Reports
Health
Wellness
|
Liquid calories or high sugar drinks are often consumed less rationally than food that is chewed. Most people do not “count” the calories they drink. However, a great deal of damage could be coming from liquid calories.
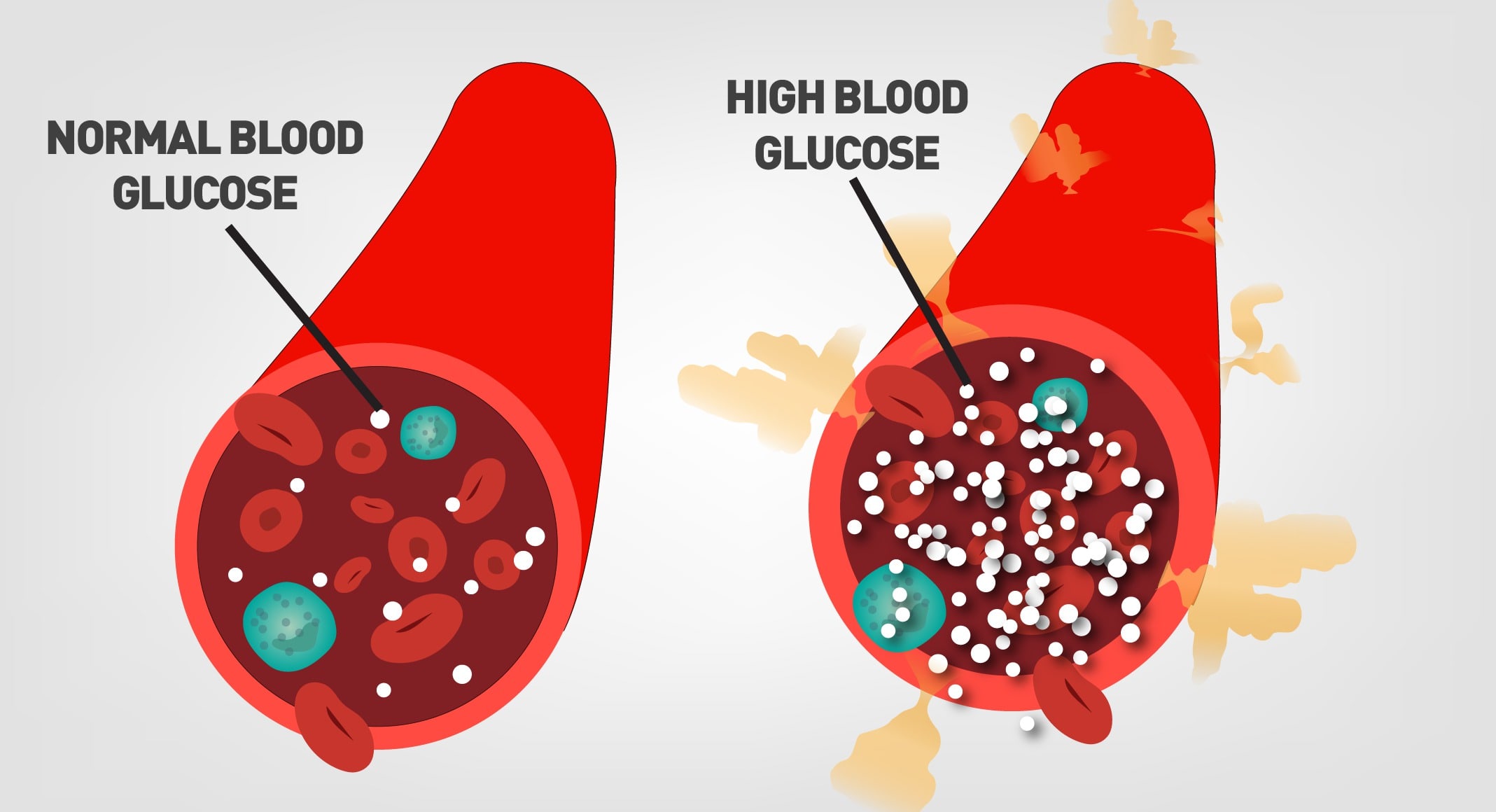
Sugar in drinks gets into the blood faster than sugar in solid foods, thus increasing blood sugar levels rapidly. Repeated increases in blood sugar levels lead to insulin resistance, which eventually leads to obesity, diabetes and other health conditions. People habitually consume colas, bottled fruit beverages with added sugar, teas and coffees with sugar, and all sorts of sugar sweetened beverages(ssb).
These drinks are consumed casually at home as a replacement for water, at entertainment centers, after sports, and at social events. Many people quench their thirst with these drinks instead of water, ignoring the calorie labels(a.k.a warning labels) on them. The fine print shows an alarmingly high level of sugar that research studies have found to be associated with a risk for obesity and thereby an increased risk for diabetes. These drinks confer risk of diabetes.
While the risk for diabetes associated with drinking sweetened beverages has always been known, a new study shows the extent of risk. Researchers from Karolinska University in Sweden showed that consuming 2 glasses of sugary drinks every day could double diabetes risk.
In the study, two or more of 200 milliliters servings(~ one and a half cans) of the sugary drinks when consumed every day was found to increase the risk for diabetes by two-fold. People who preferred drinks that were sweetened with artificial sweeteners were equally at risk for diabetes.
Diabetes risk was the same whether one consumed drinks sweetened with sugar or artificial sweetener
Josefin Edwall Löfvenborg who is a nutritionist at Sweden’s Karolinska Institute spoke about the relevance of the study “Not all studies have been able to look at sugary and artificially beverages separately. (but) it's getting more and more established that soft drinks increase the risk of type II diabetes."
‘Effect of Larger Quantities’
"We wanted to see the effect of larger intakes than two," stated Löfvenborg highlighting the second part of the study that determined diabetes risk among people who drank more than 1 liter of sugary drink every day. The risk was found to increase 10 fold in this group, reiterating the effect of consuming high sugar drink on diabetes risk.
Cups quickly add up to a liter in a day: a few cups of coffee or tea a day, some canned beverages, a can of soda or cola, cappuccino, lassi, etc. all can add up to contribute towards the risk of diabetes.
[idea]
Is soda the new cigarette?
High sugar drinks like sugary soft drinks are being additionally taxed in places like California and Berkley in the U.S. In Kerala, India, fat tax of 14.5% is levied on junk food at International food chains which include burgers and high sugar drinks consumed in these chains. Such high tax is levied to lower consumptions as high sugar drinks are implicated in the rising obesity epidemic and diabetes numbers in the world. In California and Berkley, soda consumption has dropped by one fifth after the tax on soda was executed. Cigarettes are taxed similarly to lower consumptions, this boils down to soda being on the same plane as cigarettes. [/idea]
Not everyone reacts equally to dietary risk factors, certain genes have been shown to modify (predispose or protect) disease risk. In a recent study, it was found that people with certain gene variants were at a higher risk for diabetes even when they consumed the same dietary components as others. This would mean that people who consume high sugar drinks may have a higher risk for diabetes but the level of risk may be modulated by the genes they carry.
Family history is an important genetic risk factor for diabetes. The risk for diabetes is increased if both parents are diabetic, as compared with either parent or neither parent being diabetic. Predisposition to diabetes can be determined through a simple and economical saliva-based genetic test.
Xcode’s Health Genetics test is a companion to the Master Health Checkup (MHC). This genetic test covers predisposition to diabetes, obesity, hypertension and heart disease in one, low-cost test. When taken together with blood test data from MHC, it provides a complete picture of the various risk factors. Nutritional, dietary and lifestyle counseling is provided to lower the risk towards the normal range.
You can write to us at hello+support@xcode.in to find out more.
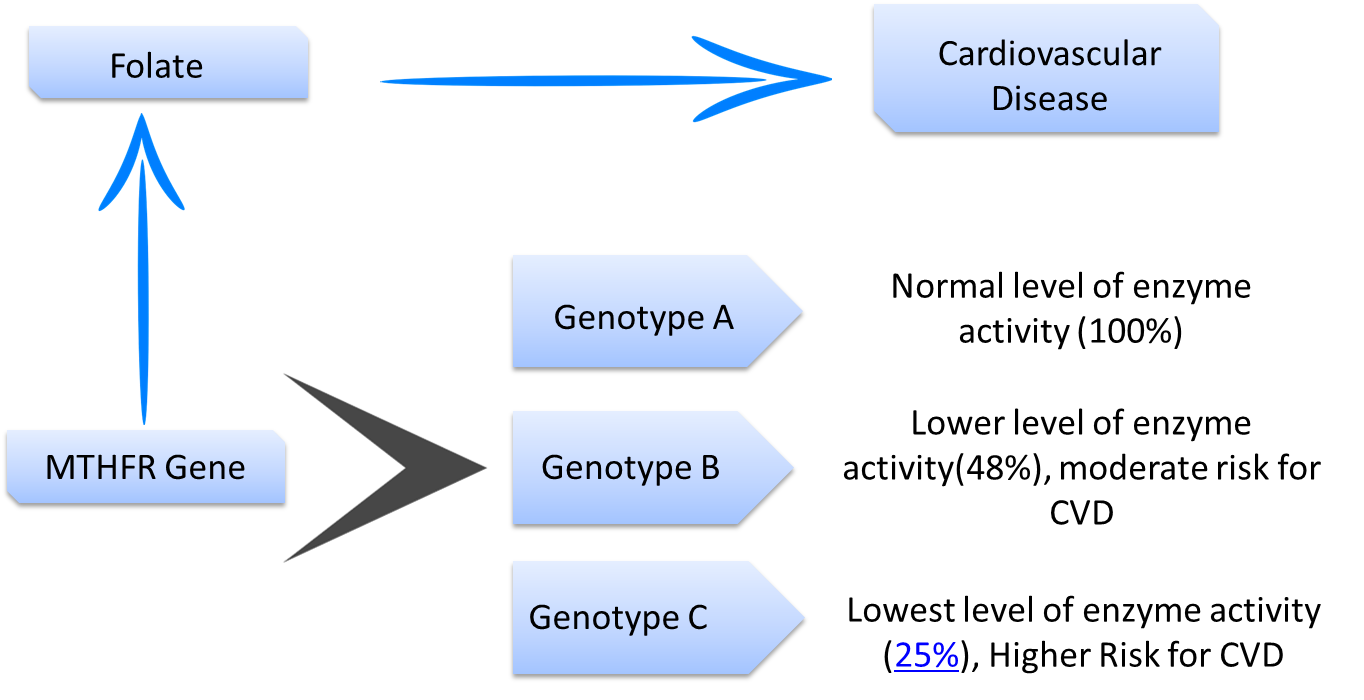
Cardiovascular disease is a group of diseases that involve the heart and blood vessels. There are a number of risk factors associated with this condition, including genetic risk factors with several mutations in several genes being associated. One such important and the independent risk factor is Homocysteine.
| Nearly 60% of the world’s heart disease occurs in India Indians are prone to premature coronary artery disease (CAD) with homocysteine found to be a significant independent risk factor for CAD in young patients. MTHFR gene polymorphism was found in 1/3rd of ischaemic stroke patients in India and was associated with a higher frequency of hyperhomocysteinemia compared with people without the polymorphism. Gene mutation implicated in homocysteine levels are significantly associated with CVD in Indians C677T MTHFR mutation was strongly associated with arterial stroke, with MTHFR allele evaluation aiding in reducing morbidity due to stroke. Multiple scientific studies have established high levels of homocysteine in the Indian population- as much as 80% according to one study. Poor maternal folate rate, indicated by plasma homocysteine levels which is a highly sensitive marker of folate levels, is associated with preeclampsia, stillbirth, preterm delivery, and spontaneous delivery. 60 to 90% of adolescents in India suffer from anemia, with folate deficiency being one of the major causative factors for nutritional anemia. 22 to 52% in India have folate deficiency in India. Conditions associated with folate deficiency, like neural tube defects with a prevalence of 1 to 5 per 1000 live births, are high in India. |
Folate (vitamin B9) is responsible for converting the harmful homocysteine to its useful form, methionine. Methionine is important for many essential bodily functions such as the production of DNA and RNA, cell, and tissue growth. Though dietary intake of folate is generally inadequate in India, that is not the only reason for high homocysteine levels. Genes also play an important role.
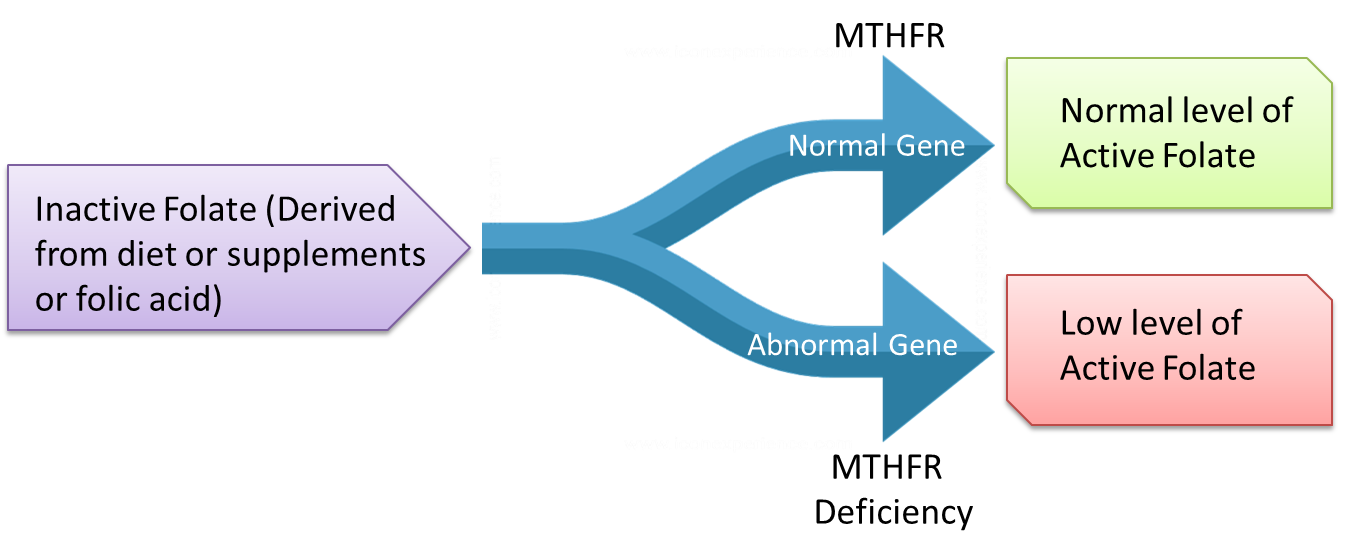
Folate is present in an inactive form in the body and is converted to its active form by the enzyme Methyl Tetra hydro Folate Reductase (MTHFR). The active form of folate is necessary for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. The gene MTHFR plays a role in the production of the MTHFR enzyme and any genetic variation in this gene could alter the level and activity of the enzyme in the body. It has been shown that the prevalence of MTHFR gene mutation is high in India, which when combined with low dietary folate intake can lead to very high levels of homocysteine and other associated conditions.
Maintenance of adequate folate levels is extremely important during pregnancy, infancy, and adolescence. Lack of methionine can lead to improper DNA synthesis and disruption in gene regulation that could lead to birth defects like neural tube defects, which are associated with folate deficiency.
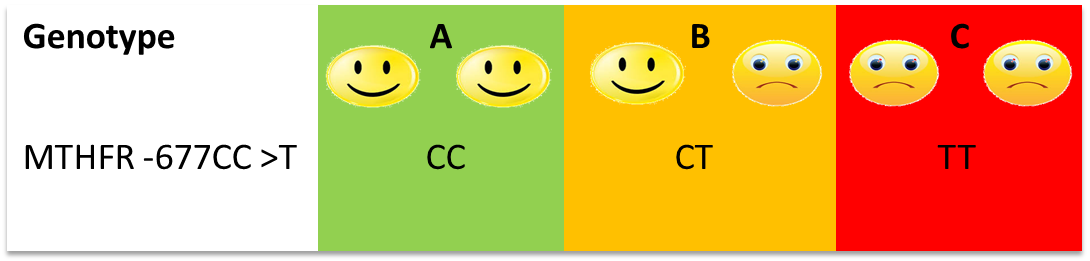
Asians show a high prevalence of 677C>T polymorphism in the MTHFR gene. People with genetic variants that are at high risk for folate insufficiency should supplement their diet with rich sources of folate. Fruits and vegetables are good sources of folate, however, in India, overcooking vegetables leads to loss of folate. Fortified cereals, grains, and cornmeal are sources of folic acid, which is a synthetic form of folate. The folate from the diet will compensate for the lowered levels due to gene polymorphism.
The type of MTHFR gene has been shown to influence the Active Folate levels in blood. Want to know what type of MTHFR gene you have? Try Xcode’s nutrigenetics test which can tell you what versions of the MTHFR gene are in your DNA. You can also learn about how your genes may influence other traits, including your risk for certain diseases. Write to us at hello@xcode.life to find out more.
Increasing nitric oxide (NO) has become the new secret weapon for athletes and bodybuilders. It is used as the primary ingredient in various dietary supplements to support the flow of blood and oxygen to the skeletal muscle and also use them to facilitate the removal of exercise-induced lactic acid buildup which reduces fatigue and recovery time.
Whilst exercise and diet can impact your Nitric Oxide levels, your genes also play a role. Specifically, your NOS3 gene can suggest whether you should be supplementing your diet with Nitric Oxide boosting foods and supplements. Or whether you have a natural advantage in terms of Nitric Oxide levels produced by your body, hence giving you a power based training advantage.
|
[idea]Other factors such as aging, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, high cholesterol, fatty diets, and lack of healthy foods may result in nitric oxide deficiency. Thus, increasing your nitric oxide levels can help increase your energy, vitality and overall wellness.[/idea]
The NOS3 gene produces the Nitric Acid Synthase 3 enzyme, which facilitates the production of nitric oxide (NO). The type of NOS3 gene that you carry influences the production levels of NO. Increased enzyme activity may result in higher production levels of NO. Although the NOS3 gene has been associated with athletic endurance performance and elite power athletic status, research into the NOS3 gene has shown that the one version of this gene has been found at a higher frequency in Polish power based athletes. Studies into Spanish power athletes also showed similar results.
Discover your genes and align your training with your genetic type. Try Xcode’s fitness genetics test which can tell you what versions of the genes are in your DNA.Write to us at info@xcode.in
The multi-tasking woman of today, who takes pride in juggling both domestic and professional commitments simultaneously, has unwittingly allowed stress to get the better of her. While it’s true that everyday life has become a hassle to many, a woman’s response to the demands of modern life often takes a heavy toll on her mind and body.
Stress can be defined as the response of an individual to a stimulus. The response, be it positive or negative, has an impact on the mental and physical well-being of the individual. During the process of a physical response to a situation that is loaded with threat or danger, the nervous system triggers the defence mechanisms through release of hormones like adrenaline and cortisol in one’s body as it prepares for an emergency action.
We have heard it often – that stress is not always bad and in fact it helps an individual to perform better and motivates him to excel. However, in the context of modern life accompanied by challenges of unrealistic goals and deadlines, broken relationships, unhealthy competitions and frustrations, stress is more often recognised as a negative response that demands a heavy price from one’s mind and body.
“Stress is like spice – in the right proportion it enhances the flavour of a dish. Too little produces a bland, dull meal; too much may choke you”, says Donald Tubesing, the famous writer who has authored several books on stress management.
Even as stress helps individuals to rise up to the occasion and meet challenges, beyond a certain point it unleashes a negative impact that damages the physical, mental and behavioural aspects of life and dilutes its quality. Response to stress varies from individual to individual. The variation in is more pronounced between men and women. A woman caught in the nightmarish whirlpool of work-life balance, gradually gets used to a stressful routine on a daily basis thereby enabling chronic stress caused due to factors related to family, finance, work, relationships etc., to creep on her. Compounding to the negative impact is the stress caused by internal factors like pessimistic attitude, low-esteem, unreasonable expectations etc., Unable to bear the overload of stress, a woman’s body and mind wilt under the pressure, releasing warning symptoms.
Instead of crumbling under the pressure of stress, what can a woman do to shield herself against the damages caused by stress? Always remember that an individual’s ability to withstand stress and overcome its pressures is hugely dependent upon factors like her general outlook on life, emotional intelligence, her relationships and genetics.
It is imperative for women to understand that stress management is all about acquiring control over the physical, mental and emotional aspects of their lives. A woman, who intends to decrease her stress level, if not totally eliminate it, should take concrete steps to improve the quality of her life.
Genetic studies now indicate that acute stress can alter the activity and control of one’s genes by altering the methylation of DNA. The stress-induced genetic expressions that are responsible for making an individual prone to illnesses are also likely to be passed on to the next generation through a process known as epigenetic inheritance. It is of paramount importance that a woman understands all the implications of becoming a victim of stress. Stressful experiences not only affect her mind and body, but also affect her genes which she, in all probability, would transmit to her children. Researchers say that epigenetic inheritance can make individuals predisposed to stress and make them less resilient in their response to stress. This leads to the onset of chronic diseases.
The all important key to one’s happiness in life depends on his or her ability to overcome stress. As a woman, if you feel that stress is inevitable in your life, you have a choice as to whether you want to let it impact your health or not. By adopting the right attitude one can convert the negative impact of stress into a positive one. Undue worry and stress not only add to tomorrow’s woes but also wipe away the peace and happiness that one is blessed with today!
Even as we inherit our genes from our parents, we also inherit some of the gene mutations that can cause significant changes in our body. Mutations are variations in the genetic code of a gene that can alter or affect its functions. These inherited mutations, however small they are, can increase our risk to certain diseases.
Research studies have established that BRCA1 (Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene 1) and BRCA2 (Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene 2) genes are linked to breast cancer. Mutations of these genes that belong to a class of genes known as tumour suppressors are linked to hereditary breast and ovarian cancers. While it is true that not all genetic changes or mutations are harmful, a woman who inherits this faulty or harmful genetic mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2 is prone to the risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer before menopause. It is also very likely that breast and ovarian cancers run in the family with some of her close family members being diagnosed with the diseases. Apart from breast and ovarian cancers, harmful BRCA1 mutations are also likely to increase a woman’s risk of developing cervical, uterine, pancreatic and colon cancer and harmful BRCA2 mutations may increase risk of pancreatic, stomach, gall bladder, bile duct cancers and melanoma. However researchers add that not all women who hail from families with a history of breast or ovarian cancer are carriers of harmful mutation and further not every woman who has inherited this deleterious mutation will develop breast or ovarian cancer.
Genetic testing plays a key role in detecting BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Genetic testing gives the woman the chance to learn if her family history of breast cancer is due to an inherited gene mutation.
BRCA gene test is conducted to identify the harmful changes in the DNA of the two breast cancer susceptibility genes. Genetic counselling by qualified professionals in the field of cancer genetics is usually recommended before and after the test to discuss with the candidate about the importance of the test, its benefits, and implications of its outcome, psychological impact and the inherent risk of passing on the mutations to one’s kids.
A woman who tests positive now understands that she has a high lifetime risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer. However she should also understand that just because she is a carrier of the faulty gene, it does not mean that she would certainly develop the disease.
The woman who has the harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation will be placed under the radar of surveillance that includes periodical mammography and clinical breast examinations in the case of breast cancer and for ovarian cancer, surveillance methods include transvaginal ultrasound, blood tests and clinical exams. Screening will go a long way in detecting breast cancers early enough to be successfully treated with minimal damage to the quality of life of the individual.
The option of resorting to surgery as a pre-emptive step to reduce the risk of developing cancer is also explored by some women. Prophylactic surgery involving removal of tissues that are more exposed to risk i.e., prophylactic mastectomy (removal of healthy breasts) and prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of healthy fallopian tubes and ovaries) might offer some degree of protection against the development of breast and ovarian cancers. However, this does not offer any guarantee against development of the diseases.
Prescription of drugs like tamoxifen has shown to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women, who are at premenopausal stage and who are at increased risk of developing the disease. Clinical studies have also proved that the drug also serves to reduce the risk of recurrence of breast cancer in women who are already undergoing treatment for a breast tumour diagnosed earlier. Similarly, raloxifene is another drug that has shown to reduce the risk of developing invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
It is imperative that women who seek risk avoidance measures like surgery or intake of drugs should discuss their options in detail with their physicians before implementing them.
Hand-Picked article for you: Worrier Or Warrior? Analyze Your DNA Raw Data For COMT – The Warrior Gene
Genetic testing for breast cancer will help in taking the fight against cancer to the next level. For those women who have known reasons like strong family history of the disease, it is essential to consider being tested for a genetic mutation. However, the risk for developing the disease in women with the faulty genes varies from individual to individual.
Though genetic testing for cancer can cause a lot anxiety, stress, anger, guilt and even chronic depression in some individuals, it can have its own benefits irrespective of the outcome of the test. While it gives a sense of direction by way of adoption of preventive measures to those who test positive for a faulty gene, those who test negative experience a great sense of relief which helps in motivating them to increase their awareness.
Apart from inheritance of harmful genetic mutations it is common wisdom that women empower themselves with the knowledge of the factors that increase or decrease their chances of developing breast or ovarian cancer. The following factors have a significant impact on the onset of the diseases:
Women who have a first degree or second degree relative with breast or ovarian cancer is at increased risk for developing the diseases. Besides, women who have already had breast cancer are at an increased risk of recurrence or developing ovarian cancer.
Age is a crucial factor. The risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer increases with age. Genetic mutations can lead to early onset of the disease.
The greater the exposure of a woman’s body to oestrogen, a hormone that stimulates breast tissue, the greater is her risk for developing the disease. Women whose menstrual periods commenced early or whose menopause set in late (after 55) and women who delivered their first child at 30 or beyond are said to be prone to breast cancer as these events in their lives indicate increased exposure of their bodies to oestrogen.
Women who undergo hormone replacement therapy for symptoms of menopause are at an increased risk of breast cancer, besides heart attack, stroke and blood clots.
Medical and hereditary risks apart, there are certain lifestyle factors like obesity, lack of physical activity, alcohol consumption and increased intake high-fat diet that contribute to the risk of developing breast cancer.
The fight against breast cancer calls for a proactive approach by empowering oneself with the knowledge about the disease and through intelligent use of the support system that has been put in place by scientists in the field of genetic research. As a woman if you have valid reasons to worry about your chances of developing the disease, it is time you explored the option of genetic testing as a preventive strategy that could embolden your spirit, imbibe confidence and direct you on the path of preventive self- care.
