Reports
Health
Wellness
Nutrigenomics and Nutrigenetics describe the science of how genes interact with your nutrition. Though we inherently recognize by observing that two people eating the same food can have significantly different outcomes. For example, not all individuals who consume high carbs become fat, and not all obese people consume high carbs. One can find many such anomalies that seem to contradict conventional wisdom, suggesting that something more intrinsic is involved in these outcomes than just what we eat and what we do.
Here are 15 incredible nutrigenomics facts, which are sure to pique your interest and make you want to understand your genetics:
Nutrigenomics Fact 1: Nearly 70% of people have a genetic variant in the ADORA2A gene that is associated with poor sleep on increased consumption of caffeine.
Nutrigenetics Fact 2: About 65% of people carry a variant of the MTHFD1 gene that is associated with an increased risk of fatty liver on low choline intake
Nutrigenomics Fact 3: 60% of people have a variant of the AGT gene which is shown to be associated with an increased risk for hypertension on high salt intake
Nutrigenetics Fact 4: Nearly 15% of people have a variant of the APOA2 gene which is shown to be associated with an increased risk for obesity on high saturated fat intake
Nutrigenomics Fact 5: Nearly 97.5% of the African American population carries a variant of the FADS1 gene, which is associated with an increased need for plant sources of PUFA. While only 50.6% of Europeans and 0% of Central Americans carry this variant.
Nutrigenetics Fact 6: Nearly 10% of people have a genetic variant in the MTHFR gene, which is associated with an increased risk of birth defects when folate levels are low.
Nutrigenomics Fact 7: About 5% of the global population carries a genetic variant in the G6PD gene that is associated with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a condition that is mostly triggered by the consumption of fava beans.
Nutrigenetics Fact 8: About 0.2% of the global population carries a genetic variant in the HFE gene and is predisposed to Hemochromatosis when its iron intake is high.
Nutrigenomics Fact 9: About 0.2% of the global population carries a genetic variant of the SI gene, which is associated with sucrase-isomaltase deficiency when their sucrose intake is high.
Nutrigenetics Fact 10: About 0.005% of the global population carries a genetic variant in the ALDOB gene, which is associated with hereditary fructose intolerance when their fructose intake is high. About 1 in 50 adults is heterozygous for a non-functional ALDOB variant and are predisposed to hereditary fructose intolerance when their fructose intake is high.
Nutrigenomics Fact 11: About 58% of Japanese men have a genetic variant in the ALDH gene, which is associated with enhanced alcohol dehydrogenase activity and enables them to have more drinks than non-carriers.
Nutrigenetics Fact 12: About 65% of the global population carries a variant in the CYP1A2 gene, which is associated with fast metabolism of caffeine and lowered the risk for heart attack by almost 52% compared to slow metabolizers.
Nutrigenomics Fact 13: About 23% of the global population carries a variant in the AMY1 gene, which is associated with low copy numbers of the gene and reduced ability to digest starch.
[or]
70% of people from agricultural populations have an AMY1 copy number variant which is shown to be associated with better starch digestion and lower risk of obesity when compared to 37% of non-agricultural populations
Nutrigenetics Fact 14: According to a nation-wide study conducted by Metropolis Healthcare on Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, and Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid), 75% of the population has shown alarming levels of deficiency.
Nutrigenomics Fact 15: About 50% of the global population have variants in the TAS2R38 gene, which is associated with increased bitter taste perception and decreased consumption of vegetables.
Also Read: Why most things you know about nutrition and weight loss are plain wrong!
Is Dr. Rhonda Patrick Diet For You? Analyze Your DNA Raw Data To Find Out Your Nutritional Needs!
|
Liquid calories or high sugar drinks are often consumed less rationally than food that is chewed. Most people do not “count” the calories they drink. However, a great deal of damage could be coming from liquid calories.
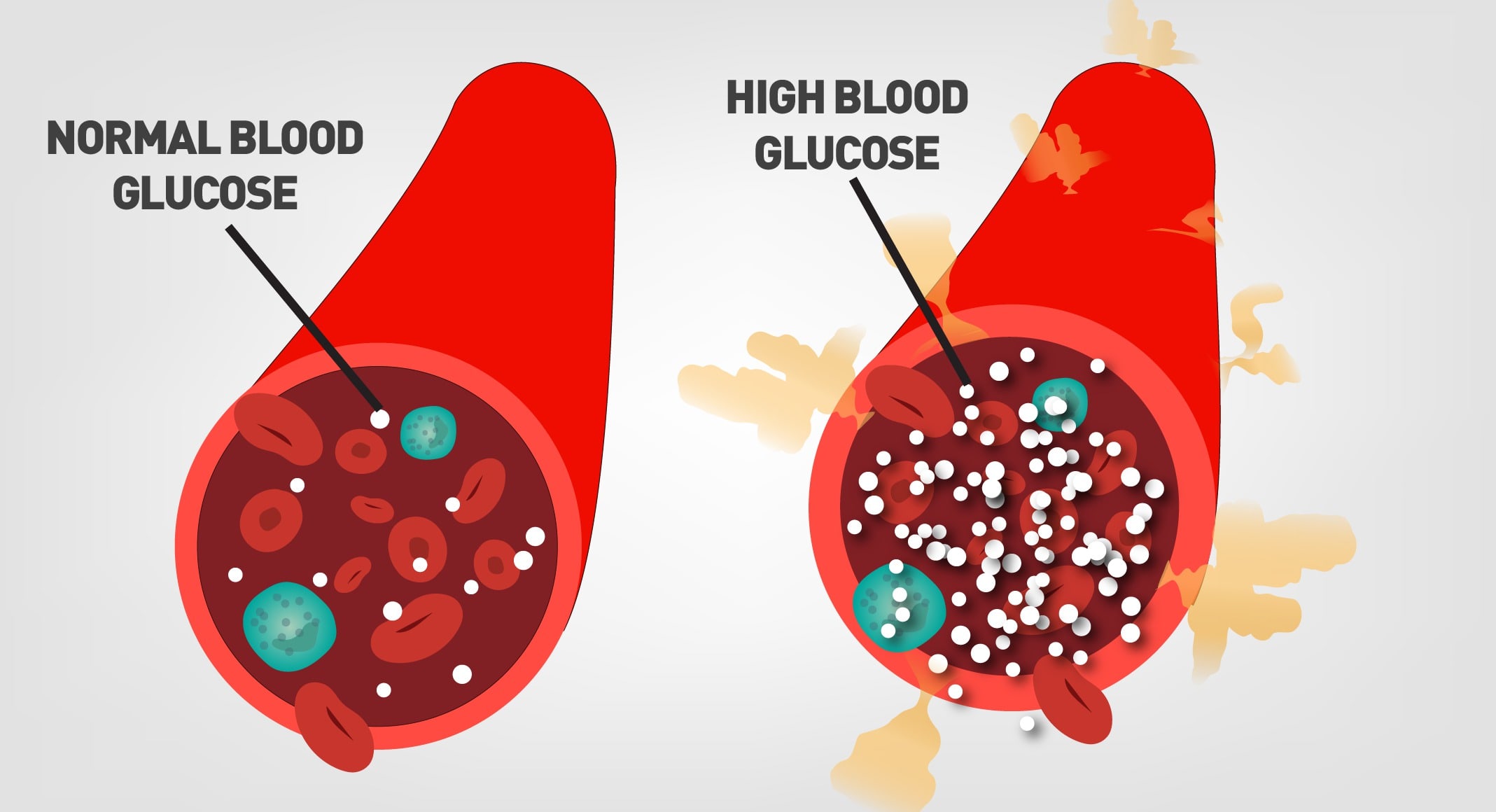
Sugar in drinks gets into the blood faster than sugar in solid foods, thus increasing blood sugar levels rapidly. Repeated increases in blood sugar levels lead to insulin resistance, which eventually leads to obesity, diabetes and other health conditions. People habitually consume colas, bottled fruit beverages with added sugar, teas and coffees with sugar, and all sorts of sugar sweetened beverages(ssb).
These drinks are consumed casually at home as a replacement for water, at entertainment centers, after sports, and at social events. Many people quench their thirst with these drinks instead of water, ignoring the calorie labels(a.k.a warning labels) on them. The fine print shows an alarmingly high level of sugar that research studies have found to be associated with a risk for obesity and thereby an increased risk for diabetes. These drinks confer risk of diabetes.
While the risk for diabetes associated with drinking sweetened beverages has always been known, a new study shows the extent of risk. Researchers from Karolinska University in Sweden showed that consuming 2 glasses of sugary drinks every day could double diabetes risk.
In the study, two or more of 200 milliliters servings(~ one and a half cans) of the sugary drinks when consumed every day was found to increase the risk for diabetes by two-fold. People who preferred drinks that were sweetened with artificial sweeteners were equally at risk for diabetes.
Diabetes risk was the same whether one consumed drinks sweetened with sugar or artificial sweetener
Josefin Edwall Löfvenborg who is a nutritionist at Sweden’s Karolinska Institute spoke about the relevance of the study “Not all studies have been able to look at sugary and artificially beverages separately. (but) it's getting more and more established that soft drinks increase the risk of type II diabetes."
‘Effect of Larger Quantities’
"We wanted to see the effect of larger intakes than two," stated Löfvenborg highlighting the second part of the study that determined diabetes risk among people who drank more than 1 liter of sugary drink every day. The risk was found to increase 10 fold in this group, reiterating the effect of consuming high sugar drink on diabetes risk.
Cups quickly add up to a liter in a day: a few cups of coffee or tea a day, some canned beverages, a can of soda or cola, cappuccino, lassi, etc. all can add up to contribute towards the risk of diabetes.
[idea]
Is soda the new cigarette?
High sugar drinks like sugary soft drinks are being additionally taxed in places like California and Berkley in the U.S. In Kerala, India, fat tax of 14.5% is levied on junk food at International food chains which include burgers and high sugar drinks consumed in these chains. Such high tax is levied to lower consumptions as high sugar drinks are implicated in the rising obesity epidemic and diabetes numbers in the world. In California and Berkley, soda consumption has dropped by one fifth after the tax on soda was executed. Cigarettes are taxed similarly to lower consumptions, this boils down to soda being on the same plane as cigarettes. [/idea]
Not everyone reacts equally to dietary risk factors, certain genes have been shown to modify (predispose or protect) disease risk. In a recent study, it was found that people with certain gene variants were at a higher risk for diabetes even when they consumed the same dietary components as others. This would mean that people who consume high sugar drinks may have a higher risk for diabetes but the level of risk may be modulated by the genes they carry.
Family history is an important genetic risk factor for diabetes. The risk for diabetes is increased if both parents are diabetic, as compared with either parent or neither parent being diabetic. Predisposition to diabetes can be determined through a simple and economical saliva-based genetic test.
Xcode’s Health Genetics test is a companion to the Master Health Checkup (MHC). This genetic test covers predisposition to diabetes, obesity, hypertension and heart disease in one, low-cost test. When taken together with blood test data from MHC, it provides a complete picture of the various risk factors. Nutritional, dietary and lifestyle counseling is provided to lower the risk towards the normal range.
You can write to us at hello+support@xcode.in to find out more.
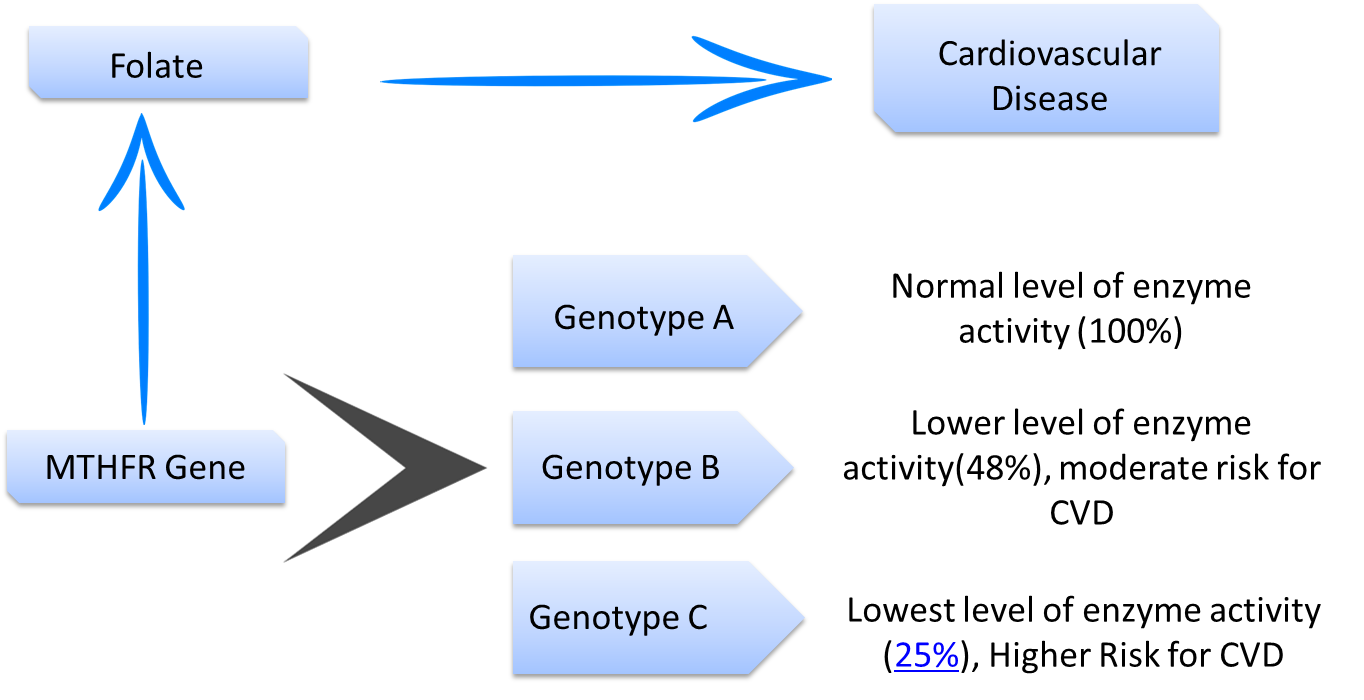
Cardiovascular disease is a group of diseases that involve the heart and blood vessels. There are a number of risk factors associated with this condition, including genetic risk factors with several mutations in several genes being associated. One such important and the independent risk factor is Homocysteine.
| Nearly 60% of the world’s heart disease occurs in India Indians are prone to premature coronary artery disease (CAD) with homocysteine found to be a significant independent risk factor for CAD in young patients. MTHFR gene polymorphism was found in 1/3rd of ischaemic stroke patients in India and was associated with a higher frequency of hyperhomocysteinemia compared with people without the polymorphism. Gene mutation implicated in homocysteine levels are significantly associated with CVD in Indians C677T MTHFR mutation was strongly associated with arterial stroke, with MTHFR allele evaluation aiding in reducing morbidity due to stroke. Multiple scientific studies have established high levels of homocysteine in the Indian population- as much as 80% according to one study. Poor maternal folate rate, indicated by plasma homocysteine levels which is a highly sensitive marker of folate levels, is associated with preeclampsia, stillbirth, preterm delivery, and spontaneous delivery. 60 to 90% of adolescents in India suffer from anemia, with folate deficiency being one of the major causative factors for nutritional anemia. 22 to 52% in India have folate deficiency in India. Conditions associated with folate deficiency, like neural tube defects with a prevalence of 1 to 5 per 1000 live births, are high in India. |
Folate (vitamin B9) is responsible for converting the harmful homocysteine to its useful form, methionine. Methionine is important for many essential bodily functions such as the production of DNA and RNA, cell, and tissue growth. Though dietary intake of folate is generally inadequate in India, that is not the only reason for high homocysteine levels. Genes also play an important role.
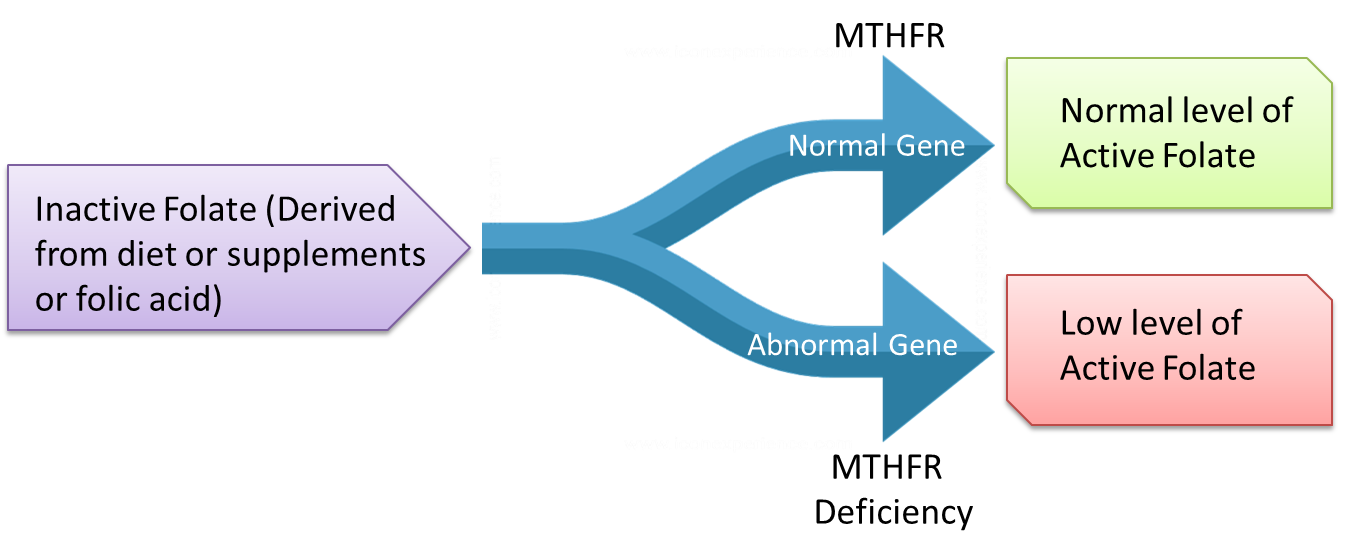
Folate is present in an inactive form in the body and is converted to its active form by the enzyme Methyl Tetra hydro Folate Reductase (MTHFR). The active form of folate is necessary for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. The gene MTHFR plays a role in the production of the MTHFR enzyme and any genetic variation in this gene could alter the level and activity of the enzyme in the body. It has been shown that the prevalence of MTHFR gene mutation is high in India, which when combined with low dietary folate intake can lead to very high levels of homocysteine and other associated conditions.
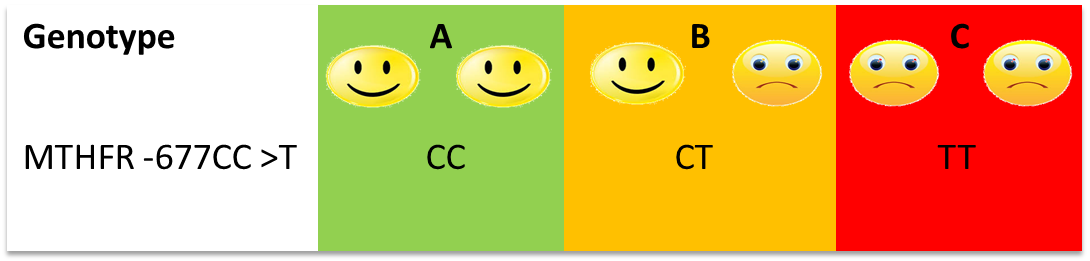
Maintenance of adequate folate levels is extremely important during pregnancy, infancy, and adolescence. Lack of methionine can lead to improper DNA synthesis and disruption in gene regulation that could lead to birth defects like neural tube defects, which are associated with folate deficiency.
Asians show a high prevalence of 677C>T polymorphism in the MTHFR gene. People with genetic variants that are at high risk for folate insufficiency should supplement their diet with rich sources of folate. Fruits and vegetables are good sources of folate, however, in India, overcooking vegetables leads to loss of folate. Fortified cereals, grains, and cornmeal are sources of folic acid, which is a synthetic form of folate. The folate from the diet will compensate for the lowered levels due to gene polymorphism.
The type of MTHFR gene has been shown to influence the Active Folate levels in blood. Want to know what type of MTHFR gene you have? Try Xcode’s nutrigenetics test which can tell you what versions of the MTHFR gene are in your DNA. You can also learn about how your genes may influence other traits, including your risk for certain diseases. Write to us at hello@xcode.life to find out more.
The onset of muscle fatigue has hampered many athletes from achieving their maximum potential. Lactic acid buildup is a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism. Under normal activity levels, the body mostly relies on aerobic metabolism and hence lactate (another name for lactic acid) buildup is not a major concern. However, with increased activity levels, specifically, when the metabolism switches from aerobic (oxidative) to anaerobic (glycolytic), as in power activities performed at high heart rates, lactate levels quickly build up, which, if not cleared from muscles, cause fatigue and a burning sensation.
But how quickly lactic acid is cleared and how quickly a person feels this fatigue is also influenced by your genetics, especially the MCT1 gene. This article provides insights into how individual differences effects the lactic acid clearance rate and muscle fatigue.
During short term power (anaerobic) exercise, our body uses substances such as ATP and creatine phosphate (CP) within the first 7 seconds to produce energy. This signals the body to start glycolysis, a process to utilize the glycogen (stored glucose) to produce energy. When glycogen is broken down to release energy, which allows the muscle movement to continue. During this process, a substance called lactic acid is formed. Small amounts of lactic acid operate as a temporary energy source, thus helping you avoid fatigue during a workout. However, a buildup of lactic acid during a workout can create burning sensations in the muscle & limits the muscle contraction, resulting in muscle fatigue. For this reason, it may be desirable to reduce lactic acid build up in the muscles. However, if you are a bodybuilder, lactic acid buildup has been shown to be highly anabolic- meaning, good for muscle building. Body builders routinely workout to feel the “burn” in their muscles.
Monocarboxylate transporters (MCT) regulates the transport of lactate and many other substances and removes lactic acid from the muscles. MCT1 gene influences the amount of MCT you produce. The more you produce, the quicker is the clearance rate, thus the delay in the onset of muscle fatigue. Individuals with faster version have shown to produce higher levels of MCT, making them more suitable for endurance based exercises than individuals with slower versions producing lower levels of MCT.
| Adequate magnesium levels in your diet will help the body deliver energy to the muscles while exercising, thus limiting the buildup of lactic acid. Foods rich in magnesium include legumes like navy beans, pinto beans, kidney beans and lima beans and seeds such as pumpkin, sesame and sunflower seeds and vegetables like spinach, greens, turnips. Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. It helps the body to break down glucose and thus can help to limit the body’s need for lactic acid. Food sources of these fatty acids include fish like salmon, tuna and mackerel, from nuts and seeds like walnuts and flax seed and from plant based oils such a olive oil, canola oil, rice bran oil. B vitamins: help to transport glucose throughout the body and help provide energy to the muscles. Food sources of B vitamins includes leafy green vegetables, cereals, peas and beans, fish, beef, poultry, eggs and dairy products. |
BOTTOM LINE: If you are an endurance runner, excess lactic acid buildup is undesirable as it leads to fatigue. If you are a bodybuilder, you need lactic acid buildup as its highly anabolic and good for muscle growth.
Discover your genes and align your training with your genetic type. Try Xcode’s fitness genetics test which can tell you whether you carry faster, slower or both versions of the MCT1 genes . Write to us at info@xcode.in
The greatest wealth that one can ever earn is good health! Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. In the recent years, one of the best aspects of health care reform is that it has started to emphasize on prevention. When we talk about prevention, it is certain that identification (or in medical terms diagnosis) of any health disorder is elemental for its prevention. Whenever there is a mention about diagnosis, we systematically follow an ‘ABCD’ pattern, that is., Anthropometry (height, weight, BMI and other physical determinants), biochemical parameters (biological markers, for instance blood, urine, sputum), Clinical presentations (Blood Pressure, body temperature, consciousness) and finally Dietary considerations (meal pattern, frequency of consumption of different foods, food allergies to name a few). But still the fact that genetic make-up of a person decides his/her physical appearance, intelligence, behavioral patterns, health outcomes and ageing pattern is compelling enough to allocate space for genetic aspects in wellness and disease prevention approaches.
The effect of dietary factors on health status has been recognized since antiquity. Food and its components directly or indirectly influence gene expression. Genetic predispositions in turn dictate unique dietary needs and requirements. Nutrigenetics, a field of Life Science aims to identify genetic susceptibility to diseases and the vital role of genetic variation in affecting the nutrient intake. While Nutrigenomics focuses on the effect of food and food constituents on gene expression. According to Nutrigenetics, the current science of food and the nutrition it provides when interweaved with genetic insights and applied mindfully, can have a myriad restorative and therapeutic capacity to cure health disorders. ‘One size fits all’ approach to dietary and fitness recommendations leaves a gap which stands miles away from best desirable results for an individual. Hence,a personalized health care approach focusing on lifestyle modification is built on the basis of genetic assessment.
A small genetic change, or variation, that occurs within a person’s DNA sequence can have an impact on his/her nutrient metabolism. Genetic assessment will give you a clear picture of your genetic information in relation to a nutrient metabolism which in turn has relevance to health conditions. Genetic risks may be offset by favorable changes in lifestyle. Lifestyle is a comprehensive approach featuring diet, physical activity, stress management and personal habits. Amongst the three strong pillars for a healthy life, that is., diet, exercise and sleep, diet is rated the top most.
Genetic assessment aims to develop rational means to optimize the lifestyle of an individual with respect to his/ her genotype. This personalized health approach promotes disease prevention in the long run. For instance, your meal pattern, meal timings and even the type of snacks can be recommended to suit you best if you understand the pattern of genes like FTO, LEP, LEPR and CCK which influence appetite, meal quantity, satiety response and the urge to snack. Individuals carrying a variation in such genes tend to have a difficulty in following proper meal timings and meal quantities and thereby they are likely to overeat. A balanced diet with adequate dietary fiber, and healthy snacks timed appropriately can prove beneficial in their weight control.
Likewise, the type of cooking oil that you should be using or the type of nuts that you should be consuming to stay heart-healthy by maintaining optimal triglyceride levels is decided by a gene called APOA5. A variation in the APOA5 gene may demand from you a revised recommendation for n-6 fatty acids (<6% of total calories compared to the general recommendation of <10% of total calories) to help you in maintaining your triglyceride levels.
Your digestive tolerance for milk & its products is also decided by your genes. Variations in MCM6 gene may demand from you fermented milk products intake to compensate for reduced lactase activity and to stay flatulence-free. Can you drink 3 cups of coffee in a day or should it necessarily be alternated with another refreshing beverage like green tea? Is another question to which the answer is in your genes like CYP1A2.
AGT gene encodes for Angiotensinogen, which causes sodium retention in the body. Individuals with a genetic variation show increased sensitivity to dietary salt intake. Revised salt restriction norms (<3.5 grams of table salt as against <5 grams given by WHO) are recommended to maintain optimal sodium levels and prevent hypertension in these individuals.
Know your genes! Sow healthy habits and reap lifelong wellness.
