allergy that you are suffering and not lactose intolerance.
To manage your symptoms, you may need to reduce the amount of lactose consumption. Most people with lactose intolerance can have some lactose without getting symptoms.
Lactose intolerance symptoms begin about 30 minutes to 2 hours after consuming lactose-containing foods.
The symptoms persist until your body manages to eliminate the lactose fully.
For some individuals, it could be about 12 hours while for others it could be much longer.
Your body will have to force the undigested dairy substance through your system and in that process, you might experience pain and discomfort.
Digestive system transit time (the time is taken to digest and eliminate any substance) can be tracked by using enough activated charcoal capsules appropriate for your weight.
The diet recommendation for lactose intolerance depends on the severity of the condition.
People with a mild case can have up to 12 grams of lactose without experiencing symptoms or maybe a few mild symptoms.
Consuming lactase products along with these can aid the digestion of lactose.
If your symptoms are severe, it is better to completely refrain from lactose-containing foods like:
Read the label carefully to see if there is any dairy or lactose-present items on the ingredient list (Whey, Curd or Yogurt, Dry milk solids, milk powder).
Handpicked article for you: Worrier Or Warrior? Analyze Your DNA Raw Data For COMT – The Warrior Gene
The primary test that your physician may ask you to take up is abstaining from dairy products and check to see if the symptoms subside.
Your stool samples can also help in making the diagnosis- a watery, loose, or foamy stool can indicate that you are lactose intolerant.
However, to confirm the diagnosis, the following tests are mostly used:
Yes, you can do this simple test for lactose intolerance at home:
Studying the mutations- C/T-13910 and G/A-22018 located upstream the gene that codes for the enzyme lactase-phlorizin hydrolase can be a useful tool to diagnose hypolactasia (The condition causing Lactose malabsorption).
Primary lactase deficiency, which is the most common cause of lactose intolerance throughout the world, is caused by an inherited genetic fault running in families.
Congenital lactase deficiency or congenital alactasia is the disorder where infants suffer from not being able to digest the lactose present in breast milk or formula, causing diarrhea.
Such infants might even develop dehydration and weight loss if they do not switch to lactose-free infant formula.
Congenital lactase deficiency in infants is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern (Both copies of the LCT gene in each cell is mutated).
The parents being individuals with the autosomal recessive condition, each carry one copy of the mutated gene, and may not experience any symptoms. However, when they both pass on the defective genes (25% chances), the infant could, as a result, be intolerant to lactose.
The type of variations in the regulatory element in the MCM6 gene inherited from one’s parents decides the ability to digest lactose in adulthood.
One copy of the altered regulatory element is enough to sustain lactase production.
Individuals who haven’t inherited such variations from either parent will have a certain degree of lactose intolerance.
Hand-Picked article for you: Have Your 23andMe Raw Data? Use It To Get 500+ Health-Related Genetic Traits!
Some cheese like cheddar and parmesan, probiotic yogurts, heavy creams have low lactose levels and can be added to your diet in minimal amounts.
When you are digesting other foods simultaneously, gastric emptying can get slower, and lactose, which makes up just a small proportion of the total food may not create many problems.
The bacteria present in yogurt and kefir can produce a lactase-like enzyme which can make your food to digest even though it contains lactose.
Lactase supplements allow the breakdown lactose into glucose and galactose so that your body can absorb the sugars without experiencing symptoms
Except for sporadic cases, every infant can produce lactase enzymes which helps the small intestine digest the lactose sugar.
But with age, one’s lactase levels can start to decline, and it can prevent the lactose you eat from going to your colon without being digested.
The bacteria there might break down the sugar and cause flatulence and fluid in that process.
It is quite common for people to develop lactase deficiency in adulthood.
Per the NIH report, about 65% of the global population has a lowered ability to digest lactose after infancy.
The genetic factors can be equally responsible for lactose intolerance.
Your body tends to secrete the enzyme lactase only when instructed to do so by the gene LCT which can get less active over time and result in lactose intolerance.
The condition which can begin as soon as a person turns two years old, may not manifest itself until a person reaches adolescence or adulthood.
The ideal diet for the lactose intolerance emphasizes on the foods to avoid more than about what to eat.
Needless to say, it is essential to avoid or reduce the amount of lactose-containing foods.
But, it is also important to read food labels to exclude canned, boxed, frozen, and prepared foods like bread, lunch meats, salad dressings, cake, cookie or pancake mixes, coffee creamers, etc., that contain lactose ingredients (like cream, cheese, butter, milk, milk solids, dried milk, whey, etc).
Excluding dairy from your diet can make you more prone to vitamin D and calcium deficiency.
Some calcium-rich, dairy-free foods include:
Vitamin D and calcium supplements can also be consumed upon your physician's advice.
Dietary fats are important for energy and for cellular growth, however, the type of fat consumed is key.
One of the popular ‘dietary advice’ is that saturated oils are bad for health and that they should be substituted instead by polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
However, this may not be true for everyone.
Every once in a while, there comes a new study that purports to debunk long-held beliefs, such as the one above.
How we respond to sunflower oil in our diet may depend on the genetic variants we carry.
Does that mean sunflower oil may be bad oil for some?
More about sunflower oil
Sunflower oil is made from sunflower seeds and has has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol and constipation.
Its benefits have, however, been more as a massage oil for helping the skin heal wounds, for psoriasis and for arthritis.
The current scientific study by The University of Finland focuses on the effect of using sunflower oil as cooking oil, stratifying the effects based on FADS1 gene variants.
FADS1 gene
FADS1 gene is associated with fatty acid metabolism and also in glucose metabolism.
The diet of an individual plays an important role in the concentration of the various fatty acids in the body.
Linoleic acid is the most common polyunsaturated fatty acid is found in plant-based oils, nuts, and seeds.
You may have come across studies that have shown how a high intake of linoleic acid helped in lowering risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes while another study may have pointed out its association with risk of low-grade inflammation.
This study helps shed new light by stating that these contradictions may be due to genetic differences.
This study opted for a unique yet preferable research setting, where the study participants were stratified based on their genotypes i.e based on their FADS1 gene variant.
This was done to find out if there was an association between FADS1 gene variant and the effect of linoleic acid on fasting glucose, on serum fatty acid composition, on C- reactive protein (CRP- a biomarker for inflammation) and insulin levels.
1,300 middle-aged men were included in the study that studied the metabolic effects, while 60 participants were included in the study on the effect of a diet based on genotype.
The participants consumed 30-50 ml of sunflower oil (linoleic acid) every day for four weeks.
The study found that the effects of linoleic acid were significantly associated with FADS1 gene variant.
This would mean that your genetic variant could determine if the linoleic acid supplement could effectively lower your fasting glucose levels and if increased intake of linoleic acid would increase or decrease your CRP levels.
Hand-Picked article for you: Have Your 23andMe Raw Data? Use It To Get 500+ Health-Realted Genetic Traits!
Knockdown mice study
One of the ways scientists determine the effect of a gene on health is to reduce the expression of the gene from mice and then study the effect that it causes.
Mice which had the FADS1 gene expression reduced were given a diet rich in linoleic acid and they showed better glucose metabolism but they also exhibited hepatic inflammation.
This confirms the results of the sunflower oil study.
What does all this mean to you?
If you have the CC genotype, a high intake of sunflower oil may lower fasting glucose levels.
However, there is an association with higher CRP (biomarker or inflammation) on high sunflower oil intake, which could mean that you run the risk of low-grade inflammation.
Low-grade inflammation is an important factor in progression to chronic diseases. Therefore, limiting sunflower oil may be better, based on this study.
If you have the TT genotype, a high intake of sunflower oil is not associated with a risk of inflammation.
Therefore, based on this study, you could switch to sunflower oil or continue to include it in your diet, if you are already doing so!
However, please note that Omega 6 which is predominantly found in vegetable and seed oils needs to be balanced with Omega 3 intake, with an optimal ratio between omega 3: omega 6 being around 1:2.
If you have the CT genotype, a high intake of sunflower oil is not associated with a risk of inflammation.
Therefore, based on this study, you could switch to sunflower oil or continue to include it in your diet, if you are already doing so!
However, please note that Omega 6 which is predominantly found in vegetable and seed oils needs to be balanced with Omega 3 intake, with an optimal ratio between omega 3: omega 6 being around 1:2.
Wondering if sunflower oil (PUFA) could increase your risk of weight gain?
Find out from Xcode Life nutrition genetics report, which analyses your genetic variants for response to macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, saturated fats, MUFA and PUFA in the perspective of weight gain.
There are more than 30 traits covered in the report including gluten sensitivity, a risk for alcohol flush, food preference and more.
Does your extra weight keep finding you over and over again, no matter how much effort you put in? Your genes may have an answer for it. Read on to learn how you can optimize your weight loss routine with the help of your knowledge of your genetic make-up.
Despite trying out the innumerable approaches for weight loss, most of you have been failing at it terribly and repeatedly.
The conventional fitness and nutrition advice would not work for everyone. Each person’s gene sequence, microbiome, environment, and lifestyle vary, and this impacts the dietary requirements and exercise habits.
Genetic testing may reveal as to why your efforts to lose weight has been failing you.
Genetic factors influence how your body processes certain nutrients. This may have a direct or indirect effect on weight loss or weight gain.
For instance, the gene “Apolipoprotein A2” (APOA2) is involved in the production of a particular protein which affects how your body responds to saturated fats.
If you happen to be one who possesses a variant of this particular gene, no matter how much you control your calorie-intake, you could still be gaining weight.
Yet, if you cut down saturated fat from your diet, weight loss may just as well be a cake walk!
It may not always be this straightforward. It is important to note that, there are other genes, variables and lifestyle habits that impact your weight.
While genetic testing may not have answers to all your questions, it can serve as guide for outlining a diet plan that is based on results as opposed to generic cookie-cutter plans.
Handpicked article for you: Is Dr. Rhonda Patrick Diet For You? Analyze Your DNA Raw Data To Find Out Your Nutritional Needs!
The ancestry genetic testing company 23andMe had launched a study in December 2017 involving 100,000 individuals to learn about the genetic variants associated with weight loss, and the effectiveness of various dietary approaches or exercises for weight loss.
The Weight Loss Intervention Study sought to identify why each person responds differently to exercise and diet.
This study focuses on behavioral weight loss, and builds on the work that went into the company’s Genetic weight report.
23andMe holds DNA data of over three million participants who sent their saliva samples, making it one of the largest DNA databases in the world.
Confused about which report to get? Use our Report Finder and find your reports of interest
Once the DNA sample is analyzed, the participants would receive a report that emphasizes the following predictions:
The researchers would send out weekly emails to guide the participants through the study, give them weight loss advice, meal suggestions, and other updates from the researcher forums.
In another effort to encourage individuals to use genetic information in the quest for weight loss, 23andMe had announced a partnership with Lark Health.
Lark Health is an Artificial Intelligence (AI) coaching service that delivers personalized weight loss advice, and tips for diabetes prevention via their app.
This collaboration enabled customers to include weight-related genetic data provided by the former into the latter’s services.
With an interest in turning its reports into actionable advice, 23andMe debates that it is simply used the data to make an already renowned and effective service, smarter.
The consumers can simply message their AI coach to find out if a particular food was a good choice for them.
According to Anne Wojcicki, CEO and co-founder of 23andMe, “Access to your genetic information is really just the beginning — using that information to prevent serious health consequences is the next critical step”.
Here’s a list of what this collaboration provides:
A popular personalized health & wellbeing company that uses swab samples or your DNA raw data from 23andMe to provide personalized diet and fitness insights and counseling.
DNAFit was founded in 2013, they have been exploring how DNA affects an individual’s response to nutrition and exercise changes.
DNAFit has recently joined the ‘Prenetics’ group- a Southeast Asian-based global leader in genetic testing and digital health.
The company interprets DNA, genetic traits and environmental data to offer actionable and interactive advice for health and fitness.
They combine a customer’s fitness goals with his/her DNA reports to create personalized recommendations.
Pathway Genomics focuses on providing users with personalized healthcare information delivered to any device.
Their app OME™ combines an individual’s personal health and wellness feedback with machine-based deep learning, and data science to provide tailored and actionable recommendations for physical well-being.
The personalized genomics company that specializes in preventative healthcare offering Nutrigenetics (the interaction between nutrition and a person’s own genetics), Fitness Genetics and Health Genetic and many more, tests to enable users to adapt to preventive and proactive health practices.
Xcode Life analyzes the two most important lifestyle factors that help in weight loss- Nutrition and Fitness.
Read more: Which are the top 10 best DNA raw data analysis tools?
The report includes more than 33+ categories of traits such which fall under broader categories such as certain behavioral tendencies, one’s genetic metabolism of macronutrients, one’s micronutrient requirement and food Sensitivities.
While macronutrients are the type of food that we require in large amounts in our diet such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc, micronutrients are those essential elements of life required in smaller quantities such as Vitamins, Copper, Zinc, etc.
In addition to the common medical problems associated with deficiencies of vitamins and minerals, it can also cause weight gain.
Micronutrient deficiency can slow one’s metabolism and increase one’s cravings for certain foods that can be high-calorie ones and thereby cause weight gain.
Also, micronutrient deficiencies can cause fatigue– that result in reduced fitness activities and thereby causing weight gain.
People of a particular genetic type tend to need more of a particular micronutrient and an Xcode Nutrition report finds out the same.
Here’s a list of various micronutrient requirement the report emphasizes:

With the amount of fat loaded into an ice cream, the different flavor options, the ‘melt in your mouth’ texture, and a variety of add-ons like chocolate chips and syrups, there seems no reason why someone would say no.
Even if you're the kind who sticks to a single flavor all the time without a topping, there's so much your genes can tell you, like what flavor you prefer, which topping you're likely to choose because of your genetic tendency to prefer sweet/bitter.
Fun Fact: Approximately 86 percent of Americans eat ice cream at least once a week and the ice cream market is anticipated to reach $10.5 billion by 2021.
Two studies conducted by 23andMe researchers looked at preference for an ice cream flavor and the associated genetic variants. When the participants were split into two groups based on their preference (chocolate or vanilla), they identified close to 740 genetic markers that were different between the two groups. This means, these markers play a role in influencing your choice of ice-cream. Some of these markers were located near genes that rule your sense of smell and taste.
What the studies also showed is how the senses of smell and taste are closely interlinked by the genes you carry. (Ever heard of the idiom, taste with your nose?) One good example is, if your genes predispose you to bitter taste, you're more likely to choose dark chocolate than the plain ol' vanilla.
Also important for flavor preference is the receptors present in the nose and tongue that are encoded by the genes you carry. Some variants of these genes prefer one odor over the other in the nose, and one taste over the other in the tongue. The signals from both these sets of receptors are important for determining taste. Similar genetic variants were identified in another similar study on preference for vanilla, chocolate or strawberry.
A world-wide survey conducted showed that vanilla still stands at number one as the most popular ice cream flavor, closely followed by chocolate in the second place. Other flavors like strawberry, mint chocolate chip, and cookies N’ cream also made the list. Another study conducted by the 23andMe research team showed the women generally prefer chocolate over vanilla, while favor both (52% vanilla and 48% chocolate).
Upload your DNA raw data to Xcode Life to get insights into 700+ health-related traits! Our Gene Nutrition Report covers over 33 categories such as the tendency to prefer sweet foods, fatty foods, bitter or salty foods, and tendency to gain weight among many others.
Would you like a cup of tea or coffee? This is probably the most asked question at ‘tea time’, however, the answer to that could lie, in part, in our genes. Scientists from The Northwestern University carried out a study that showed that genetic predisposition to bitter taste perception may play a role in whether we prefer tea or coffee.
The study was published in the Journal Scientific reports and included data from over 400,000 UK adults of largely European ancestry between the ages of 37 and 73 years. The study highlighted that people with certain receptors for the bitter taste of coffee were less likely to drink tea and more likely to drink more than four cups of coffee.
There were three variants in genes that were studied by the researchers. One was associated with perception of bitterness of caffeine, of quinine (found in both tea and coffee) and in the synthetic molecule propylthiouracil (PROP).
Do you prefer coffee? The study showed that individuals who had increased sensitivity to quinine and PROP, as identified by their genetic variants, were less likely to prefer coffee. In short, the genes that increased sensitivity to bitter taste in cruciferous vegetables like brussels sprouts, were also less likely to drink coffee. Such people preferred tea to coffee.
Coffee drinkers had an increased sensitivity to the bitterness of caffeine.
This brings us to the question, how do some people with increased sensitivity to another bitter taste, caffeine, prefer coffee? Shouldn’t they be put off by the taste of caffeine? The study researchers believe that people probably associate caffeine with the ‘buzz’ that they get from coffee. The psychostimulant effect of caffeine helps coffee lovers associate caffeine with the ‘good things’. The ability to taste caffeine better makes them drink more than 4 cups of coffee everyday or places them at 20% higher risk of becoming heavy drinkers.
Another takeaway from this study is that people who have increased sensitivity to bitter taste PROP are less likely to prefer coffee and more likely to prefer tea. This could be due to the fact that tea has lesser bitter compounds than coffee. So, if coffee is too much to handle, then tea it is.
Low cost of genetic testing has allowed many people to access their genetic data. Though genes are only one part of the puzzle, identifying the genetic predisposition will help in understanding preferences independently of environmental factors.
Genetic variants in MTHFR and vaccines induced reactions have been discussed since the publication of the study titled “Genetic basis for adverse events after smallpox vaccination”, conducted by the Dartmouth Public School. The study was carried out to identify the basis for adverse reactions among certain individuals to vaccines.
 There were two independent studies that were detailed in the study about MTHFR and vaccinations. It was found that study subjects who were vaccinia-naïve subjects developed pock formation at the site of vaccination. A section of the study subjects also developed fever, lymphadenopathy or even rash, prompting the researchers to find out if genetic polymorphisms made them more susceptible to such systemic effects.
There were two independent studies that were detailed in the study about MTHFR and vaccinations. It was found that study subjects who were vaccinia-naïve subjects developed pock formation at the site of vaccination. A section of the study subjects also developed fever, lymphadenopathy or even rash, prompting the researchers to find out if genetic polymorphisms made them more susceptible to such systemic effects.
A single nucleotide polymorphism in MTHFR gene (rs1801133) has been associated with adverse reactions to vaccines, in the study involving small pox virus. This polymorphism leads to a change in amino acid from alanine to valine, affecting both the quality and the quantity of the MTHFR enzyme.
Top 3 Functions of MTHFR enzyme:
Effects of MTHFR Gene Mutations:
MTHFR genetic variation is associated with
The study details that an increase in homocysteine levels, associated with a certain genetic variant of MTHFR, could stimulate an inflammatory response. According to the study, this could lead to the adverse reaction due to the effect of MTHFR and vaccine injection.
An alternate pathway to explain MTHFR gene mutation and vaccines induced side effects is that the rapid proliferation of cells caused by vaccination can increase the need for DNA synthesis. Genetic polymorphism in the MTHFR gene, and thereby the activity of the MTHFR enzyme, may be significantly associated with this process. The study also noted that genetic variation in MTHFR and vaccines induced cardiac events should be evaluated in future research studies.
Though there does not seem to be considerable research associated with MTHFR mutation and vaccines, there is a lot of speculation about the safety of vaccination. This genetic variant in the gene MTHFR has prompted many groups to advocate against vaccination for children. However, we have not found sufficient scientific evidence to support this notion.
Insufficient evidence for MTHFR kids vaccination induced injury
Vaccine injury is one of the major topics of debate and, in the United States, there is an exemption from liability for drug manufacturers as well as for the physician. Though there are severe instances of vaccine injury, which includes permanent disability, an autoimmune condition or even death.
While there is under-reporting of vaccine injury, with symptoms showing up even after a few weeks, there have been very few gene based studies of significance.
Apart from the C677T variant in MTHFR, vaccines induced adverse effects were also found, in the study, to be significantly associated with genetic variants in the following genes
Since smallpox has been eradicated from most parts of the world, the relevance of this study and the genetic basis of MTHFR vaccine injury is questionable.
Apart from this study on small pox vaccine, another study was conducted on MTHFR MMR vaccine. This study conducted in 2014 was aimed at identifying genetic variants among children with MMR associated fever. There are 5 genes which were found to be associated with vaccine injury
Mercury is known to be a potent neurotoxin, however, a study conducted in 2014 showed a potential genetic basis. The study showed an initial association between A1298C (rs1801131) variant of MTHFR and vaccine injury. Another variant associated with variance in response to mercury was identified in PON1 (rs662). However, none of the vaccines currently in use include mercury.
Let’s look at the incidence of occurrence of serious adverse effects of vaccines.
Compare that with the number of people who are homozygous for C677T, the variant under study
Since 40% of the U.S population carries at least one copy of C677T polymorphism, and comparatively, very few people develop adverse effects, testing for MTHFR-vaccine effect is not appropriate, till further validation studies confirm the need for such screening.
Upload your raw data to find your MTHFR variant
MTHFR variants play an important role in the amount of folic acid supplementation required, as well as in the need for detoxification.
MTHFR and detox:
Some people are more susceptible to mold exposure or may require a longer period of detoxification to help their liver recover from all the pollutant exposure, but how do you find out who does? Upload your 23andme raw data or your ancestry DNA raw data to identify the variant present in your genes.
Though this information may not aid in understanding MTHFR and vaccine adverse effect correlation, it will help in identifying the variant carried and steps to align your lifestyle for better health.
References:
Food intolerance or food sensitivity describes the difficulty in digesting certain foods and can lead to unpleasant reactions like intestinal gas, abdominal pain, or diarrhea.
The symptoms of food intolerance appear only after a few hours of consuming the food.
It can be difficult to identify food intolerance as the symptoms are often mistaken for other conditions.
Some common symptoms of food intolerance include:
Food intolerances aren’t life-threatening. However, they can be very problematic for those affected.
Some causes of food intolerance are the absence of certain digestive enzymes (proteins that help with the digestion of food), some chemicals/additives in the food, and toxins.
Common food intolerances seen in people are:
While food intolerance is a problem with digesting food, food allergies are due to our immune system reacting to the food item itself.
Food allergy occurs when the immune system sees a specific component in the consumed food as an “enemy” to the body and sends out a response that results in allergic reactions.
The symptoms of food allergy occur soon after eating the food and are much more severe than those seen in the case of food intolerances.
In rare cases, food allergies can result in a reaction called ‘anaphylaxis’ where your blood pressure drops and your airway narrows down - this can potentially be life-threatening.
Mushrooms are loved worldwide as they contain flavor enhancers and are a gourmet’s delight. This makes them the most popular choice for pizza topping, after pepperoni!
Some nutritional facts about mushrooms
Mushrooms are a “powerhouse of nutrition” and not a white food to be avoided.
Some research studies show that they can be used to lower the risk of diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s.
Also known as SLC22A4, this gene is located on the long arm or the q arm of chromosome 5.
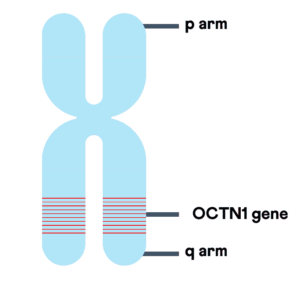
OCTN1 produces a protein that is responsible for the transport of positively charged compounds - in this case, ergothioneine - a substance present at high levels in mushrooms.
A study established an association between the OCTN1 gene and mushroom intolerance risk.
This interaction was observed among patients with Crohn’s disease.
Crohn’s falls under a group of diseases (called the inflammatory bowel diseases) that affect the digestive tract - the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Crohn’s results in the inflammation or swelling of the digestive tract, which can lead to side effects like stomach pain, diarrhea, and weight loss.
rs1050152 of the OCTN1 gene has an association with mushroom intolerance. In a study conducted in the New Zealand population, among the people who were mushroom intolerant, it was found that the T allele of rs1050152 was present in a higher number (in people with and without Crohn’s disease). This suggests that having a T allele in rs1050152 can increase your risk for mushroom intolerance.
rs1050152 was previously found to be associated with a risk for Crohn’s disease.
The shiitake is an edible mushroom native to East Asia. Shiitake mushroom intolerance is one of the most common forms of mushroom intolerance.
The American chemical society in 2005 stated that mushroom contained the highest concentrations of ergothioneine, higher than either of the two dietary sources, wheat germ and chicken liver - which were previously believed to contain the most.
When compared with the other types of mushrooms cultivated in the US, the shiitake variety contained the highest amount of L-ergothioneine, which explains why shiitake mushroom intolerance is more common.
There have been reported instances of people developing sudden mushroom intolerance, without any prior incidents.
This could either be due to the type of mushroom consumed or a mushroom allergy.
The best way to find out is to take up a food intolerance test.
People at high risk for mushroom allergy include:
The best and the only way to avoid mushroom intolerance is to remove mushrooms from the diet completely.
The available study on the reason behind mushroom intolerance identified ergothioneine as the ‘component’ that leads to intolerance. So, it is also important to be wary of foods containing ergothioneine. Foods high in ergothioneine include:
Updated 13th March, 2021
