Reports
Health
Wellness
Autism is a part of a spectrum of disorders and is a complex, life-long developmental condition that affects the brain.
Autism impacts how an individual perceives and socializes with others, often resulting in interaction and communication.
The signs and symptoms of autism usually show up in early infancy or childhood.
Each child with autism shows a unique pattern of symptoms and behavior.
The exact cause of autism is still unknown.
However, studies suggest that genetics and environmental factors can affect one’s risk of developing the condition.
Few risk factors associated with an increased likelihood of one developing autism are:
Studies have also suggested that autism is four times more common in males and females due to genetics.
The effect of genetics on autism has been known since the 1970s. Several studies on twins suggest that autism is inheritable.
Though genetics cannot be solely blamed for autism and ASD, it is a combination of environmental factors that activate the autism gene, resulting in the condition.
For example, environmental factors like exposure to the maternal immune response in the womb or complications at birth may cause autism or intensify its traits.
Abnormal changes in the genes or mutations are known to cause autism. These mutations may be passed directly from the parents or may develop in the individual.
There is no single gene or mutation responsible for autism.
Several genes have been studied concerning autism, including PTEN, ACTL6B, and others.
No single gene can be directly blamed for the development of autism.
In fact, over 100 genes have been studied so far to have strong links to autism and ASD.
Most of these genes are involved in communication between neurons and controlling the expression of other genes.
Several conditions associated with autism arise from mutations in a single gene, including the Fragile X syndrome.
A few autistic individuals show macrocephaly or a larger than normal head for their age.
Extreme macrocephaly in individuals with ASD has been associated with the PTEN or Phosphate and Tensin Homolog gene.
Individuals show overlapping symptoms with PTEN-Hamartoma Tumor Syndromes like polydactyly and pigmented macules on the penis.
The PTEN gene gives instructions for the production of an enzyme that acts as a tumor suppressor (it prevents abnormal and uncontrolled growth and multiplication observed in cancer)
So, autistic individuals with macrocephaly are recommended to undergo PTEN sequencing.
Studies have shown that around 10% to 20% of autistic individuals with macrocephaly show mutations in the PTEN gene.
This gene plays a role in regulating the structure of DNA.
CHD8 is the closest to being an “autism” gene.
It is active both in the brain and in the nerve cells of the gut and contributes to intellectual and gastrointestinal issues in autism.
Prenatal screening of congenital and hereditary conditions is common in most countries worldwide.
Since no single gene is associated with autism, genetic testing for autism and related disorders can be challenging.
However, a few standard genetic tests for syndromes associated with autism, such as the fragile X syndrome, detect if an unborn baby is likely to develop autism in the future.
A new study by Azrieli National Centre for Autism and Neurodevelopmental Research researchers in February 2022 stated that a routine ultrasound might help identify the early signs of ASD.
Genetic Testing For Autism: Use Your DNA Raw Data
Autism is a developmental disorder that affects communication and social interaction.
Some people with autism have difficulty with verbal and nonverbal communication, repetitive behaviors, and interests that are specific to them.
People with autism experience challenges in everyday life, including finding employment, interacting with others, and accessing community resources.
Although a single gene does not cause autism, there is evidence that genetics play a role in the development of the disorder.
Studies have found that people with autism are more likely to have relatives who also have autism and that the risk of developing autism increases with the number of relatives who have the disorder.
It is still unclear why some people develop autism, and others do not, but researchers are exploring all possible causes.
Studies have found that some people with autism have a higher than the average number of genetic markers associated with the disorder.
However, there is still much to learn about the genetics of autism and how it contributes to the development of the disorder.
Studies have shown that autism is predominantly a genetic disorder, with 40-80% heritability.
While researchers are still working to identify all of the genes associated with autism, they do know that some genetic mutations can increase your risk of developing autism.
If you have a family member with autism, you may want to consider talking to your doctor about getting screened for genetic mutations that could put you at higher risk.
Children in families with a history of other mental conditions like ADHD, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder are also at a higher risk for developing autism.
According to an article on Spectrum News, “Children who have a first-degree relative — a sibling or parent — with a brain condition other than autism have up to 4.7 times the odds of having autism and up to 7.6 times the odds of having both autism and intellectual disability.”
In almost 50% of the cases where there’s only one child in the family with autism, the cause appears to be spontaneous mutations.
Spontaneous mutations are genetic mutations that are absent in the parents and siblings of affected children.
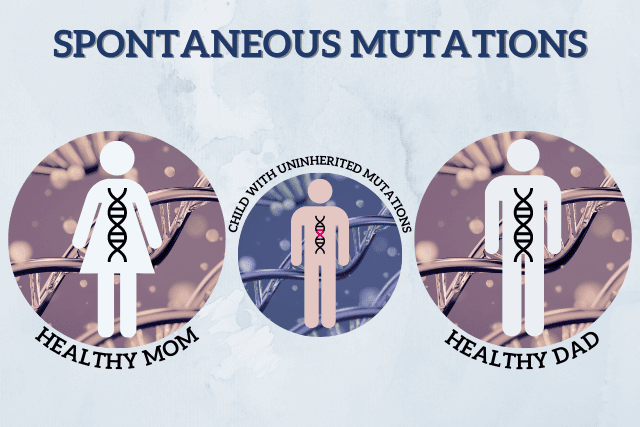
Image: Spontaneous mutations
Researchers have long noted that parents of autistic children display some of the traits seen in their children in a much more muted manner.
A 2020 study examined the role of familial relationships in explaining similarities in behaviors across family members.
The study found a relationship between parents and children's behavioral traits and maternal polygenic scores and broad autism behavior traits in children.
This means that traits in children with autism may take after the mother's subtle autism-like behaviors.
For example, if a mother has issues communicating in a social setting, then her autistic child may have communication difficulties themselves.
On the other hand, a large study based on the analysis of 9,275 whole genomes suggests that some mutations tied to autism may be passed down from fathers.
The study focused on flanking gene regions, where mutations are rarely observed.
The researchers reported that such rare variants are inherited from fathers twice as much compared to mothers.
The protective effect
Studies have revealed that a type of mutation called the copy number variation seen in autism was three times more common in girls than boys.
Another type of mutation called the single base substitution was also a third more common in girls.
But according to the protective effect theory, women appear to have a shielded effect from these genetic mutations but still leave these mutations down to their sons.
They function a lot better than their male counterparts with the same mutations.
Due to its lower prevalence in females, autism was always thought to have a maternal inheritance component.
However, research also suggests that the rarer variants associated with autism are mostly inherited from the father.
Ultimately, autism is a complex condition with 100s of genes involved.
In a child with autism, it is very challenging to tease apart maternal and paternal genetic contributions.
Even without a family history of mental disorders, autism can occur in a child due to spontaneous mutations.
Genetic tests can help understand the risk for autism, explain the possible causes, and shine a light on optimal management and treatment options.
Cacao beans are extensively popular fruit seeds due to their high phenolic and flavanol content. More than 200 chemical compounds (cocoa flavanols) have been identified in cacao beans. Cocoa flavanols offer certain health benefits, such as lowering blood pressure, preventing blood clots, and improving blood flow. A recent study has reported that long-term cocoa flavanol supplementation can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
CVDs are a group of heart and vascular system diseases that results in the narrowing of the blood vessels supplying blood throughout the body. It is one of the prominent causes of death in the United States.
Every year about 1 million Americans die due to cardiovascular problems.
Physical inactivity is one of the prominent reasons which increases the risk of CVDs.
Besides physical inactivity, other risk factors include obesity, smoking, and alcohol intake.
The risk of CVDs can be reduced by making small lifestyle changes.
A healthy diet and exercise regimen is the most effective change for preventing this disease.
Exercise decreases unwanted fat and cholesterol, thereby eliminating the strain on the heart.
A nutritious diet with low sugar content and appropriate servings of fruits, vegetables, eggs, nuts, lean meats, and whole grains can reduce the risk of CVDs.
Recently a study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition reported that long-term consumption of cocoa flavanol could reduce the risk of CVDs.
Nearly 21,442 participants were included in the study and were followed for approximately 3.6 years.
The participants were divided into four groups:
Cardiovascular events refer to conditions including heart attack, stroke, unstable angina, carotid artery disease, and coronary revascularization.
The study bears clinical evidence that cocoa flavanol intervention can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events and deaths due to CVDs.
The study also suggested that the supplementation must be regular and long-term to achieve the extensive health benefits of cocoa flavanol.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520706/
Get Actionable Health Insights From Your 23andMe, AncestryDNA Raw Data!
Our guts host trillions of microbes that play a very important role in our health. From helping with digestion to aiding immune function, gut microbes interact with our body in numerous ways. A recent study on bumblebees has shown that gut bacteria can even affect memory learning. The abundance of a species of Lactobacillus was associated with better memory and learning ability.
Our digestive system has about a hundred trillion bacteria, both good and bad.
The gut bacteria specifically refers to the ones living in your intestines.
Scientists now call gut bacteria the “forgotten organ,” owing to their significant roles in health and diseases.
Some of the good bacteria in our gut include Lactococcus, Lactobacillus, and Bifidobacteria.
They are commonly found in foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, tempeh, kimchi, and miso.
Clostridium perfringens, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus are the bad bacteria that cause diseases like skin infection, cholecystitis, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia.
E.coli is found in foods raw or undercooked ground meat products, raw milk, and fecal contamination of vegetables.
C. perfringens infection include meat, poultry, gravies, and other foods cooked in large batches.
Most frequently implicated in cases of staphylococcal food poisoning are poultry and cooked meat products such as ham or corned beef.
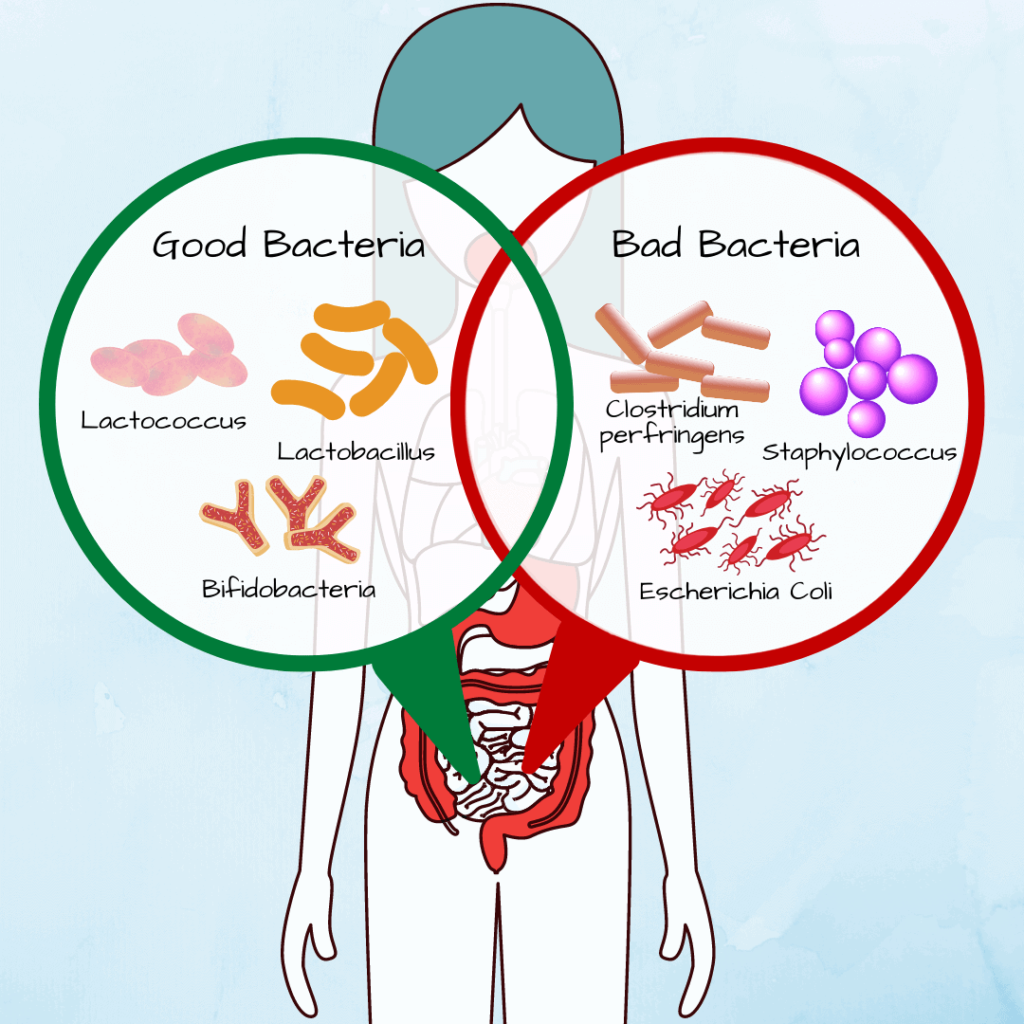
Image: Good and bad bacteria in the gut
Recent research suggests we get exposed to some microbes while inside the womb itself!
In fact, Bifidobacteria grow inside the babies' intestines to allow proper digestion of breast milk.
As we grow, the gut bacteria diversify to adapt to play various roles in the body.
Gut bacteria have been linked to various health conditions like obesity, colon cancer, depression, diabetes, arthritis, and anxiety.
Some important roles played by the gut bacteria
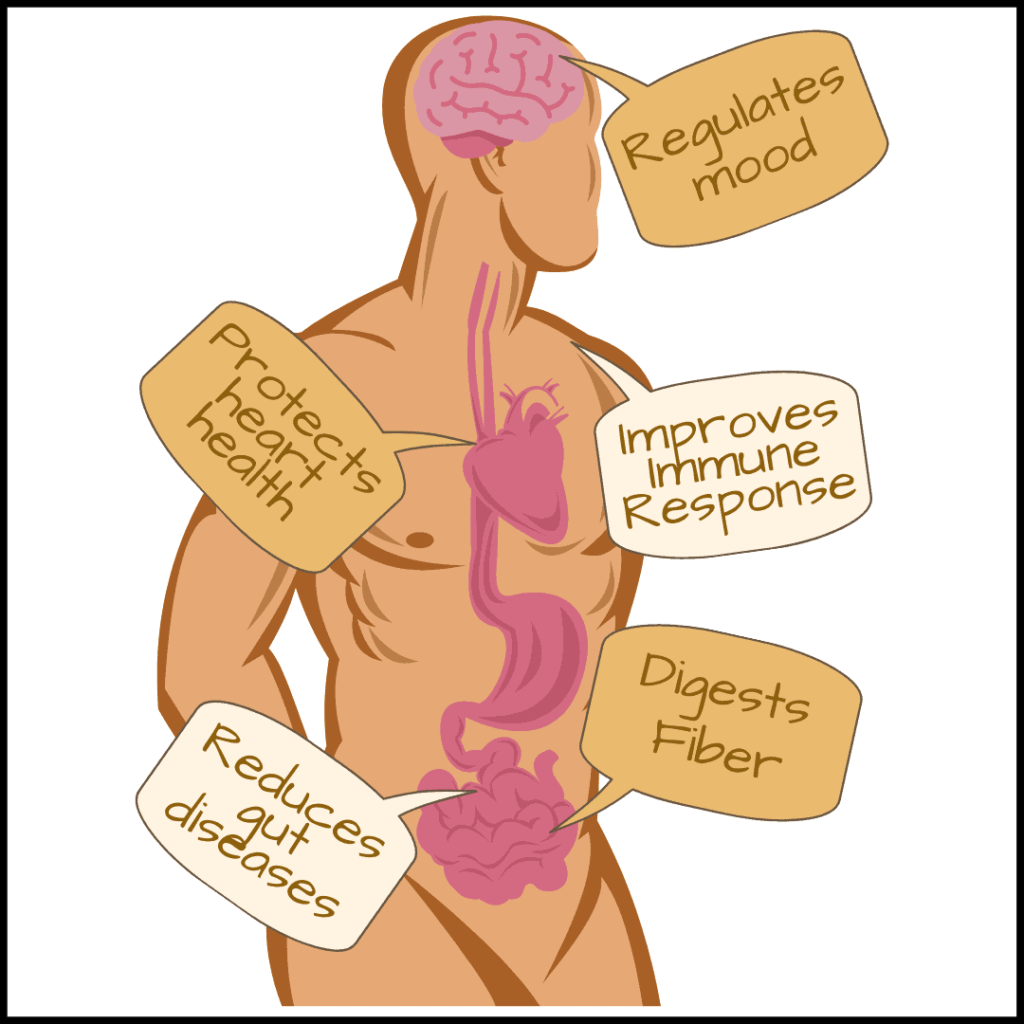
Image: Roles played by gut bacteria in the body
Have you ever "gone with your gut" or "felt butterflies in your stomach" when you're nervous?
Well, there is a reason! Our gut is sensitive to emotions.
There is a direct connection between the gut and the brain.
The vagus nerve acts as a highway, connecting the gut, heart, and lungs to the brain.
When we undergo stress, the brain, along with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, responds to it.
The HPA axis is closely linked to the brain-gut axis. Long-term stress can interfere with the normal functioning of the HPA axis.
Since it is connected to the brain-gut axis, long-term stress can damage the bacteria living in the gut.
Now, the connection between the brain and the gut is a two-way street.
The diversity of the gut bacteria can affect the way you feel.
A reduction in diversity can put you at risk for several mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
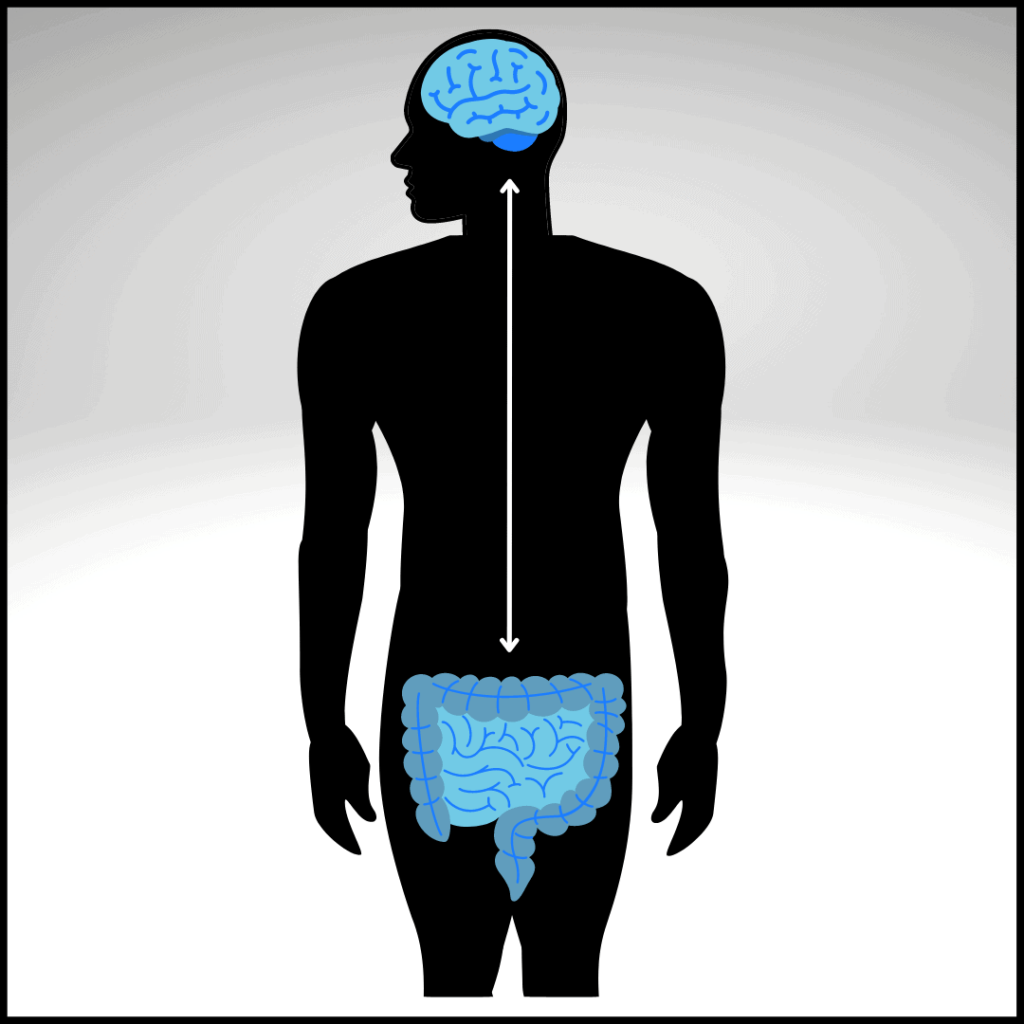
Image: Gut-Brain Axis
The study led by scientists from Jiangnan University, China, in collaboration with other researchers, identified a species of gut bacteria that is associated with enhanced memory and learning.
Like fingerprints, the gut bacteria composition of each individual is different. The same goes for bumblebees.
The differences in the composition can arise for changes in the nest environment, pathogen exposure, their activities and social interaction, and the pollination environment.
In order to test the memory and learning capacity of the bees, the researchers created 10 different artificial flowers.
Five of them had sweet sucrose solution, while the other five had a bitter solution with quinone, which is a repellent for the bees.
The bees were then observed to check how long they took to identify the colors associated with the sweet reward.
In a 3-days follow-up, the bees were tested to see if they retained this information.
The gut samples from the bees were finally analyzed to compare the differences in memory and learning with the levels of different bacteria in their guts.
The study identified elevated levels of a specific species of bacteria called the Lactobacillus apis in the bees that showed enhanced memory and learning capabilities.
To further confirm the findings, the researchers added this bacteria to the bees' diet and conducted the same experiment.
Bumblebees that were fed with food containing more of this species of bacteria were found to have more long-lasting memories.
This highlights a causal effect - Lactobacillus apis causes enhanced memory and learning functions.
The lead author of this study says that further research can help understand “if and which bacteria species might have the same effect on humans.”
Probiotics are available as supplements and formulations.
Fermented foods are natural sources of probiotics.
They include fermented vegetables, yogurt, kimchi, kombucha, etc.
Probiotics can promote healthy gut bacteria and prevent intestinal issues.
Constant exposure to high levels of cortisol or the stress hormone is a big no-no for good gut health.
It can disturb the gut bacteria composition.
Regular physical activity, meditation, and adequate rest can help manage your stress.
Foods rich in sugar can impact gut bacteria negatively.
According to a study, aspartame, a type of sweetener, increases the number of bacterial species that are associated with diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart diseases.
Antibiotics are usually taken to combat any bacterial infections.
While they kill the bacteria responsible for the infection, they also affect the good bacterial population.
The effect of antibiotics on gut bacteria can last up to even 6 months after using them.
Inadequate sleep (<7 hours) and poor sleep quality can affect your gut bacteria.
This increases the risk of several inflammatory conditions.
Getting between 7-9 hours of sleep a night and maintaining a regular sleep schedule can keep your gut healthy.
According to a study, athletes have a greater diversity of gut bacteria.
This can help prevent obesity.
Engaging in regular exercises like walking, running, swimming, or playing sports can be very beneficial for your gut.
Sleep is the best way to relax and rejuvenate your body. It curbs all physical and mental stressors and reduces the risk of various health conditions, including cardiovascular complications. Researchers have found an "ideal time" to fall asleep that is best for your heart health. According to this study by the British Academics, going to bed in the "golden hour" can reduce your risk of dying from a heart attack or stroke.
While there are many reasons to prioritize a good night's sleep, protecting your heart tops the list!
From sleep quality to sleep duration, many parameters of your sleep affect your heart health.
According to the American Heart Association, poor sleep is associated with increased calcium build-up in the arteries. This can result in plaque formation, increasing your risk for heart attacks.
In fact, just one hour more sleep each night is associated with a 33% decreased risk of calcium build-up in arteries.
Image: Calcium plaque formation in the heart's artery
Not getting enough sleep (7-9 hours per night) can induce hormonal changes - especially those that regulate hunger. It increases the levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin and decreases the levels of the satiety hormone leptin. This can lead to overeating and obesity, which is again a risk factor for heart diseases.
Excessive sleeping (>9 hours) can also increase the risk of developing a range of heart conditions.
Check Out: Gene Sleep Report - Your Guide to a Good Night’s Sleep
Heart conditions associated with bad sleep include:
This study from the United Kingdom used an accelerometer device to examine the sleep onset and waking time in the study participants.
Accelerometers are devices that monitor sleep by sensing movements.
103,679 participants (in the UK Biobank recruited between 2006 and 2010) were made to wear the accelerometer for 7 days, and accelerometer data were studied.
After some filtering, a total of 15,653 participants were excluded from the study for reasons like:
The sleep-onset time (SOT) of the remaining 88,026 patients was recorded, and the relationship between SOT and heart diseases was investigated.
The study was done over a period of 6 years and reported that 3.6% of subjects later developed heart disease.
There was a U-shaped relationship between increased risk of heart disease and SOT - this suggests that there is an optimal SOT for reducing heart disease risk.
Image: Relationship between sleep-onset time and heart disease risk
Any deviations from this range - earlier SOT or later SOT can increase heart disease risk.
The findings
Image: Study Results
The findings of this study do not show a causal relationship between SOT and heart disease risk - it just implies a correlation.
However, there is a mountain of evidence that sleep is related to other risk factors of heart disease, like diabetes, obesity, and hypertension.
Creating a consistent sleep pattern: Waking up and going to bed at the same time every day (even during weekends and holidays) can help your sleep cycle function well.
Planning your naps: Midday naps, if not done correctly, can interfere with a good night's sleep. A short nap during the afternoon can help you get through your midday lull and not disrupt the night's sleep!
Getting enough sunlight: Natural light, especially during the day, can help your body's clock to function well, thereby promoting good quality sleep.
Improving your bedtime routine: Instead of looking at devices like mobile phones and laptops that emit blue light, listening to music, reading, or taking a relaxing warm bath before bed can help with the quick onset of sleep.
Having an early dinner: The CDC recommends not eating or drinking anything within a few hours of bedtime to give your body enough time to wind down.
Light therapy is one of the effective treatments used for seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a type of depression related to changes in seasons.
A group of scientists from the University of Friborg used mouse models to investigate how light therapy affects mood.
Light therapy triggered the PER1 gene (circadian clock gene) in mice and showed an antidepressant effect.
SAD is a kind of depression that is triggered by a change in seasons. It happens around the same time every year and typically gets worse in the winter. Symptoms can last for approximately 40% of the year.
SAD is known to affect 11 million people in the U.S. every year.
Some symptoms of SAD are:
Light therapy is also called phototherapy. It is a treatment in which a person is exposed to an artificial light source of a specific wavelength. It is used to treat SAD, other types of depression, as well as sleep disorders.
Light therapy or phototherapy is a treatment in which a person is exposed to an artificial light source of a specific wavelength.
Light therapy is used to compensate for the lack of exposure to sunlight. The light seems to trigger the release of the feel-good hormone serotonin, which helps improve mood.
Research suggests that light therapy in the night activates the CLOCK gene PER1, which appears to improve symptoms of depression.
PER1 gene or Period 1 gene or circadian clock gene responsible for sleep-wake cycles and mood swings. The PER1 gene is found in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). The SCN is located in the hypothalamus of the brain and is the central pacemaker of the circadian timing system.
The PER1 gene is light-sensitive. Upon exposure to light, it switches the body to awake and alert mode with elevated energy levels.
Researchers exposed mice to a pulse of light at different points during the night and then tested them for depressive behavior. They found that light exposure at the end of the dark periods (2 hours before daytime) had an antidepressant effect on the mice.
The pulse of light, activated the PER1 gene in a region of the brain called lateral habenula, which plays a role in the mood. It also resulted in the resetting of the circadian rhythm. This caused a spike in energy levels, which in turn, brought about antidepressant effects.
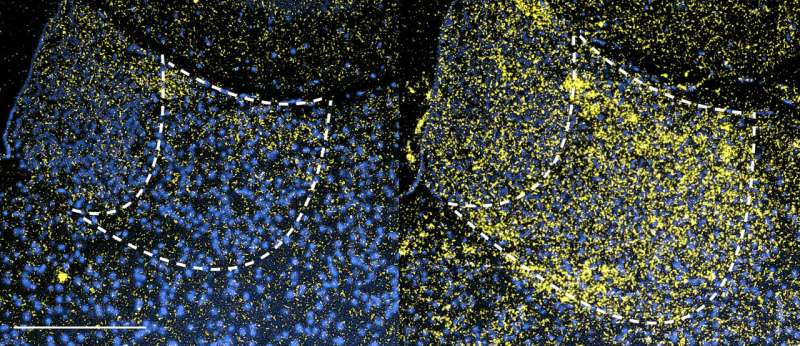
Image: PER1 gene expression before (left) and after (right) 15-minute light therapy
Light therapy at other times did not seem to have any effect. When the PER1 gene was deleted, the mice did not experience the antidepressant effect of light therapy.
Mice responding to light therapy during the early hours before daytime is similar to findings in humans - patients with SAD responded better to light therapy in the early morning than in the evening.
However, since mice are nocturnal creatures, scientists caution against making too many direct comparisons to humans.
Xcode Life’s Gene Health report profiles genes that are shown to influence the risk of certain health conditions. This report is aimed at helping you understand your risk for diseases based on your genes so that you can modify your lifestyle accordingly.
Certain diseases, like diabetes, run in families. This means, if a person in your family has diabetes, you may be at an increased risk for it as well. A family history of certain health conditions can predispose you to it. For many health conditions, however, you can break the chain by taking a few measures.
When you learn about your predispositions, you have an opportunity to take preventive action by changing your lifestyle. Research shows that lifestyle intervention reduces the risk of health conditions like heart diseases and diabetes considerably.
According to a New England Journal of Medicine study, even with a high genetic risk for heart disease, people can significantly lower their risk by leading a healthy lifestyle.
The Gene Health Report aims to help you understand your body better, align your lifestyle to your genetics, reduce your risk for diseases, and improve your chances for a disease-free life.
The Outcome Table in the report indicates your outcome for each trait.
Based on your genetic makeup, your risk for over 45 health conditions is indicated in the report. Each health condition comes with the following information
The report analyzes your genetic risk for more than 45 health conditions, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, cardiomyopathy, migraine, and glaucoma. For a comprehensive list of the traits covered, click here.
For a sample health report/ preview of the report, click here.
Glaucoma, prevalent in more than three million Americans, is the leading cause of blindness in the United States. Recent research reports that consuming large amounts of caffeine daily may more than triple the risk of glaucoma - for those with a genetic risk for high eye pressure. The study suggests individuals with a family history of glaucoma must cut down on caffeine intake to reduce the risk of glaucoma. However, further research is required to understand these gene-diet interactions affecting our glaucoma risk.
Glaucoma is an eye disorder damaging to the optic nerve. It results from increased eye pressure due to fluid build-up in the eye.
Glaucoma is of two major types:
It is the most common type of glaucoma. It occurs gradually when the eye does not drain fluid, resulting in eye pressure build-up damaging the optic nerve. This type of glaucoma causes no vision changes initially and is painless.
It occurs when the iris is very close to the drainage angle in the eye and ends up blocking it. When the drainage angle is completely blocked, eye pressure rises quickly. It is an acute condition and requires immediate medical attention.
The less common kinds of glaucoma include:
Studies have identified various genetic factors that increase the risk of glaucoma.
Changes in the following genes account for 10% of global cases of open-angle glaucoma:
Genes that influence the risk of angle-closure glaucoma are:
But, how these genes contribute to glaucoma is not clear.
In the US, only 15% of children with congenital glaucoma have a mutation in CYP1B1.
Genes influencing other types of glaucoma include FOXC1, FOXE3, PITX2, PITX3, PAX6, LMX1B, and MAF.
Xcode Life's Gene Health Report analyzes 35 gene markers for glaucoma. You can learn about your genetic risk for glaucoma here.
A genetic study led by researchers at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine aimed to understand the impact of caffeine intake on glaucoma and eye pressure.
The study was conducted with data of 502,506 individuals from UK-based Biobank. Participants aged between 39 and 73 during the years 2006-2010 provided their health records and DNA samples to generate genetic data.
The study also used data from dietary questionnaires focusing on caffeine intake and vision, including specifics on family history of glaucoma. In addition, the study measured the eye pressure of the participants.
The researchers analyzed the impact of multiple variables to estimate the association between glaucoma and eye pressure. They also used a genetic risk score that combined the effects of 111 genetic markers associated with eye pressure to examine the between genes and caffeine intake.
Findings of the study suggested that regular coffee drinking is weakly associated with decreased eye pressure. Results also depict a null association between caffeine intake and glaucoma.
However, among individuals with an already existing genetic risk of increased eye pressure, greater caffeine intake was linked with higher eye pressure and increased glaucoma risk.
The study calls for more research to be done in order to identify the gene-diet interactions and provide nutritional recommendations for caffeine intake based on glaucoma risk.
The FDA has recommended that healthy adults can consume 400 milligrams of caffeine a day (4-5 cups of coffee) without experiencing dangerous, negative effects.
If you consume caffeine in amounts higher than your tolerance level, you may experience symptoms like:
More reading: How Genes Influence Caffeine Tolerance?
Opt for alternatives with lower caffeine content like tea or cocoa. Studies report significantly lower levels of caffeine in tea when compared to coffee. Other healthy sources of caffeine include green tea, matcha, Guarana berries.
Include foods that support eye health in your diet every day. Sunflower seeds, raw bell peppers, salmon, eggs, sweet potatoes, dark green leafy vegetables, and carrots contain nutrients that are good for your eyes.
Regular comprehensive eye exams can help detect glaucoma in its early stages before significant damage occurs.
Regular exercising may help regulate eye pressure and thereby lower your risk for glaucoma.
Hydroxychloroquine is a derivative of chloroquine that has both anti-inflammatory and antimalarial activities. It is also used as an antirheumatic agent (used to treat joint pain) in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.
The exact mechanism of hydroxychloroquine action is unknown. It has been documented that its activity hampers the parasite’s ability to break down hemoglobin, preventing its normal growth and replication.
Studies have also shown that it inhibits the stimulation of toll-like receptor (TLR) 9 family that induces inflammatory responses by activating the innate immune system.
Several in vitro studies have confirmed the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine on severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus. Multiple clinical trials are currently being conducted to identify the effect of hydroxychloroquine on COVID-19.
The IL-10 gene contains instructions for the production of a cytokine protein, which plays an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory role in lymphocytes. A study in mice documented that the cytokine functions as an essential immunoregulatory in the intestinal tract. Genetic variations in this gene may alter the production of IL-10 and influence the susceptibility to autoimmune diseases.
rs1800896 and Hydroxychloroquine Response
The rs1800896 is a single nucleotide polymorphism or an SNP in the IL-10 gene associated with the regulation of IL10 production.
Studies have shown that rs1800896 is associated with susceptibility to asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, and other chronic infections.
In a case-control study on patients with SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus), people with TT genotype responded better to hydroxychloroquine.
