Reports
Health
Wellness
Insulin resistance is a condition that prevents the body from responding to insulin the way it should. When the cells don't absorb and utilize sugar for energy, glucose builds up in the blood, ultimately resulting in diabetes. A study by Standford Medicine scientists has established a relationship between insulin resistance and major depressive disorder.
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas.
It instructs the cells to take up glucose from the blood and utilize it for energy.
This is achieved by the insulin receptors (proteins that bind to insulin) present on the surface of the cells.
In people with insulin resistance, the insulin receptors do not function well.
As a result, the cells don’t respond to insulin and uptake glucose.
This leads to increased levels of glucose in the bloodstream.
Some causes of insulin resistance include obesity, inactive lifestyle, excessive carbohydrate intake, smoking, hormonal disorders, and sleep disorders.
Prediabetes often occurs in people with high insulin resistance.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, around 1 in 3 people in the United States have prediabetes.
Insulin resistance is usually asymptomatic until diabetes develops.
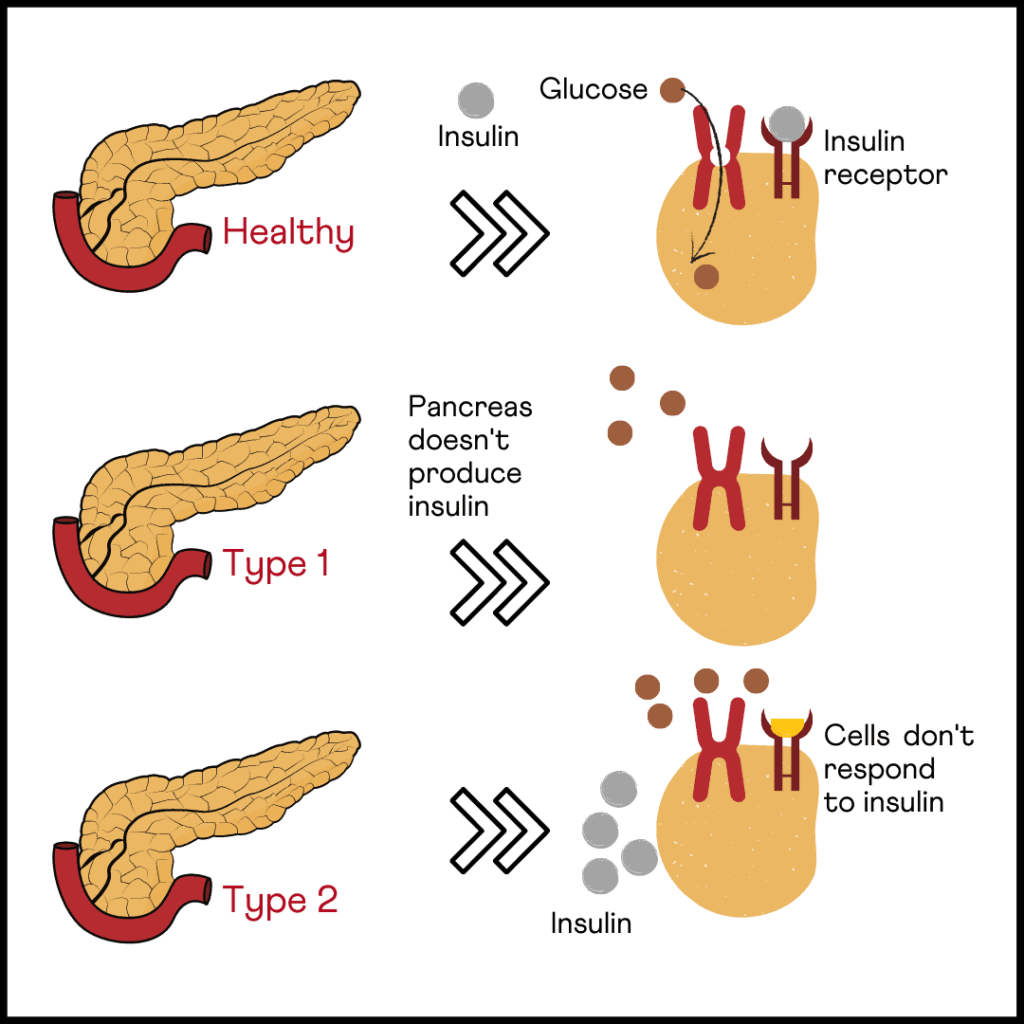
Image: Insulin and Diabetes
Living with diabetes or insulin resistance often affects mood and mental health.
Blood glucose fluctuations may lead to mood swings, resulting in stress, depression, and anxiety.
Studies reveal that about 40% of people who experience mood disorders are insulin resistant.
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a mood disorder.
People with MDD struggle with persistent depression, lack of interest in activities, and behavioral problems.
It is one of the most common mental health conditions in the United States.
Several factors, including biological, psychological, and social causes, contribute to this condition.
Medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes can effectively treat people with MDD and help them manage their symptoms.
The study conducted by the researchers of the Stanford team used the data collected from the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety to learn the causes and consequences of depression.
For the first phase of the study, the researchers considered a pool of 601 men and women.
They checked the data for the three common markers of insulin resistance- fasting blood glucose levels, waist circumference, and serum fat levels.
Those found to be insulin resistant were then observed for their risk for developing MDD over a period of 9 years.
It was found that:
However, in a few members of this batch, there was little clarity about when they developed insulin resistance.
The next phase of the study thus involved studying 400 participants who had no signs of depression and insulin resistance at the onset of the study.
Among these, those who became insulin resistant (one-fourth of the phase 2 study group) at the 2-year point were more like to develop MDD in the next 7 years than the others whose blood glucose levels were normal.
While the study was unable to establish a strong relationship for parameters like waist circumference and cholesterol levels, fasting glucose emerged as a significant factor for MDD.
“Those developing prediabetes within the first two years of the study had 2.66 times the risk for major depression by the nine-year follow-up milepost, compared with those who had normal fasting-glucose test results at the two-year point.”
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-09-insulin-resistance-major-depressive-disorder.html
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/prediabetes.html
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/depression/symptoms-causes/syc-20356007
Gums in the mouth seal around our teeth and hold them in their place. Unfortunately, poor dental hygiene can damage your gums, which may go unnoticed as they are mostly painless. Ruinous gums can lead to gum diseases like periodontitis and gingivitis, causing inflammation of gums. A recent study has reported that periodontitis can give rise to a series of mental health conditions, autoimmune diseases, and cardiometabolic diseases.
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disorder that affects the gums.
Gums are soft tissues surrounding the teeth.
Periodontitis can affect any one tooth to all the teeth.
It is mainly caused due to the plaques that build upon our teeth every day.
The plaque buildup makes the gums bleed, inflamed, and red.
Therefore, it is necessary to brush the teeth properly to avoid plaque building up.
The initial stage of periodontitis is gingivitis - the swelling of the gums.
Usually, gingivitis does not cause any pain; hence it gets unnoticed in some people.
Gingivitis can be cured easily by following good dental practices, proper brushing, and flossing at home.
However, if left untreated, the condition progresses into periodontitis.
The study led by researchers at the University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, reported that periodontitis could increase the risk of diabetes, heart diseases, mental illness, and autoimmune diseases.
The study was published in the journal of BMJ Open.
The team collected data from nearly 64,400 UK patients with a history of gum disease.
They further compared the data with a group of 251,161 people without gum disease.
After a follow-up of three years, the study reported that the people with gum disease had
The outcomes of gum disease - bad breath, tooth loss, gum pockets can have psychological impacts leading to loss of confidence, inability to mingle with others, and fear of judgment (symptoms of depression and anxiety).
Periodontitis causes autoimmune diseases due to the changes in proteins caused by a periodontal pathogen.
This, in turn, releases antibodies (proteins produced by the body's immune system ) that act against healthy cells.
Whether gum disease causes these problems or vice versa is ambiguous; hence further research is required to know more about the association.
https://www.westervilledental.com/what-is-the-ideal-oral-health-routine/ https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/study-links-gum-disease-to-mental-health-conditions
Every day we are exposed to numerous chemicals present in the food we intake, water, air, and products we use. Exposure to chemicals leads to an array of health risks. Inhaling or ingesting chemicals during pregnancy may cause problems for both the mother and baby. A recent study has reported that exposure to a common chemical disrupts a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy.
Phthalates are a class of chemicals involved in the manufacture of plastics.
They are generally described as plasticizers and provide durability to plastics.
They are also used to dissolve certain substances as they have a high boiling point and low melting point.
Phthalates are found in substances like ink, paints, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and surprisingly, food products.
People are exposed to phthalates when they eat or drink food stored in containers made up of phthalates.
They also enter our body through our lungs when we breathe phthalate particles in the air.
When pregnant women are exposed to phthalates, their levels of sex hormones like estrogen and thyroid hormones get deranged.
As a result, they might experience a decrease in the pregnancy duration and other birth outcomes - preeclampsia, cryptorchidism, and decreased anogenital distance in babies.
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy disorder characterized by hypertension. It can lead to various health ailments for the mother and the baby.
Cryptorchidism is a genital disorder that occurs in newborn male babies. The testicles (male sex organs) are improperly aligned in this disorder.
Usually, phthalates break down into small particles in the human body and leave our body through urine.
CRH regulates the body's functions in response to physical and emotional stress.
The hormone also plays a vital role in pregnancy.
The placenta synthesizes and discharges the CRH into the circulating blood during pregnancy.
Thereby the levels of CRH increase at the time of delivery.
The level of CRH found in pregnant individuals is 1000 - 10000 times greater than that of non-pregnant individuals.
The CRH regulates fetal maturation, labor timing, and the placenta's blood flow to the baby.
The CRH levels are usually low during mid-pregnancy.
But high levels of perinatal stress can increase the CRH levels during mid-pregnancy, resulting in adverse birth outcomes.
At the same time, lack of CRH during labor can also lead to various pregnancy outcomes - premature birth, miscarriages, preeclampsia, retardation of the baby's growth.
The study appears in the journal of Environmental International.
It has elucidated the association between exposure to phthalates and pregnancy.
The women were tested only twice during their pregnancy.
Since phthalates have a fleeting life in the human body, a single spot urine test cannot determine the exposure levels.
More than half of the study participants were black women. They tend to have higher exposures to chemicals due to their lifestyle but are marginalized in pregnancy studies.
So, it is advised to avoid them or limit their usage during pregnancy.
Rather than drinking water directly from the tap, using a filter can help you avoid phthalate exposure.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23385670/
Diabetes has almost become a household name - 1 in every 10 Americans has the disorder. According to the National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020, diabetes has been on the rise among the youth. Type 2 diabetes (T2D) accounts for almost 90-95% of cases in the US. According to new research presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2021, the commonly used osteoporosis drug alendronate can help reduce the risk of T2D.
Diabetes occurs due to either the body’s incapability to utilize insulin or produce insulin.
It can also happen if there’s an overproduction of insulin (diabetes insipidus).
Diabetes has two forms - type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
General symptoms of diabetes include:
The most common form of diabetes, T2D, is characterized by insulin resistance.
The body’s cells stop utilizing insulin, and blood glucose levels start rising.
T2D usually develops over time, and many people might not notice until the disorder has progressed quite a lot.
In addition, T2D is a multifactorial disorder, i.e., the condition may get triggered by both genetic and environmental factors.
Know about your genetic predisposition for type 2 diabetes and 50+ other health conditions with Xcode Life’s Gene Health Report!
In type 1 diabetes (T1D), the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy pancreas cells, which would otherwise produce insulin.
In the event of the death of enough pancreatic cells, the body becomes incapable of making insulin.
This leads to a rise in blood sugar levels.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder and usually occurs due to inheritance.
An individual develops the condition when one or more family members also suffers from it.
Symptoms of T1D usually progress pretty rapidly once it gets triggered, sometimes within weeks or months.
Image: Types of Diabetes
Osteoporosis is characterized by decreased bone strength which increases the risk of fractures.
This occurs due to a combination of low bone mass, reduced bone quality, and slight structural deformities.
Diabetes and osteoporosis share quite the comorbidity that is still being widely investigated.
The risk of fractures increases approximately 6% in T1D due to low bone mass.
In T2D, even though bone mass may be maintained, inferior quality of bone increases the risk of fractures by almost twice in the general populace.
Several factors actively contribute to the comorbidity of osteoporosis and diabetes, such as:
The study led by Dr. Rikke Viggers of Aalborg University Hospital, Denmark, explored the effects of the osteoporotic drug alendronate on type-2 diabetic patients.
Rikke Viggers and colleagues examined patient data from the Danish National Patient Registry from 2008-2018.
These were individuals who were 50 years old and more and developed diabetes after 2008.
Furthermore, the patients’ prescription records were examined to check for the usage of alendronate and its effect on the onset of diabetes.
Image: Study Results
The study’s findings suggest a possible protective effect of alendronate against diabetes.
However, the researchers concluded that further clinical research on this front was needed to confirm the protective effects.
Get Actionable Health Insights From Your 23andMe, AncestryDNA Raw Data!
Mothers are the only source of nutrition for the child's physical and mental development. Poor nutrition during pregnancy and breastfeeding can highly affect the child's growth in the womb and throughout their early childhood. Recent research suggests that adding more choline to the pregnancy diet can improve the child's sustainable attention.
The time spent on any activity without getting distracted or losing interest is called the attention span.
Distraction refers to shifting attention from the ongoing activity to other tasks or sensations.
The attention given to an activity or task can be differentiated into two types:
Attention spans differ for each child but follow a specific pattern.
The average attention span of a healthy child is believed to be two minutes per year of age.
According to the child's age, the attention span increases two-three times the age.
Maternal nutrition refers to the mother's nutritional requirements during antepartum and postpartum periods.
The disparity in maternal nutrition can affect infants' average growth and development as the child depends on the maternal plasma for its nutrients.
Pregnancy and infancy are the crucial periods for the formation of a child's brain and the development of a child's cognitive, motor, social, and emotional skills.
Nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy can cripple the child's development, leading to neurological defects and poor cognitive development.
Poor maternal nutrition is associated with many adverse short and long-term outcomes - increased infant death rates and childhood morbidity.
Preventing nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy can have widespread benefits for individuals and societies.
The study, led by researchers from Cornell University, was published in the Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
It reported that consuming twice the recommended amount of choline during pregnancy improves children's attention span.
Choline is a nutrient produced by our liver in meager amounts.
It is also naturally present in egg yolks, red meat, beef liver, cauliflower, and broccoli.
Choline intake during pregnancy is vital as it impacts the child's brain and spinal cord development.
After a follow up of seven years, the study reported the following:
The results suggest that maternal choline supplementation can improve children's cognitive functions.
Consuming two eggs per day can provide you with 294 mg of choline, 50% of the recommended choline level.
Organ meats like liver and kidney provide 65% of recommended daily intake level of choline.
Consuming cruciferous vegetables with eggs and organ meat can help you meet the daily needs for choline.
Dermatoglyphics is the study of fingerprints and ridges in our palms and soles. Fingerprints are critical areas of interest under research as they are unique and reveal an individual’s true identity. However, only a little is known about the reason behind the variation of fingerprint patterns. A recent study by the researchers at the Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health has revealed that genes involved in limb development influence the fingerprint patterns in humans.
Fingerprints are the patterns formed by ridges on the surface of our fingertips, palms, and the soles of our feet.
The number, shape, size, and position of the ridges do not change even when we grow up.
The patterns are contrasting for every individual.
It is fascinating that no two fingerprints can be the same, even in the case of twins.
The ridges on our hands and feet develop in the growing fetus from approximately 8 - 18 weeks of embryonic development.
The fingerprints are generally classified into three types: Whorls, Loops, and Arches. Loops represent staple-shaped ridges.
Image: Types of fingerprints
They are further organized into radial, ulnar, double, and central pocket loops.
The most common pattern is the loops, constituting 65% of the total fingerprint patterns. At the same time, the arches are the least common pattern.
The limbs develop from a circular structure called limb bud in the embryo.
The limb bud develops during the 4-8 weeks of embryonic development. After the eighth week, the limbs begin to enlarge in size.
The BMP4 gene contains instructions for producing bone morphogenetic protein 4.
It regulates the formation of limbs and is essential for osteoblast (bone cells) differentiation.
Did You Know: The BMP4 gene contributes to Achilles Tendinopathy Risk
The EVI1 gene produces an essential protein for appropriate murine and human development.
They are also responsible for limb development and oocyte development (egg cells) in the ovary.
The study led by Wang and his colleagues found that limb development genes influence the variations in human fingerprint patterns.
The study was published in the journal of Cell Press and reported that the genes underlying limb development are not linked to skin formation but rather to fingerprint formation.
The team began by scanning the DNA of 23,000 participants to detect the genetic basis of the finger patterns and found that at least 43 genomic regions were related to limb development.
The team concentrated on the EVI1 gene - a primary limb development gene in humans to confirm the finding.
But, first, they modified the expression of EVI1 in mice.
They found that the mice with altered EVI1 levels developed abnormal skin patterns compared to normal mice.
The finding suggests that EVI1 is responsible for influencing fingerprint types in humans and hence holds up the idea that fingerprint patterns are related to finger length.
The exact mechanism by how the genes determine the fingerprint patterns is still unknown.
But research suggests that the shapes of the volar pads influence where and what type of fingerprint forms.
Volar pads are transient swellings of tissue on the palmar surface of the hands and soles of the feet of the developing baby.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/01/220106111552.htm
https://hastingsmuseum.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Fingerprint-Info-Activities.pdf
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women after leprosy. In America, breast cancer is among the top causes of cancer-related deaths. The spread of cancer cells from the breast to other organs is also a concerning case as it is the leading cause of death resulting from the disease. A recent study has reported that downregulating the gene involved in the sense of smell can reduce the spread of cancer cells from the breast to the brain.
Receptors are proteins on the cell surface that can selectively receive and bind to specific substances or signals.
Olfactory receptors are proteins present in the nasal cavity playing a pivotal role in the sense of smell.
They recognize and bind to odor molecules entering the nasal activity.
After binding, they send signals to the brain's olfactory system, resulting in odor perception.
There are nearly 400 olfactory receptors in humans to detect odors. Besides recognizing smell, the odor receptors also play a role in specific physiological processes such as cancer.
Receptor genes provide the instructions (encode) for making the receptors.
The olfactory receptor genes are responsible for making the olfactory receptors.
There are nearly 800 genes in the olfactory receptor family, and each gene encodes for each odor receptor; so, we can smell various compounds.
In breast cancer, the breast cells undergo uncontrolled proliferation (growth) resulting in tumors.
It affects both genders, but it is rare in men.
Breast cancer-related complications are among the top causes of death in women.
The study led by researchers at Massachusetts General university has reported that inhibiting the olfactory gene - OR5B21 decreased the spread of breast cancer to other organs, especially the brain.
The Olfactory Receptor 5B21 gene contains instructions for producing olfactory receptor 5B21.
According to research, the gene also acts as an oncogene (cancer-causing gene), driving the movement of cancer cells from one organ to another.
Previous studies have suggested that olfactory genes are known to be overexpressed in various cancers - prostate, melanoma, liver, and lung cancer.
However, the expression of olfactory genes in breast cancer is less studied.
The current study aimed to study the effect of olfactory genes in breast cancer.
The researchers performed the study on animal models with the OR5B21 gene that enhanced the spread of breast cancer cells.
Epithelial cells are a type of cell lining the surface of our body with no differentiation capacity, whereas mesenchymal cells can differentiate into various cell types.
While the study reported that the olfactory gene induces metastasis in breast cancer cells, the exact mechanism behind the metastasis is yet to be studied.
Introducing a molecule that inhibits the action of olfactory genes can pave the way to arrest the metastasis of cancer cells.
The simplest of daily physical activity almost all people accomplish is walking. The advancement of technology has made it easier to track the number of daily steps with wearable devices. A study recently published in JAMA discovered that individuals taking 7000 steps or more per day lowered their risk of death.
The health benefits reaped from regular physical activity, be it moderate- or vigorous-intensity, are many. From reducing the risk of heart diseases to promoting mental wellbeing, the list is long.
According to the CDC, almost a dozen of health conditions can be prevented or managed with routine physical activity:
According to some stats, about 6-10% of the health burden of chronic diseases worldwide and 9% of premature death can be attributed to physical inactivity.
The 2019 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommends adults to engage in weekly 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity or 75-150 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity.
Image: Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans
Every individual has a different body type and consequently different bodily needs. Therefore, the realization of a personalized therapeutic approach has aided in the fitness world too.
A strength-based approach uses healthcare professionals in close collaboration with clients - wherein the focus is put on clients’ abilities, objectives, and present situation.
Strength-based personal approaches to exercise regimes have been observed to bring about more excellent patient outcomes.
Xcode Life’s Gene Fitness Report analyzes your body’s genetic predisposition for fitness traits and gives personalized recommendations. Click here.
A study in 2020 found a reduction in mortality risk by 40% when subjects followed the 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans and engaged in both aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities. Further, individuals who engaged in either aerobic or muscle-strengthening activities decreased their mortality risk by 29% and 11%, respectively.
According to data, between 1997-2014, only 15.9% of 479,856 Americans followed the recommended physical activity guidelines.
A 2015 study on European subjects showed a 14% reduction in mortality risk with only 15 minutes/day of exercise.
Further, in a study done in 2020 on a group of 70-years olds, a higher step count was associated with a reduced incidence of diabetes.
The study led by Amanda Paluch was part of a Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study which drafted subjects from four States - Alabama, Illinois, Minnesota, and California.
The study analyzed a subset of 2110 participants belonging to the age group of 38-50 years. Out of 2110, 1205 participants were women, and 888 were Black.
The researchers grouped the participants into three categories:
Between 2005-2006 and a follow-up in 2015-2016, participants wore an accelerometer for seven days to measure average step count. The accelerometer was only allowed to be removed during sleep and any water-related activities.
At the end of the follow-up period of an average of 10.8 years, 72 participants had died.
Additionally, the participants’ highest number of steps per minute in any 30 minutes was measured. The time duration each day in which the participants took 100 steps a minute was also tracked.
The researchers considered several other health-related factors like alcohol intake, weight & BMI (body mass index), smoking, cholesterol & fasting glucose levels, blood pressure, medication history & heart disease.
Compared to participants who took less than 7000 steps each day, participants who took at least 7000 steps each day reduced mortality risk by 50-70%.
Neither a step count exceeding 10,000 steps each day nor the step intensity had any additional impact on reducing mortality risk.
The study’s findings bear clinical significance as remote patient monitoring devices are gaining ground. Wearable devices to track daily step count is an easy way to track and promote routine physical activity. While many individuals may be reluctant to engage in planned-out exercise regimes, walking to accomplish step goals can be an acceptable form of daily activity.
The autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene is crucial for distinguishing the body's cells from foreign cells. A recent study has found that the absence of the AIRE gene results in infertility problems in males. In addition, the study found that AIRE deficient infertile mice exhibited symptoms similar to an autoimmune disorder in men. The study further suggests that autoimmune diseases can impact fertility.
The AIRE gene provides instructions for making a protein called an autoimmune regulator. This protein is primarily expressed in the thymus, an organ located near the breastbone. The crucial function of this protein is to protect the body's cells from foreign invaders. The malfunction of this protein leads to a condition called autoimmunity (inability of the immune system to distinguish body cells and foreign cells, resulting in self-injury).
Male factors like ejaculation issues, inability to produce healthy sperm and dilated veins around the testicles have been estimated to contribute to infertility to a large extent. The absence of the AIRE gene is one of the determinant factors of infertility. A deficiency in this gene leads to the loss of proteins responsible for sperm production, resulting in infertility.
AIRE-dependent central tolerance is a process by which male fertility is protected by preventing autoimmune attacks on the reproductive targets. An impaired AIRE- dependent central tolerance could lead to male infertility.
Researchers began by mating AIRE deficient male mice and normal male mice with normal female mice.
The research study made the following observations in the AIRE deficient male mice
It was also found that AIRE deficient mice had low testosterone levels (male sex hormone), and that their immune system injured their reproductive organs, especially epididymis.
Researchers further made the following suggestions:
